Method for stem cell differentiation in vivo by delivery of morphogenes with mesoporous silica and corresponding pharmceutical active ingredients
a technology of mesoporous silica and stem cell differentiation, which is applied in the field of stem cell differentiation in vivo by delivery of morphogenes with mesoporous silica and corresponding pharmceutical active ingredients, to achieve the effects of enhancing cell survival, improving initial survival of transplanted stem cells, and maintaining long-term viability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Induced Differentiation of Transplanted Human Embryonic Stem Cells with Shh and Retinoic Acid Delivered with Mesoporous Silica
[0116]Background:
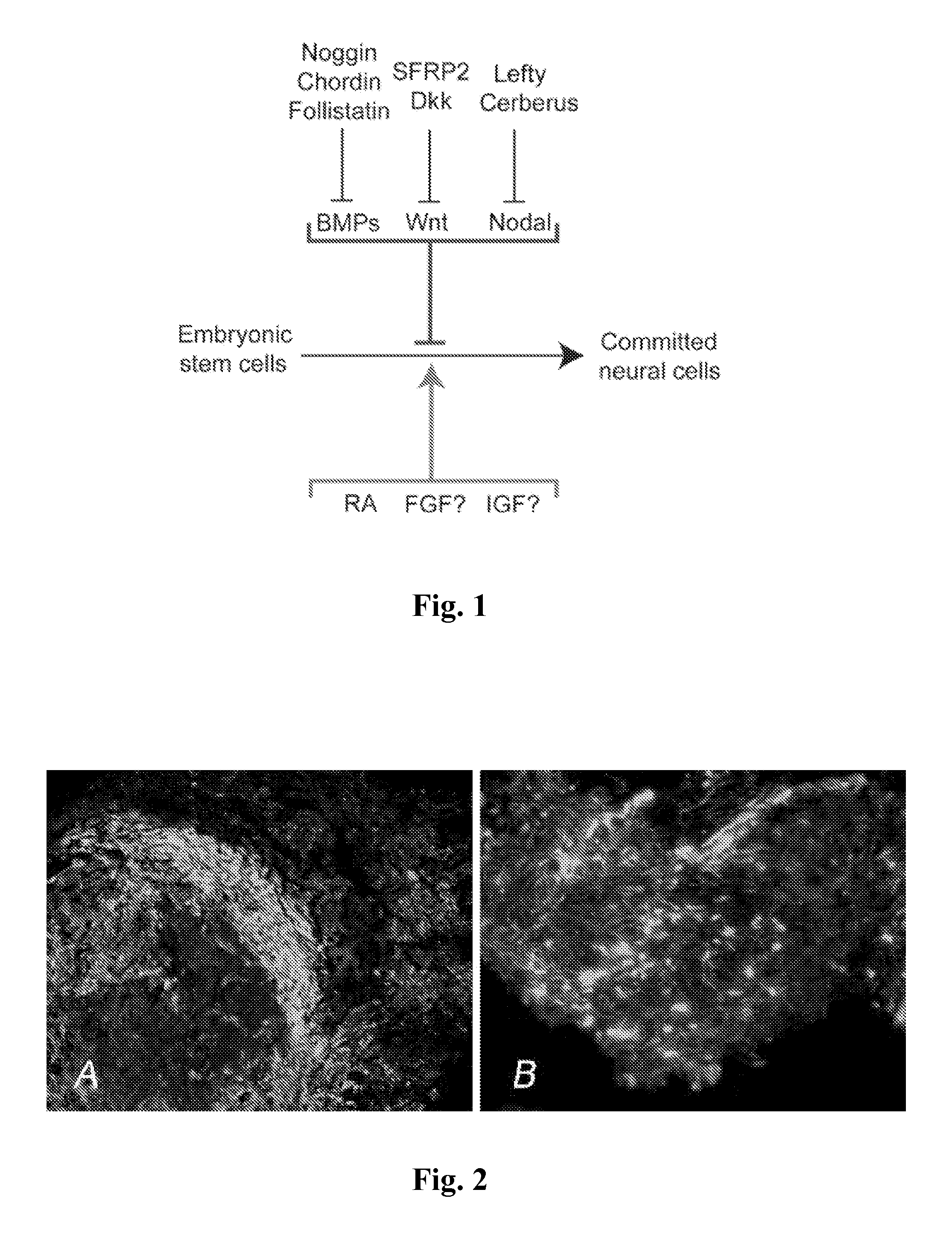
[0117]Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) differentiate into motor neurons, establish functional synapses with muscle fibers, and acquire physiological properties characteristic of embryonic motor neurons when cultured with sonic hedgehog (Shh) agonist and retinoic acid (RA) (Wichterle H, Lieberam I, Porter J A, et al. Directed differentiation of embryonic stem cells into motor neurons. Cell 2002; 110:385-97; Miles G B, Yohn D C, Wichterle H, et al. Functional properties of motoneurons derived from mouse embryonic stem cells. J Neurosci 2004; 24:7848-58). ESC-derived motorneurons transplanted into the developing chick neural tube projected axons toward muscles, received synaptic input, and developed electrophysiological properties similar to endogenous motor neurons (Soundararajan P, Miles G B, Rubin L L, et al. Motoneurons derived from embryonic ste...
example 2
Differentiation of Neural Crest Stem Cells Toward Neuronal Phenotype In Vitro by RA Delivered with Mesoporous Silica
[0129]Background:
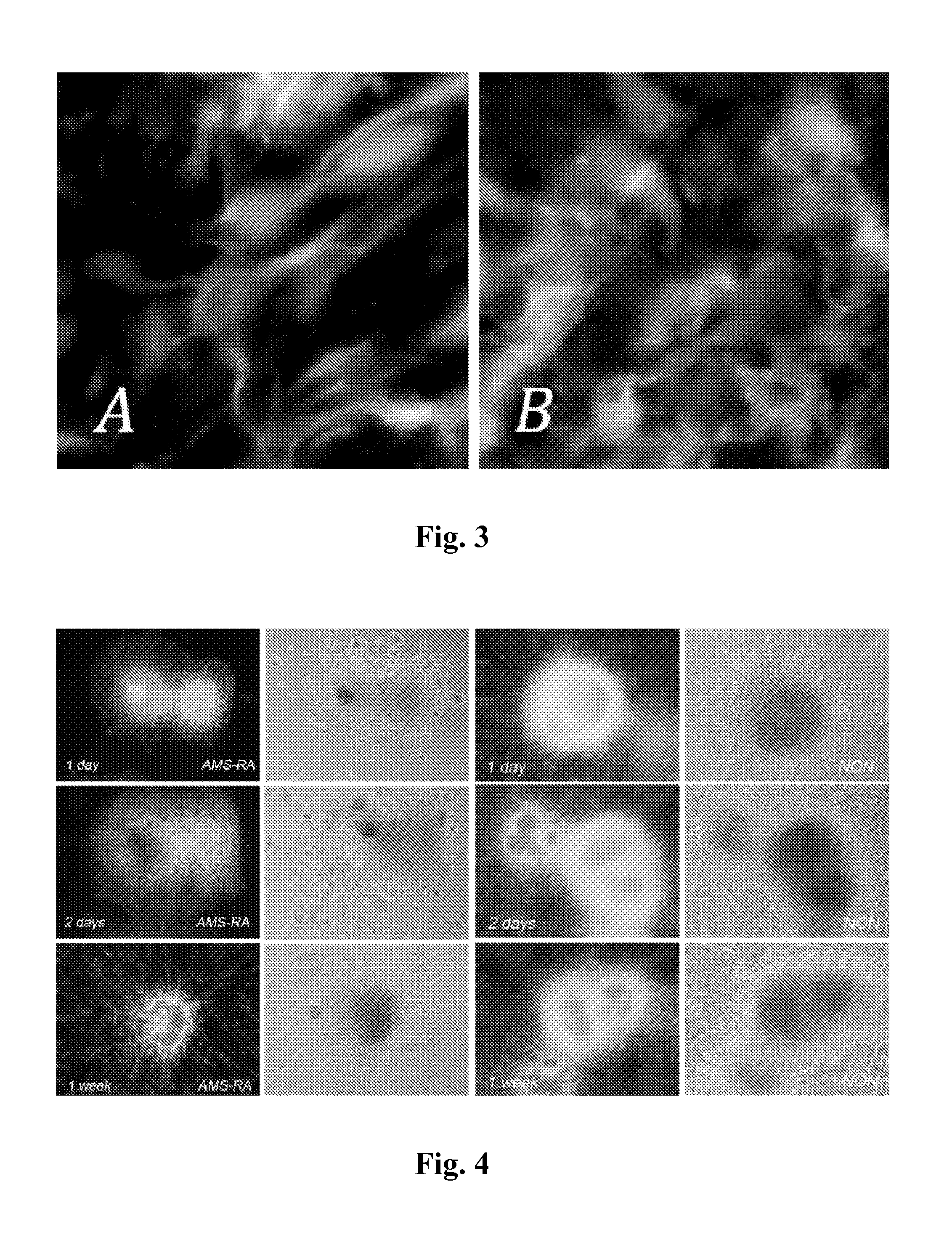
[0130]The RA receptor RAR-beta2 is expressed in dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neuron subtypes. It was shown that retinoid signaling has a role in neurite outgrowth in vivo (Corcoran J, Shroot B, Pizzey J, et al. The role of retinoic acid receptors in neurite outgrowth from different populations of embryonic mouse dorsal root ganglia. J. Cell Sci 2000; 113:2567-74; Dmetrichuk J M, Spencer G E, Carlone R L. Retinoic acid-dependent attraction of adult spinal cord axons towards regenerating newt limb blastemas in vitro. Dev Biol 2005; 281:112-20) by demonstrating that in a peripheral nerve crush model there is less sensory neurite outgrowth in RAR-beta null compared to wild-type mice. In vitro experiments identified sonic hedgehog (Shh) as a downstream target of the RAR-beta2 signaling pathway since it is expressed in the injured DRG of wild-type but not RAR-...
example 3
Differentiation and Migration of NCSCs in the Presence of AMS Under the Kidney Capsule
[0145]Background:
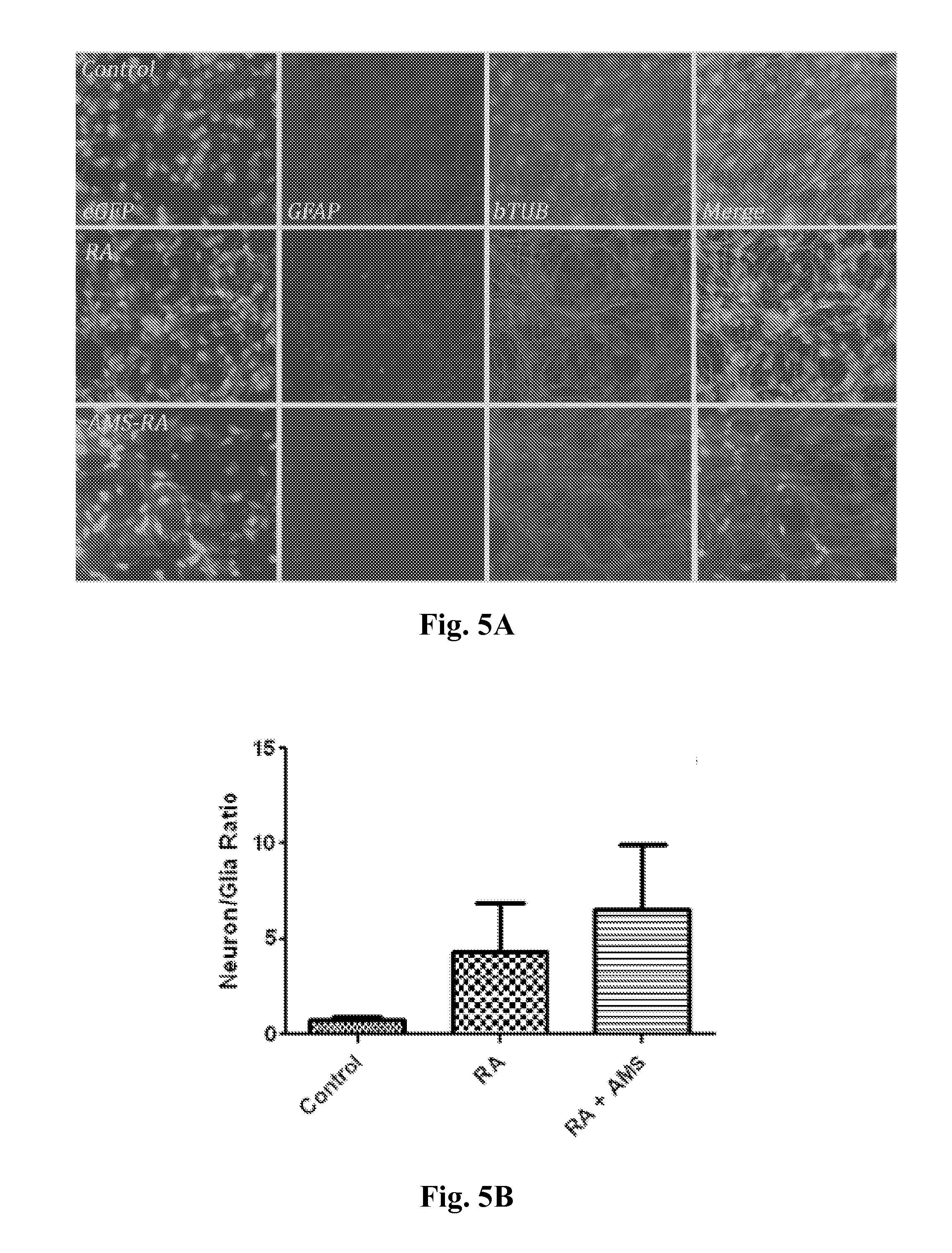
[0146]We previously showed that NCSCs transplanted under the kidney capsule of one pole of the kidney extensively migrate towards co-transplanted pancreatic islets placed in the opposite pole of the same kidney (Olerud J, Kanaykina N, Vasylovska S, et al. Neural crest stem cells increase beta cell proliferation and improve islet function in co-transplanted murine pancreatic islets. Diabetologia 2009; 52:2594-601. Erratum in: Diabetologia. 2010; 53:396. Vasilovska, S [corrected to Vasylovska, S]; Kozlova E N, Jansson L. Differentiation and migration of neural crest stem cells are stimulated by pancreatic islets. Neuroreport 2009; 20:833-8). The purpose of these previous studies was to develop a new protocol for improved outcome after transplantation of pancreatic islets. Transplantation of pancreatic islets is an established therapy in selected patients with type 1 diabetes. The sur...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| sizes | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com