Cross-laminated timber structures having reduced inner-layer material and methods of optimization
a cross-laminated timber and inner-layer material technology, applied in the field of optimization of cross-laminated timber (clt) panels, can solve the problems of difficult to define global low-carbon building materials, difficult to manufacture clt panels efficiently, and often heavy floor systems using timber beams and clt floors. achieve the effect of improving the stiffness to weight ratio of the resulting clt panel
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0029]The following definitions are useful for interpreting terms applied to features of the embodiments disclosed herein, and are meant only to define elements within the disclosure.
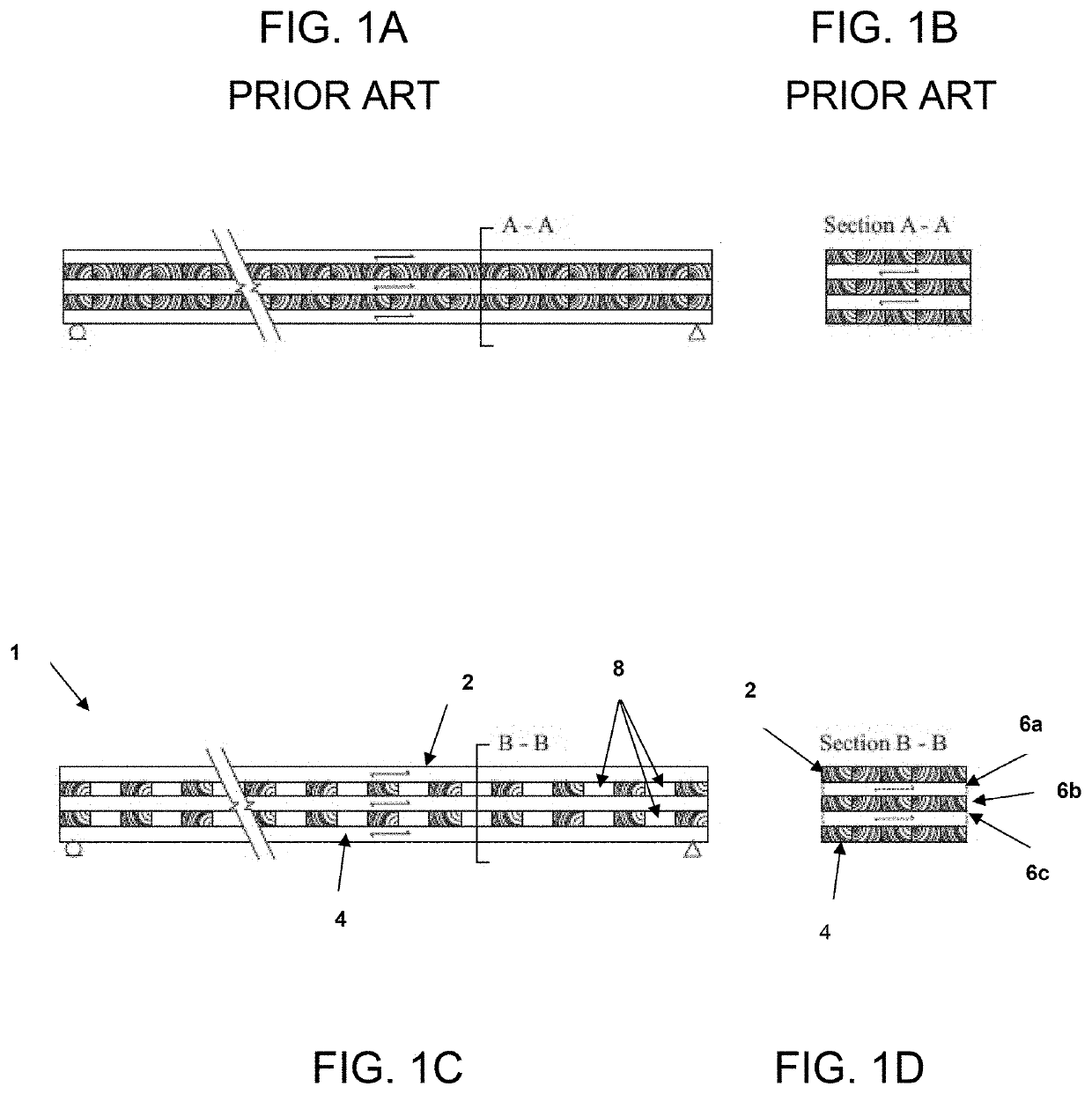
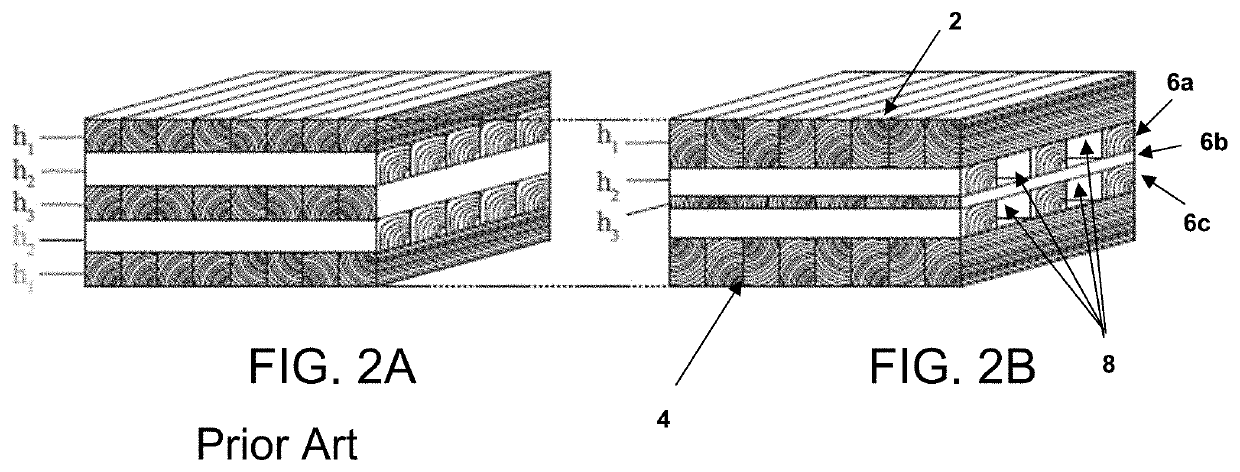
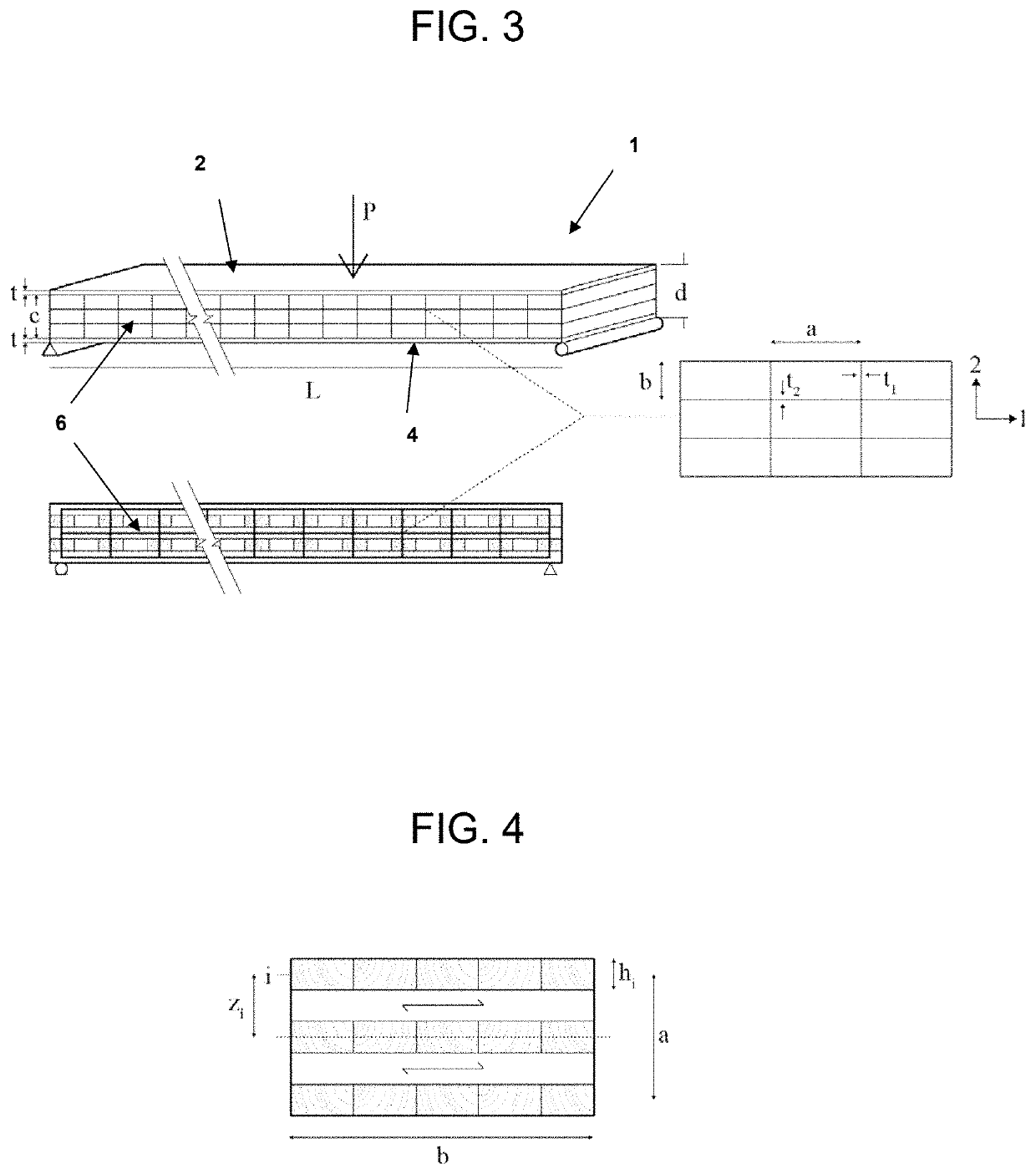
[0030]As used herein, the term “outer layers” when used to describe the outer layers of a CLT panel, refers to the outermost layers of the CLT panel. As such, the term “outer layers” refers to the bottom layer and top layer of the CLT panel.
[0031]As used herein, the term “inner layers” or “innermost layers” refers to all layers of a CLT panel disposed between the outer layers. As used herein, the terms “longitudinally extending layer” or “longitudinal layer” refers to layers of the CLT panel having a wood grain that extends lengthwise along the CLT panel, and will generally comprise the sequentially odd numbered layers beginning with a first layer (layer 1) positioned at the top of the CLT panel, the sequential layers after the first uppermost layer being numbered 2, 3, 4, etc. Longitudinal layers are a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| stiffness-to-weight ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com