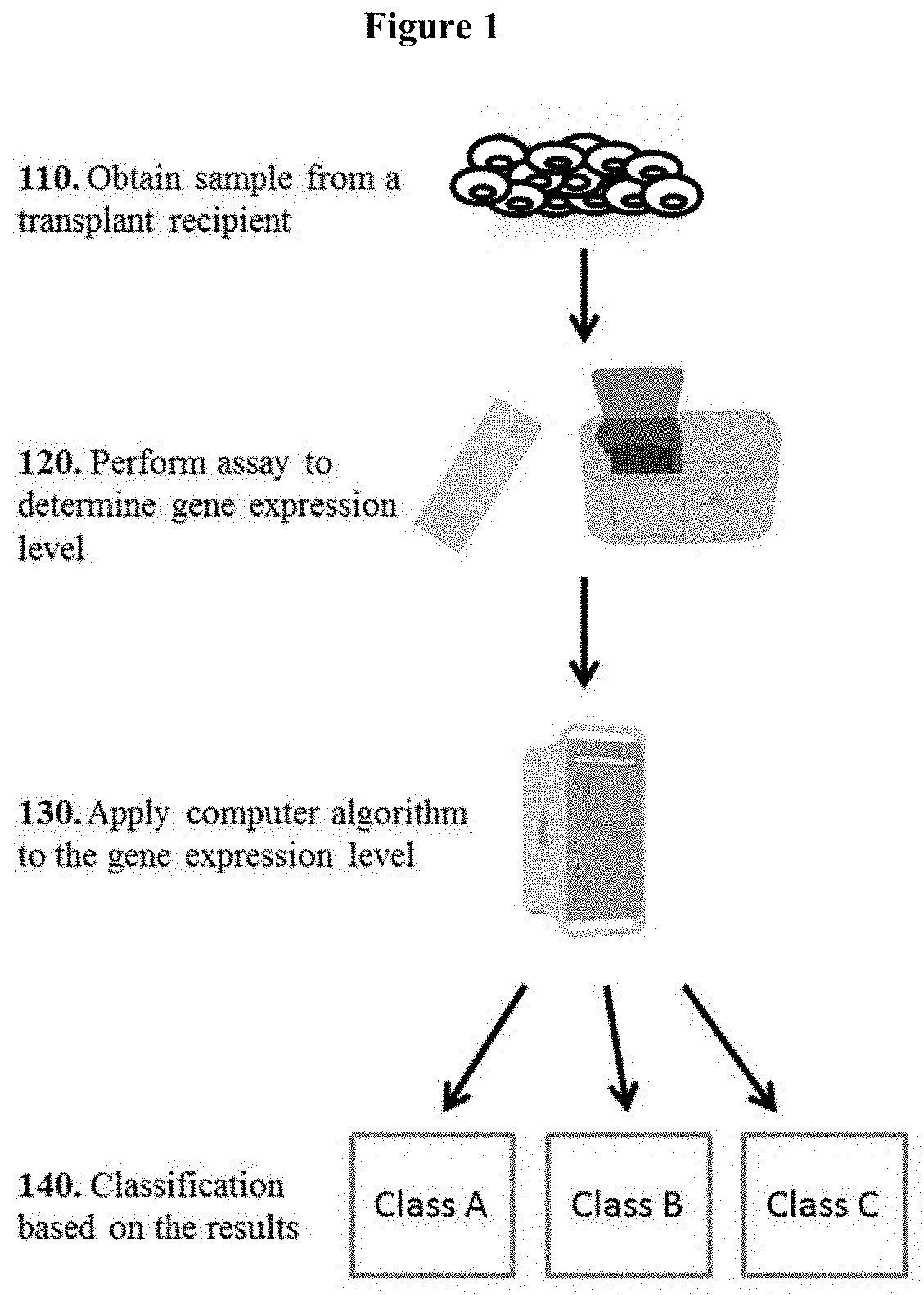
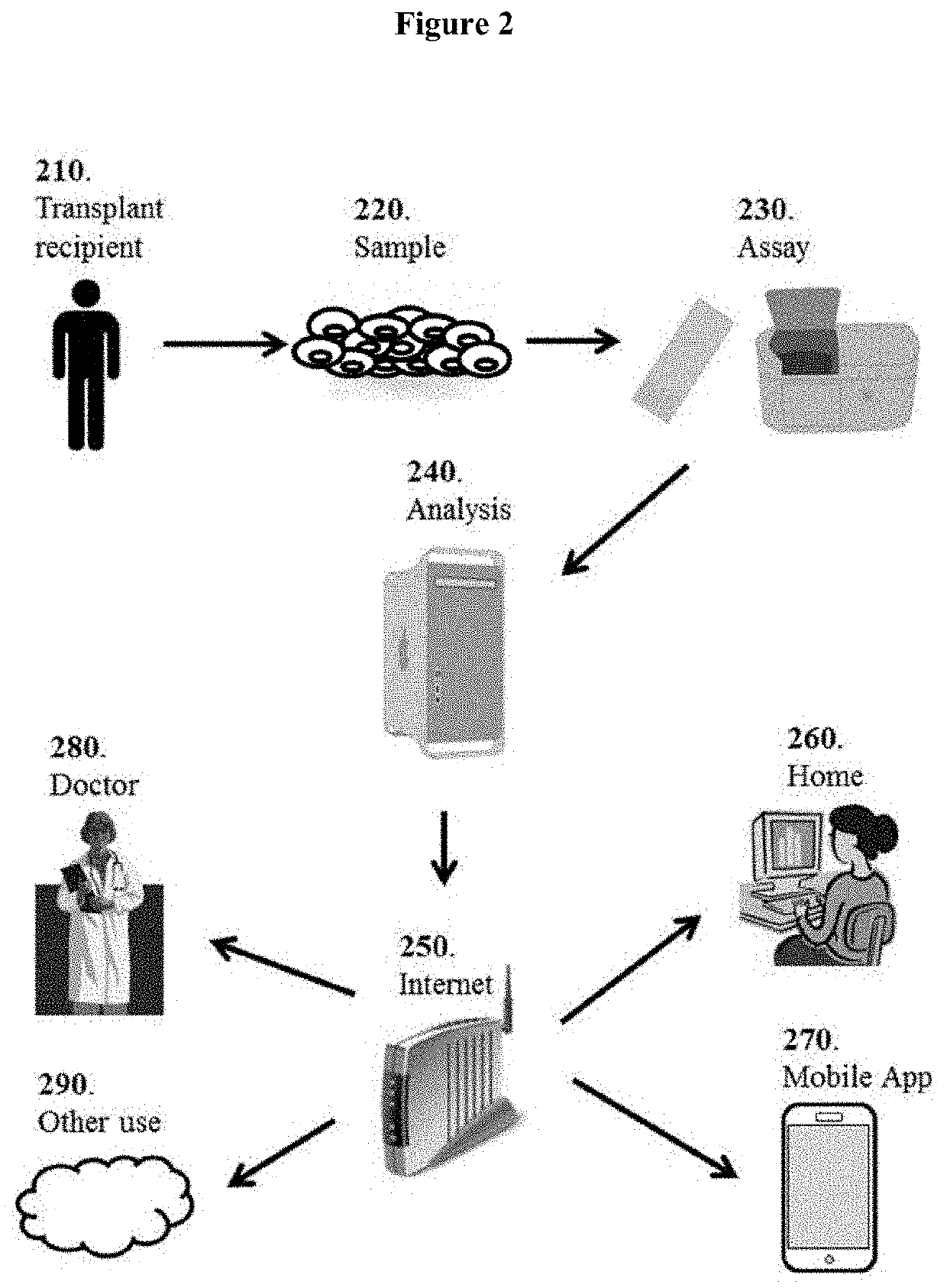
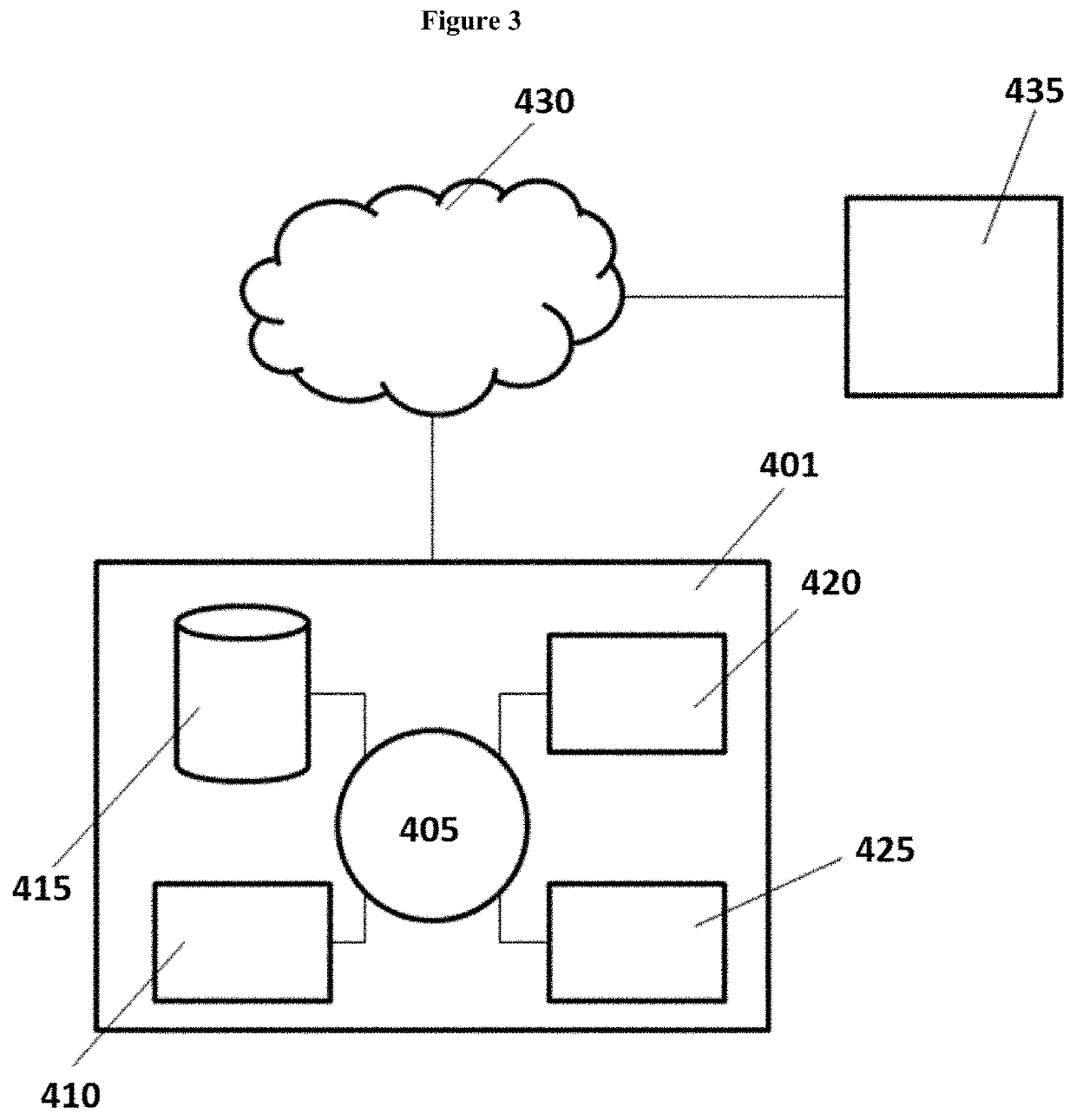
Tissue molecular signatures of kidney transplant rejections
a kidney transplant and molecular signature technology, applied in biochemistry apparatus and processes, instruments, ict adaptation, etc., can solve problems such as hampered the therapeutic potential of kidney transplantation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
ially Expressed Genes Associated with Kidney Transplant Rejections
[0121]This Example describes global analysis of gene expressions in kidney transplant patients with different types of rejections or injuries.
[0122]A total of biopsy-documented 274 kidney biopsy samples from the Transplant Genomics Collaborative Group (TGCG) were processed on the Affymetrix HG-U133 PM only peg microarrays. The 274 samples that were analyzed comprised of 4 different phenotypes: Acute Rejection (AR; n=75); Acute Dysfunction No Rejection (ADNR; n=39); Chronic Allograft Nephropathy (CAN; n=61); and Transplant Excellent (TX; n=99).
[0123]Signal Filters: To eliminate low expressed signals we used a signal filter cut-off that was data driven, and expression signals <Log 2 4.23 in all samples were eliminated leaving us with 48882 probe sets from a total of 54721 probe sets.
[0124]4-Way AR / ADNR / CAN / TX classifier: We first did a 4 way comparison of the AR, ADNR, CAN and TX samples. The samples comprised of four d...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| immune reactivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| blood pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compatibilities | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com