Use of electroretinography (ERG) for the assessment of psychiatric disorders
a psychiatric disorder and electroretinography technology, applied in the field of mental disorders, can solve the problems of no reliable diagnostic test for psychiatric disorders, hallucinations, delusions,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Materials and Methods
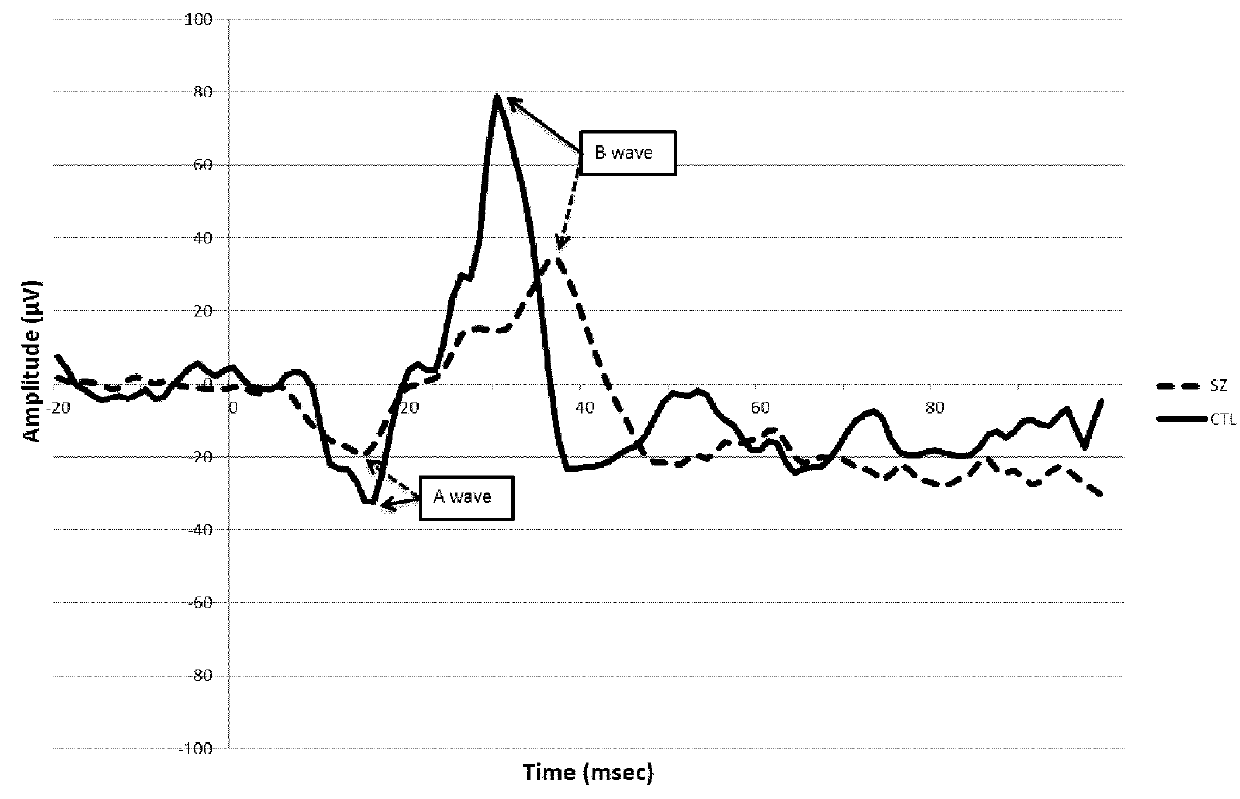
[0534]Study subjects for the Schizophrenia studies. The characteristics of the affected SZ patients and control subjects, are depicted in Table 1
TABLE 1Characteristics of the sample: 150 SZ cases and 150 controlsSZ casesControls(N = 150)(N = 150)Mean (SD) or N (%)Age39.4 (9.9) 40.6 (9.5)% Male*80.762Age of onset25.0 (6.4) —Duration of illness13.7 (9.3) —IQ b, *82.6 (12.9)102.9 (11.7)GAS-S (T3) a52.5 (8.8) —GAS-S (T1) a29.3 (10.1)—Olanzapine28 (19%)0Quetiapine32 (21%)0Clozapine45 (30%)0Risperidone32 (21%)0Abilify ®12 (8%) 0Lithium7 (5%)0Synthroid 1 (.7%)0*Comparison between groups: p a GAS-S for lifetime Global Assessment Scale-Severity, at two different period: - the time of first admission or first episode of illness (T1), - the last 6 to 24 months before the ERG recording (T3).b The IQ was measured on 127 SZ, and 121 controls.
[0535]ERG procedure. The ERG technique and protocol used in the present studies is as described in Hébert et al. (Hébert, M., et al. Bio...
example 2
Assessment of ERG Parameters in SZ Patients and Controls
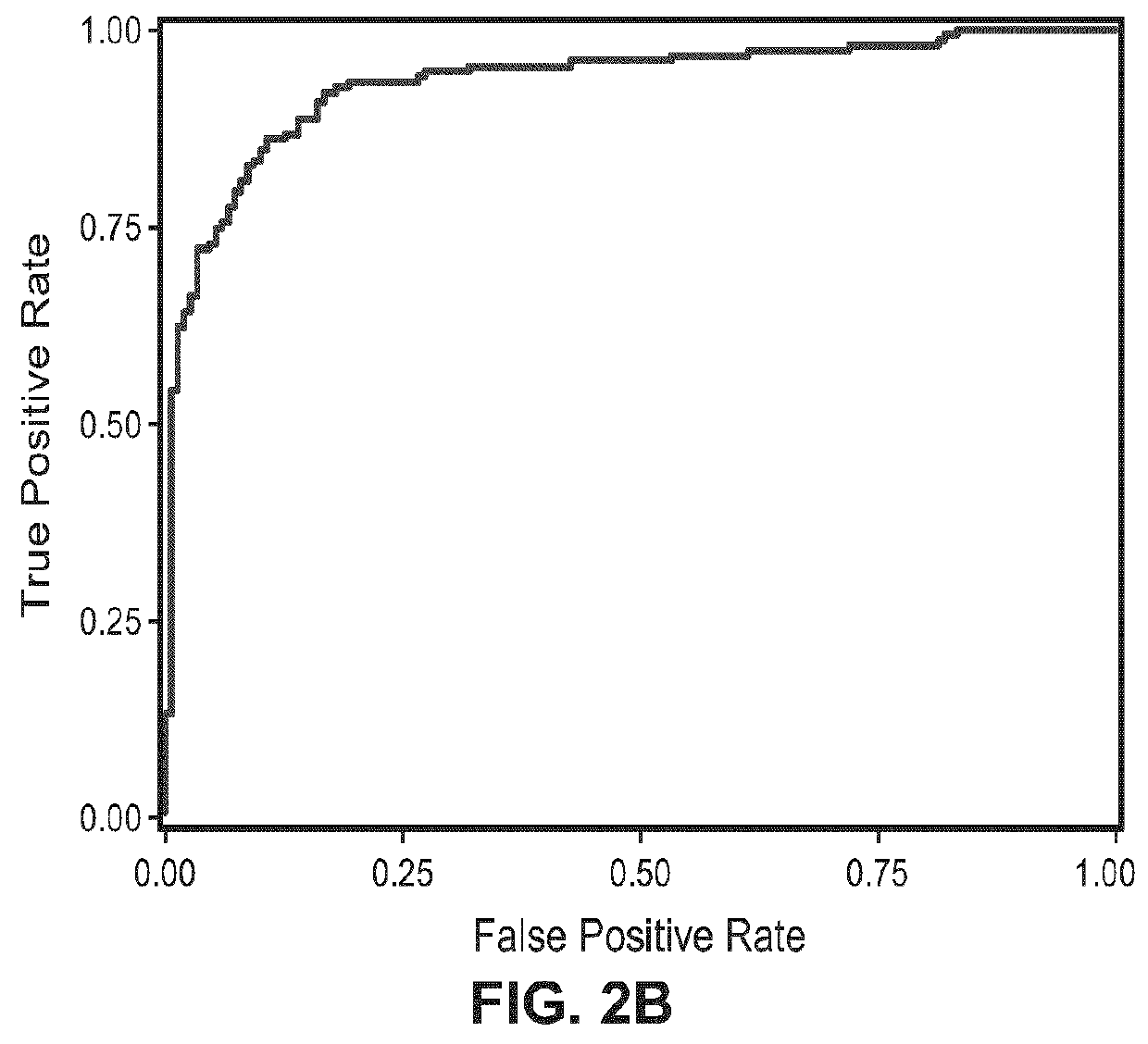
[0546]The comparison of SZ patients to controls on each of the eight ERG parameters is depicted in Table 2. As can be seen in the section “Effect size (p-value)” of Table 2, the SZ subjects differ significantly (p<0.0001) from controls on at least five ERG parameters (cone a-wave amplitude, cone b-wave amplitude, cone b-wave implicit time, rod a-wave amplitude and rod b-wave amplitude) with effect sizes ranging from 0.49 to 1.31 (in absolute value). These univariate results show that prediction modeling based on multiple logistic regression may detect a judicious subset of ERG parameters that best predict the group membership, as detailed below.
TABLE 2Comparison of the 150 SZ patients to 150 controls on ERG parametersERG FlashMean (SD)Effectparametersintensitya150 SZ150 CTsizeP-valueConesa-Wave int112.58 15.60 0.64amplitude(5.2)(4.7)a-Wave 3-int14.60 14.80 0.210.064implicit time(1.0)(0.9)b-Wave Vmax83.25 92.45 0.51amplitude(19....
example 3
ERG Profile and Response to Psychotropic Treatment
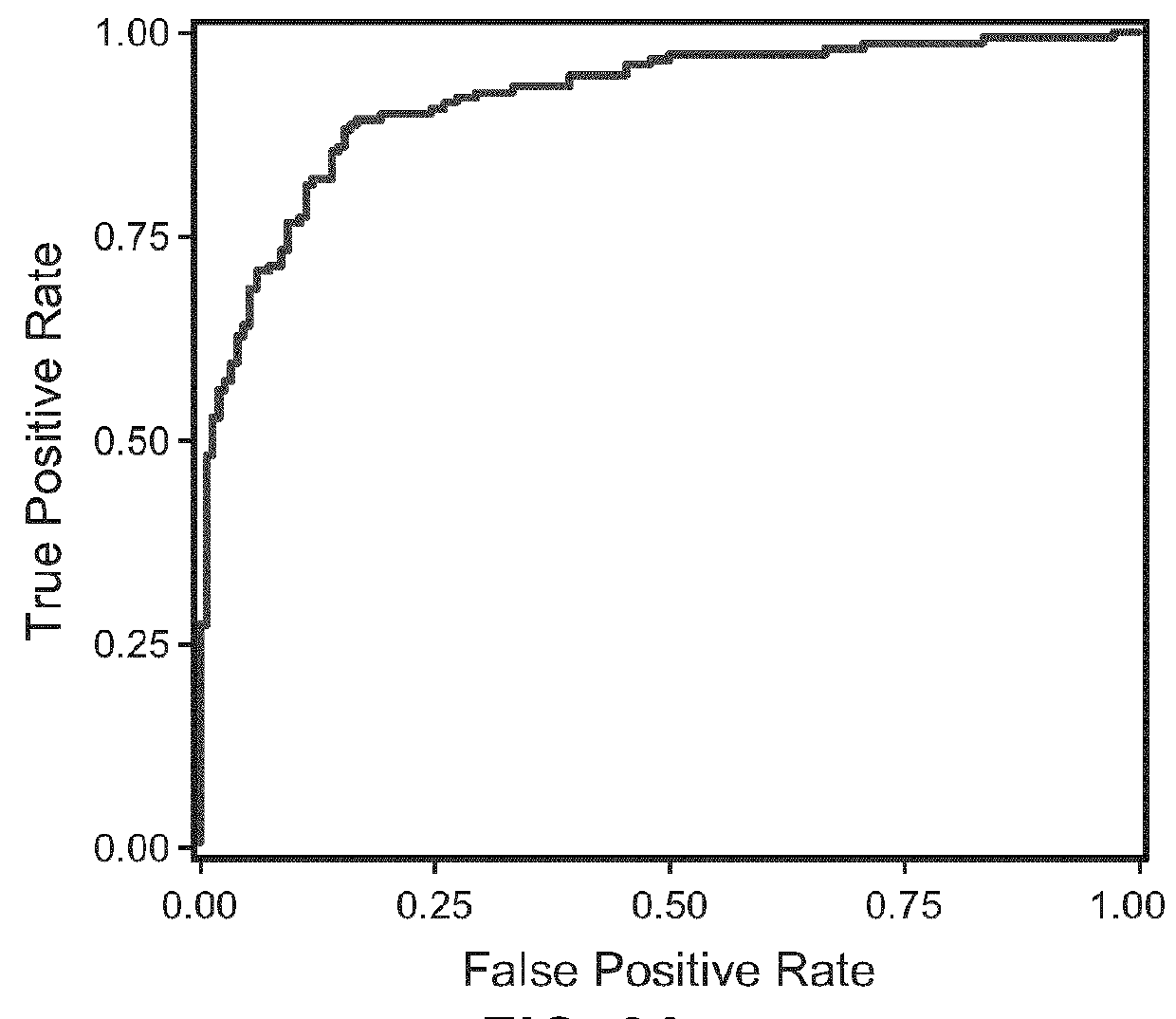
[0558]The response to antipsychotic treatment in patients of the different ERG strata is depicted in Table 4. The Chi-square test for this 2×2 table revealed a significant p-value (p=0.0015) indicating that the strata are related to the response to psychotropic treatment. Indeed, stratum 1 contains SZ subjects having a very high probability (0.76) of being good responders, while strata 2 or 3 predict rather low chance (0.31 or 0.35) to respond well.
TABLE 4Response to antipsychotic treatment depends on ERG strataPoor-ERGGoodintermediateStratumresponseresponseTotal176% (22)24% (7) 29231% (8) 69% (18)26338% (20)62% (33)53458% (14)42% (10)24X23 = 15.4, p = .0015
[0559]In univariate analysis, when, on each ERG parameter, the good responders to any medication (antipsychotic treatment) were compared to the poor-intermediate responders, significant differences were observed on two ERG parameters (cone a-wave amplitude, with an effect size of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com