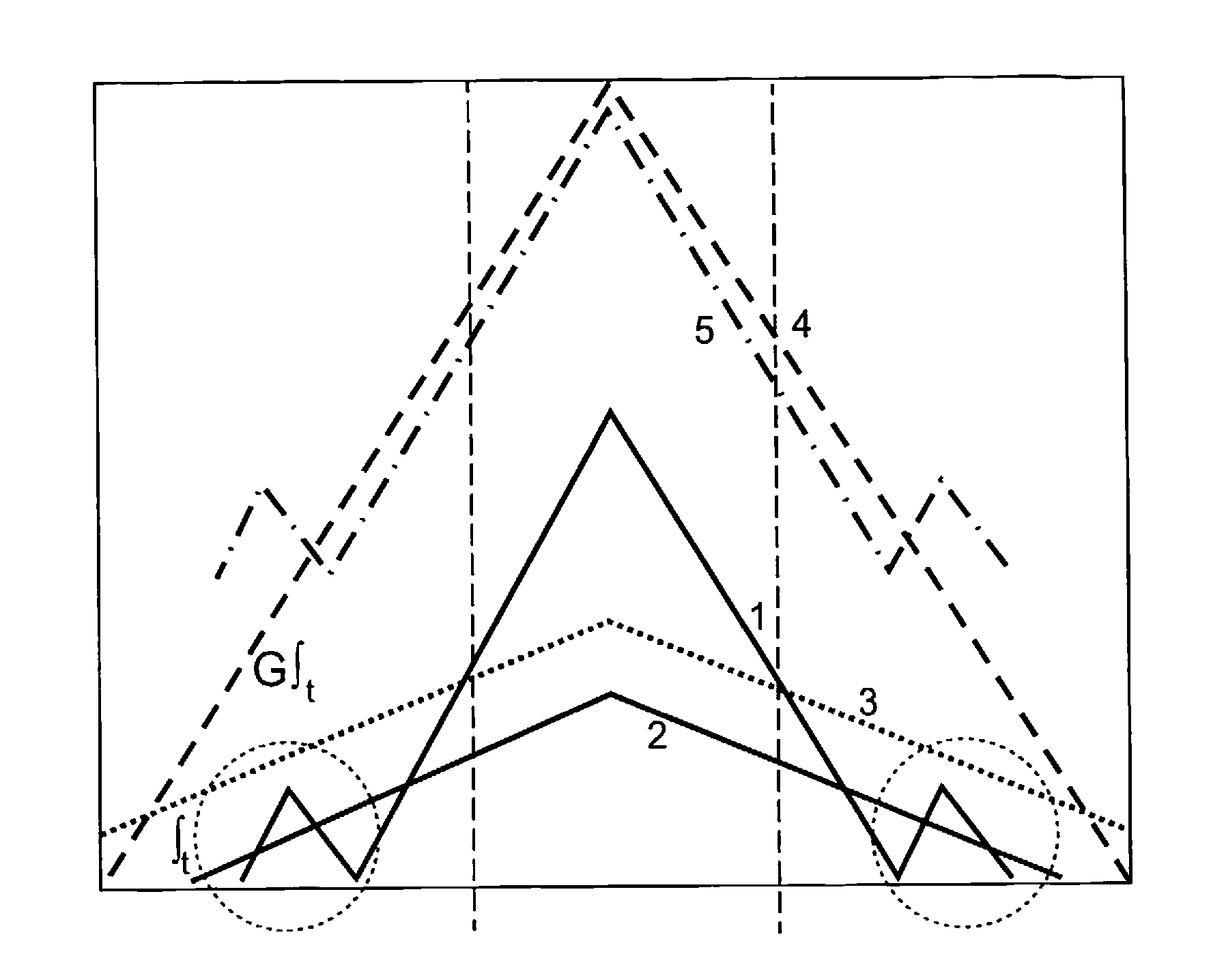
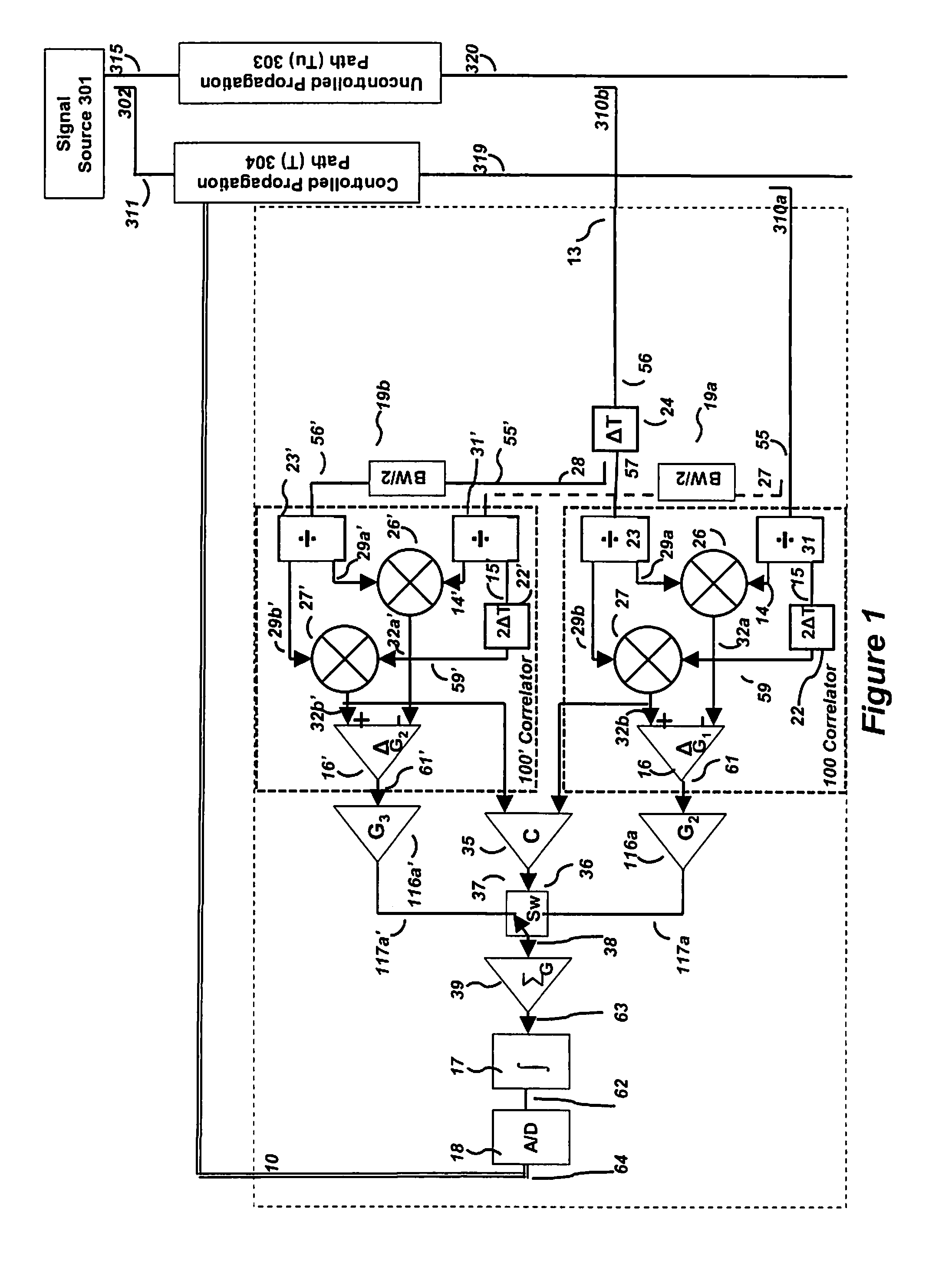
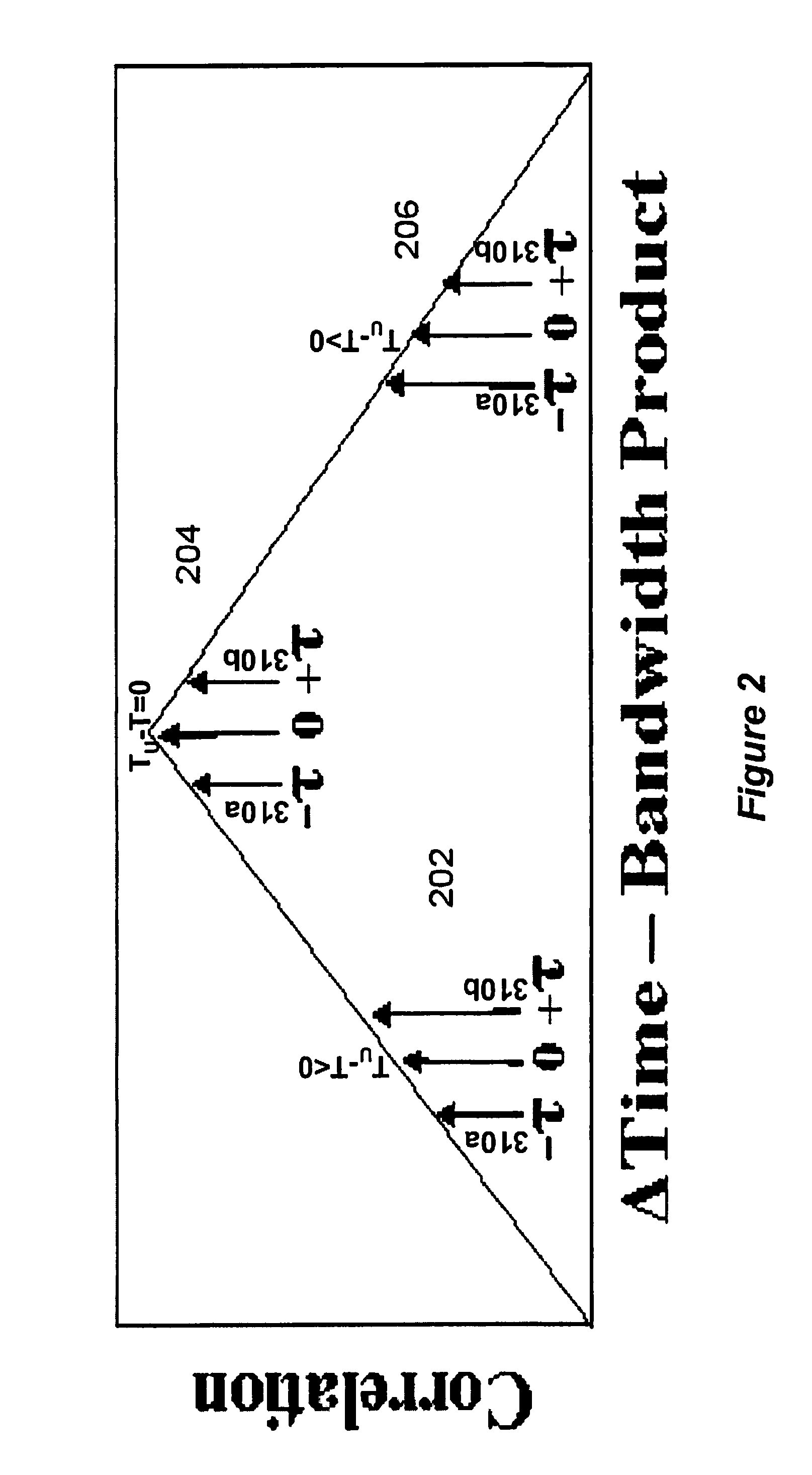
Control interval expansion of variable time delay control structure for channel matching
a control structure and control interval technology, applied in the field of radio communication, can solve the problems of limiting the range of scenarios in which it is operational, limiting the range of operation, and limiting the channel matching range in signal processing paths requiring joint processing, so as to achieve extended time-delay convergence range, and greater initial mismatch in time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0038]In the following discussion, numerous specific details are set forth to provide a thorough understanding of the present disclosure. However, those skilled in the art will appreciate that the present disclosure may be practiced without such specific details. In other instances, well-known elements have been illustrated in schematic or block diagram form in order not to obscure the present disclosure in unnecessary detail. Additionally, for the most part, details concerning network communications, electromagnetic signaling techniques, and the like, have been omitted inasmuch as such details are not considered necessary to obtain a complete understanding of the present disclosure and are considered to be within the understanding of persons of ordinary skill in the relevant art.
[0039]The present description illustrates the principles of the present disclosure. It will thus be appreciated that those skilled in the art will be able to devise various arrangements that, although not e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com