Metabolite Biomarkers for the Detection of Esophageal Cancer Using NMR
a metabolite biomarker and esophageal cancer technology, applied in the field of small molecule biomarkers, can solve the problems of not being able to predict the treatment outcome, no current reliable method for early detection or treatment, and unable to prevent the progression of be or hgd to esophageal cancer
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
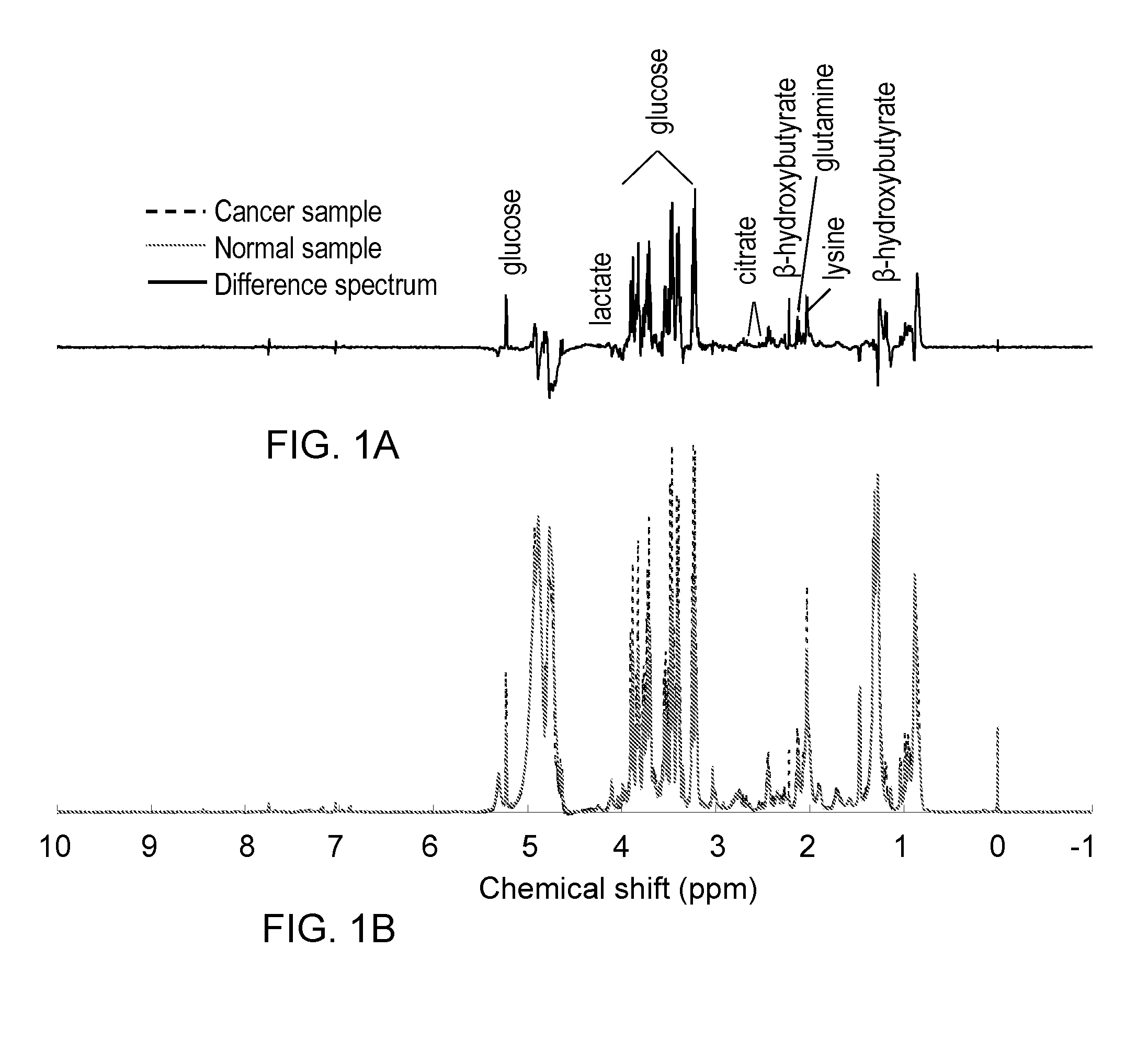
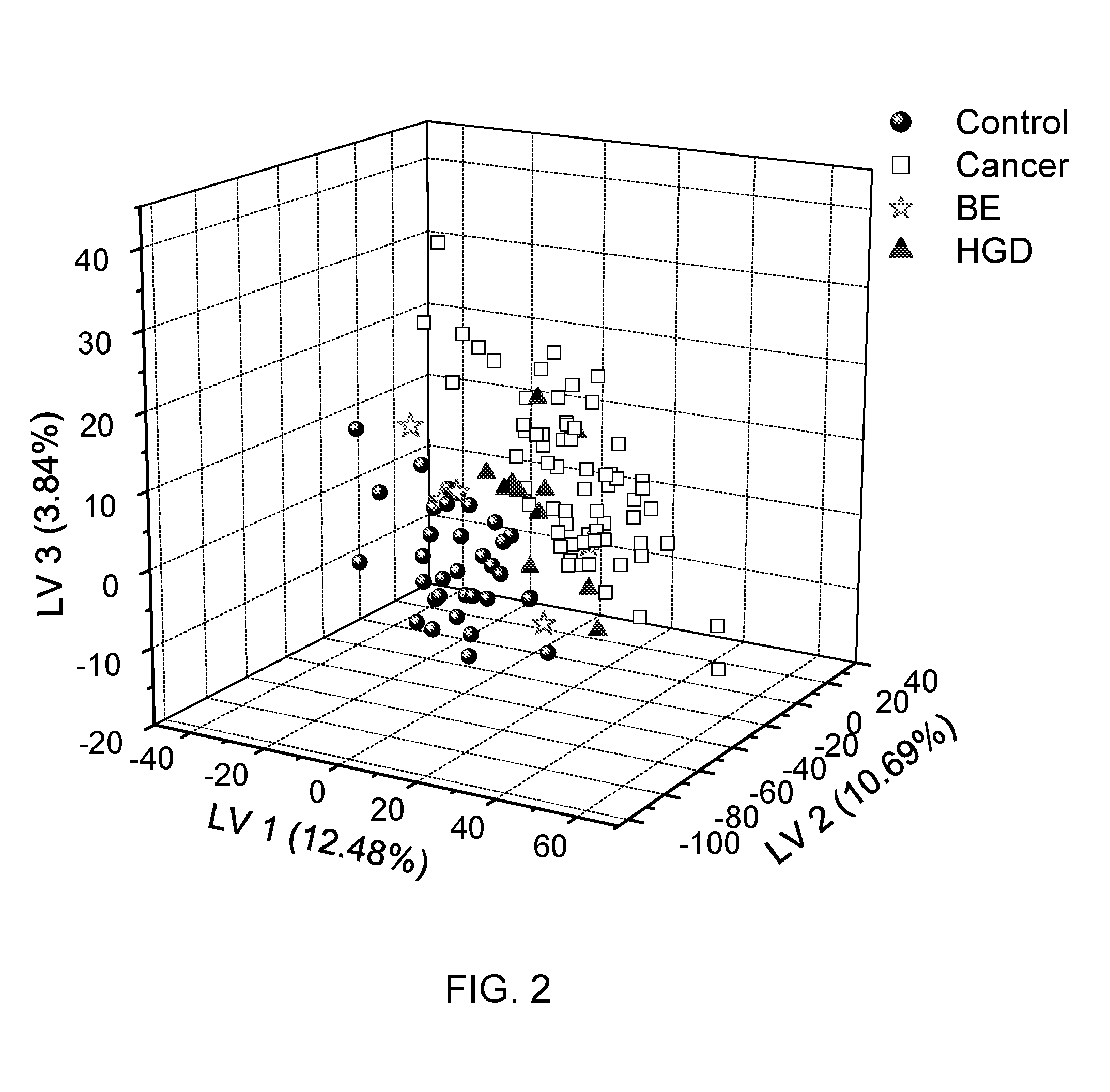
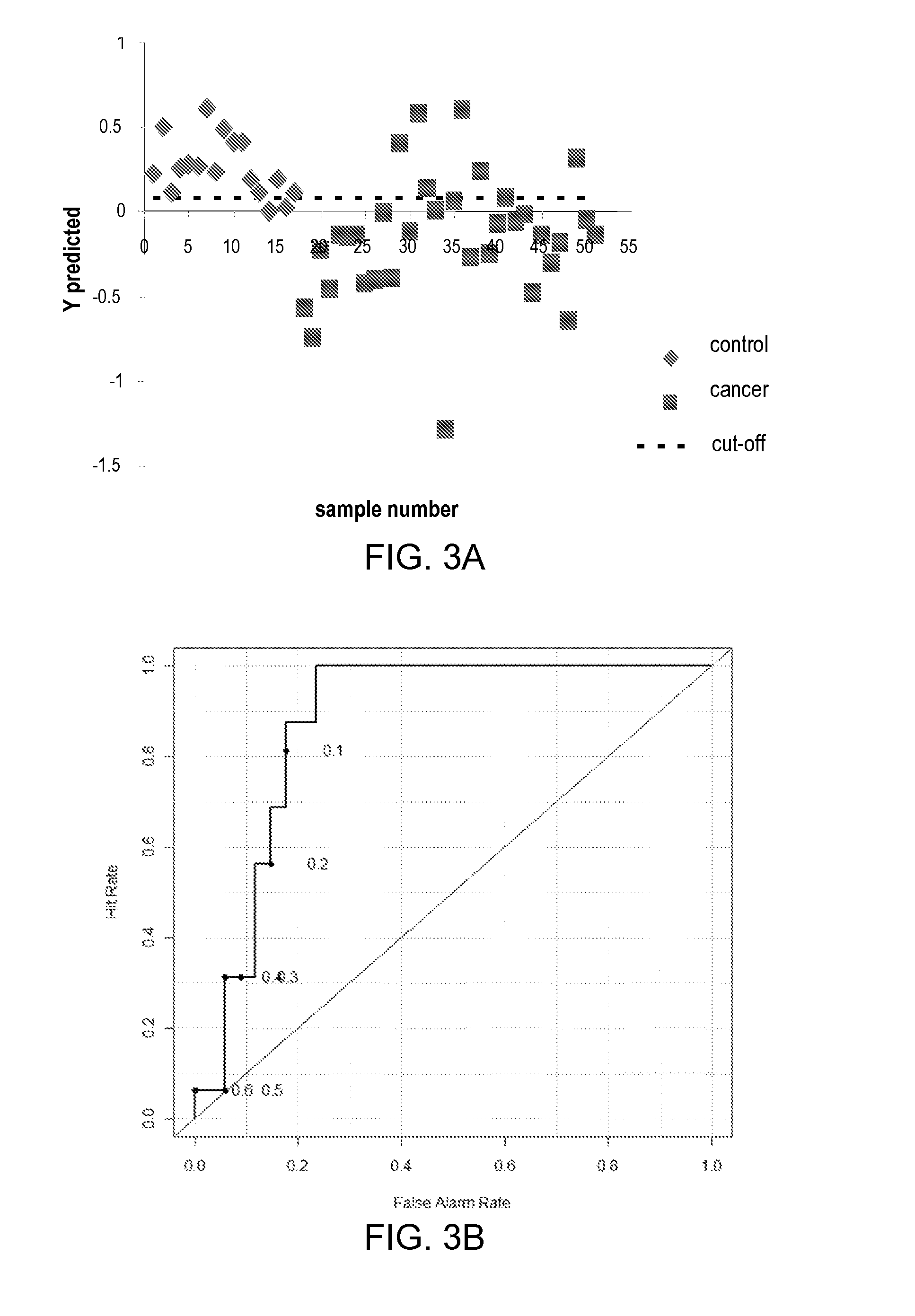
[0071]1H NMR-based metabolite profiling analysis is shown to be an effective approach for differentiating EAC patients and healthy subjects. Eight metabolites showed significant differences in their levels between cancer and control based on the Student's t-test, as shown in Table 4 and FIG. 3A-3D. A PLS-DA model built on these metabolites provided excellent classification between cancer and control, with the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) of >0.85 for both training and validation sample sets. Evaluated by the same model, the BE samples were of mixed classification and HGD samples were mostly classified as EAC samples. A pathway study indicated that altered energy metabolism and changes in the TCA cycle were the dominant factors in EAC biochemistry.
[0072]Chemicals. Deuterium oxide (D2O, 99.9% D) was purchased from Cambridge Isotope Laboratories, Inc. (Andover, Mass.). Trimethylsilylpropionic acid-d4 sodium salt (TSP), tridecanoic acid, chlorophenylala...
example 2
[0094]The LC-MS spectrum for each serum sample consisted of more than 5000 features of which nearly 1400 peaks were assigned to metabolites using the Agilent database. Peaks from the spectra that were missing in more than 10% of the samples from any group were omitted from further analysis. The use of this filter and the Agilent chemical library resulted in a total of approximately 200 identified metabolites common to all the groups. These identified metabolites were analyzed using univariate analysis. The results showed that 40 metabolites varied significantly (p<0.05) between either EAC and normal controls, EAC and high-risk patients (BE and HGD patients), or high-risk patients and normal controls. Thirteen of these metabolites could be verified from the mass spectra and retention times of the authentic commercial compounds.
[0095]Table 9 lists the verified metabolites from LC-MS along with their formulae, masses and retention times. Similarly, as shown in Table 10, fifteen patient...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com