Barley with very low levels of hordeins
a technology of hordein and barley, which is applied in the field of barley with very low hordein levels, can solve the problems of difficult to reproduce the quality and low cost production of barley beer with these grains, coeliac disease, and health risks, and achieve the effect of avoiding or reducing the incidence or severity of coeliac diseas
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
and Methods
Plant Material
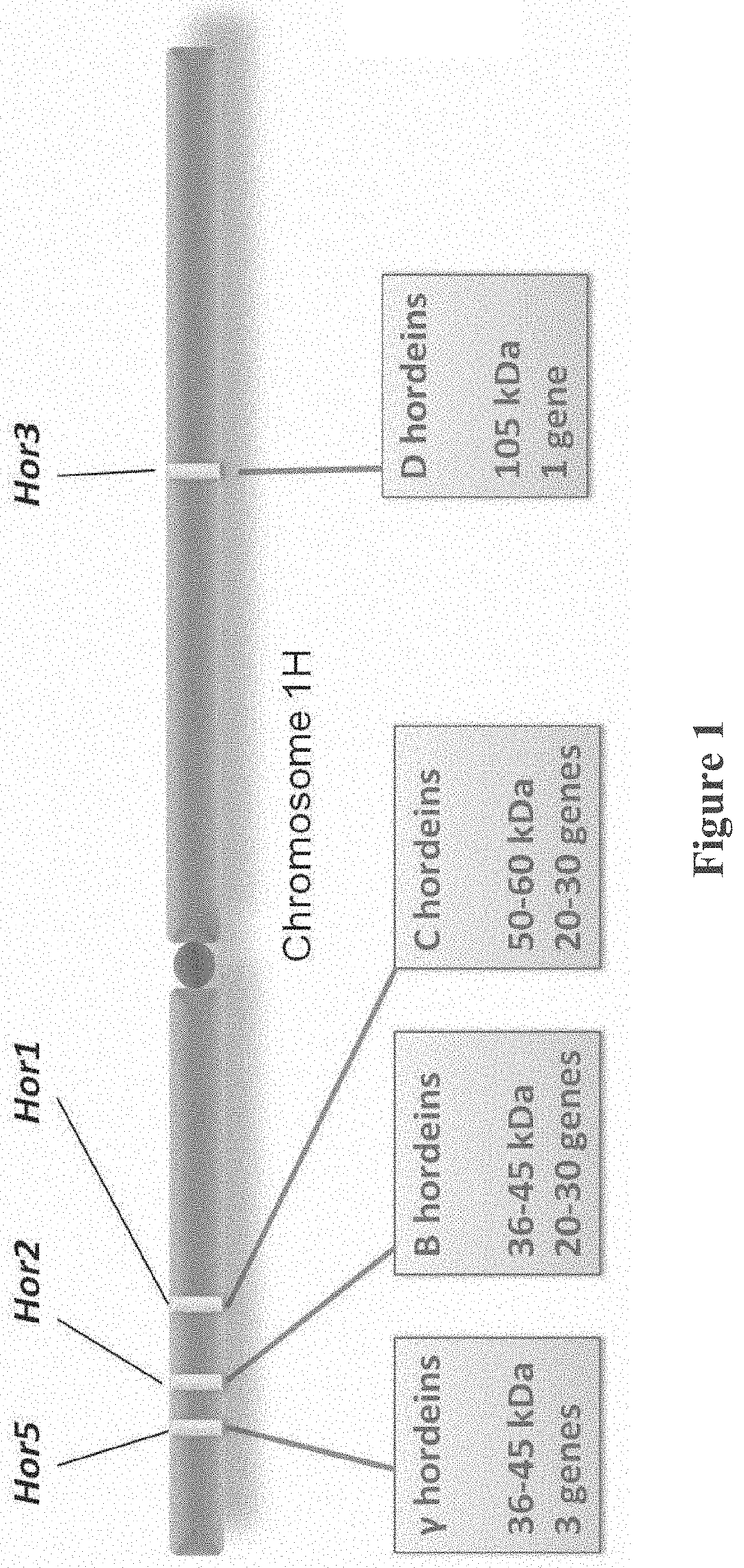
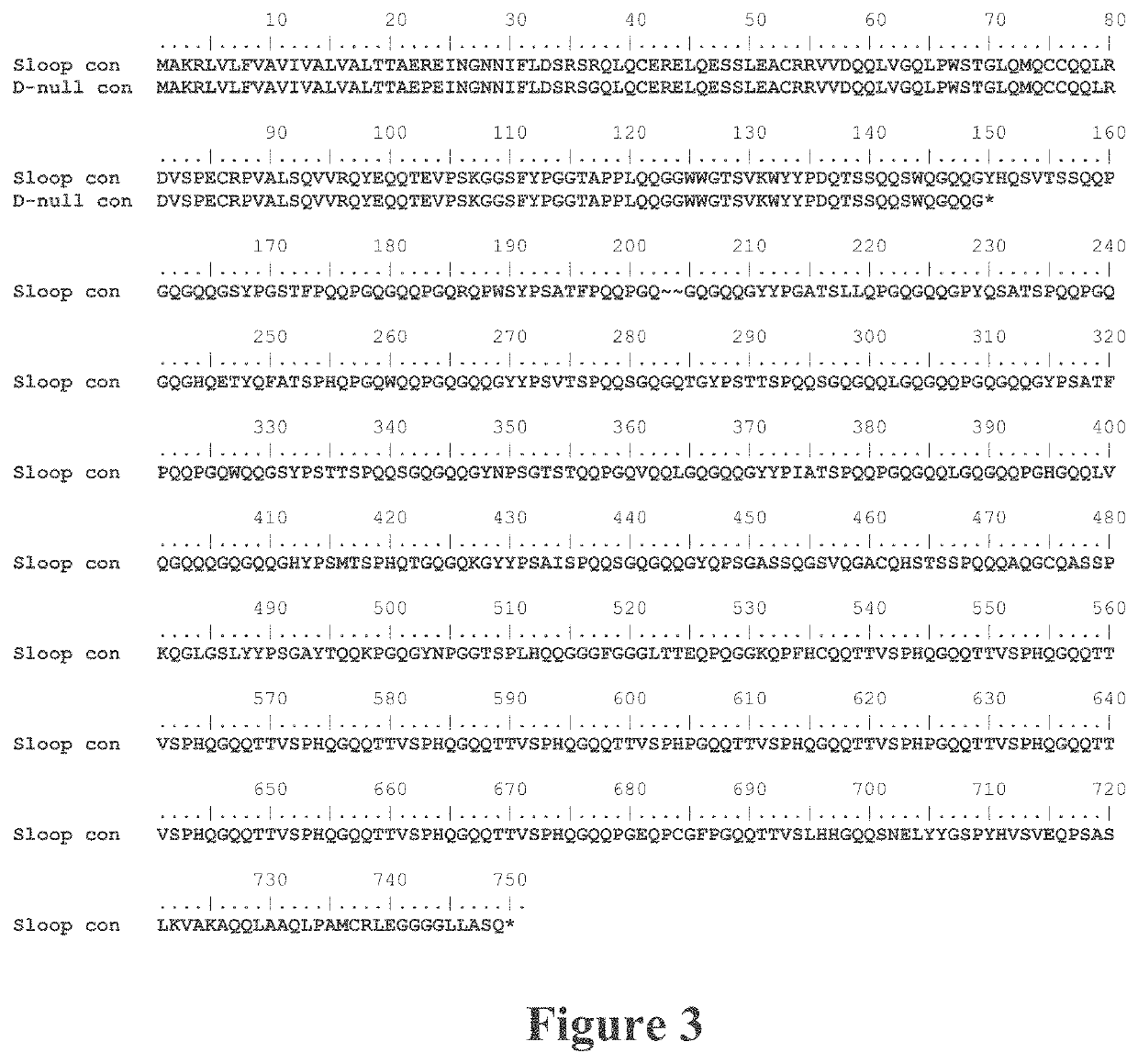
[0260]Barley line cv Sloop (wild-type) was obtained from the Australian Winter Cereals Collection (Tamworth, Australia). Riso 56 (expressing no B-hordeins) and Riso 1508 (expressing no C-hordeins and decreased D- and B-hordeins) (Doll, 1973; Doll, 1983) were obtained from the Nordic Germplasm Bank (Alnarp, Sweden). Riso 1508 was an ethyleneimine induced mutant carrying a mutation in the lys3a gene on chromosome 5H which reduced accumulation of C-hordeins. Each of these lines are publically available. Plants were grown in glasshouse conditions at 25° C. days and 20° C. nights and harvested seeds inspected to exclude contamination. For malting and brewing experiments, plants of cultivars Sloop, Riso 56 and Riso 1508 were grown side by side at CSIRO Ginninderra Experimental Station, Canberra, in the field, and 10 kg grain of each harvested. The grains were malted and 20 L batches of beer brewed using standard techniques.
Prolamin Extraction from Flour
[0261]To ex...
example 2
ization of Hordeins in Barley Flour
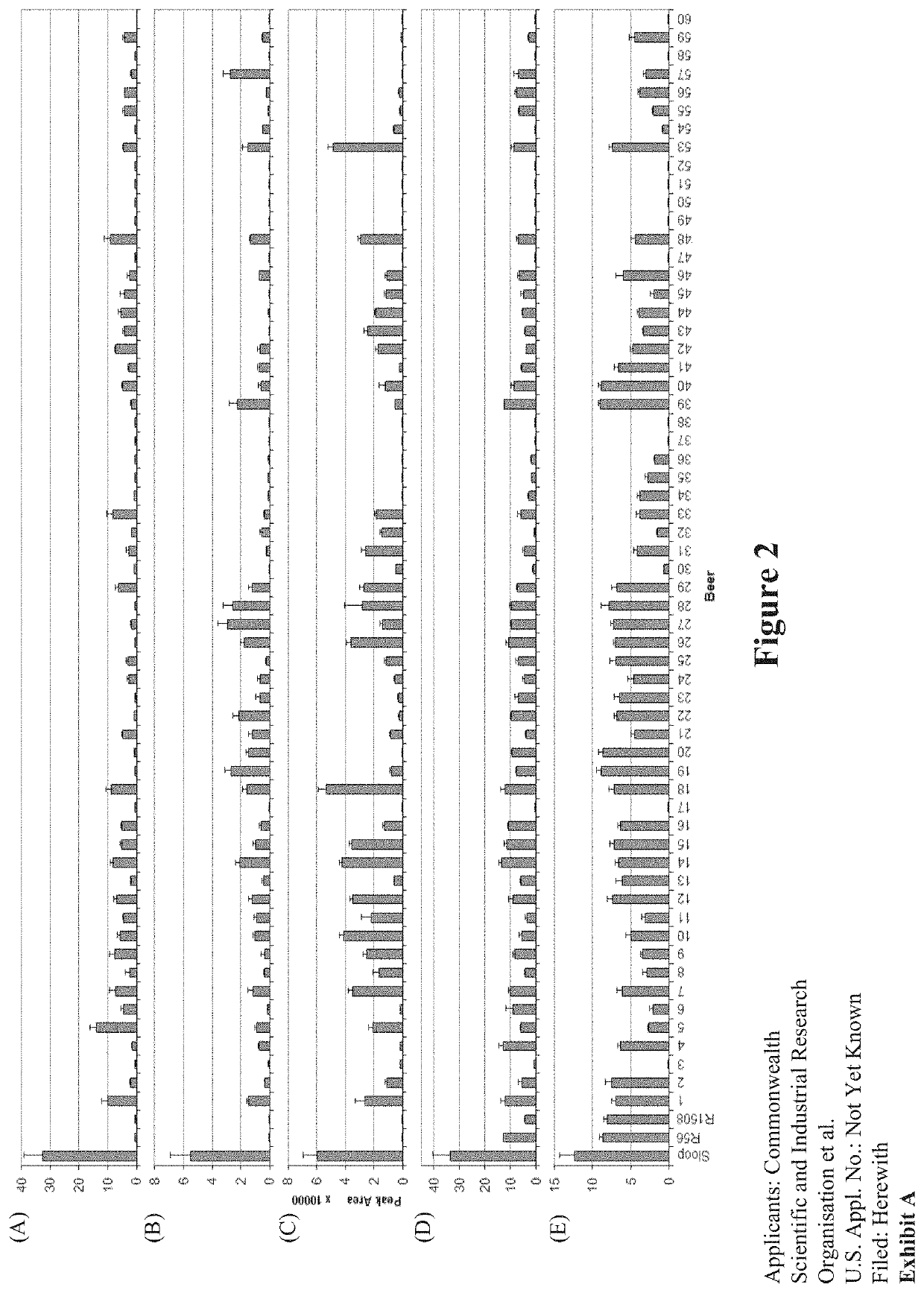
[0273]Hordeins extracted from barley flour (wild-type cv Sloop) by solubilisation into an alcohol solution were purified by FPLC as described in Example 1. The purified hordein fractions were reduced, alkylated and subjected to either trypsin or chymotrypsin digestion. Following enzymatic digestion, the sub-10 kDa fraction was analyzed by LC-MS / MS to identify the hordeins present in the purified prolamin fraction from flour to provide the complete suite of hordein proteins that might be expected to be found in beer brewed from this flour. Using a 1% false discovery rate (FDR), a total of 144 proteins were identified after trypsin digestion and a total of 55 proteins were identified after chymotrypsin digestion.
[0274]Table 1 lists the hordein protein products detected from flour following tryptic digestion. Among the most abundant proteins detected were the previously reported B3-hordein (Accession No. P06471, Kristoffersen et al., 2000), γ-3-hordei...
example 3
ization of Hordeins in Wort and Beer
[0276]Analysis of wort, the liquid extracted from the mashing process during brewing, and beer were then conducted and a similar suite of prolamins were identified (Table 3). A total of 27 proteins were identified in wort and 79 in beer, with the most abundant proteins being non-specific lipid transfer protein 1 (LTP1) and the α-amylase trypsin inhibitors (CMd, CMb, CMa). The gluten proteins identified in wort included the avenin-like A protein (18 peptides), γ-hordein-3 (10 peptides) and D-hordein (4 peptides) that were previously observed in the enriched hordein fraction. It was interesting to note, however, that >50% of the peptides were semi-tryptic (cleaved at one end at a site other than Lys / Arg), suggesting that significant degradation of the proteins had occurred during the brewing process. The avenin-like A protein (GenBank Accession No. BE195337) identified from the EST database search was detected with >60% sequence coverage (12 peptide...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com