Staggered horizontal well oil recovery process
a horizontal well and oil recovery technology, applied in the direction of fluid removal, earth-moving drilling, borehole/well accessories, etc., can solve the problems of thermal inefficiency in transferring heat to oil within the reservoir, and high cost of steam recovery methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Staggered Well (Air Injection) Method
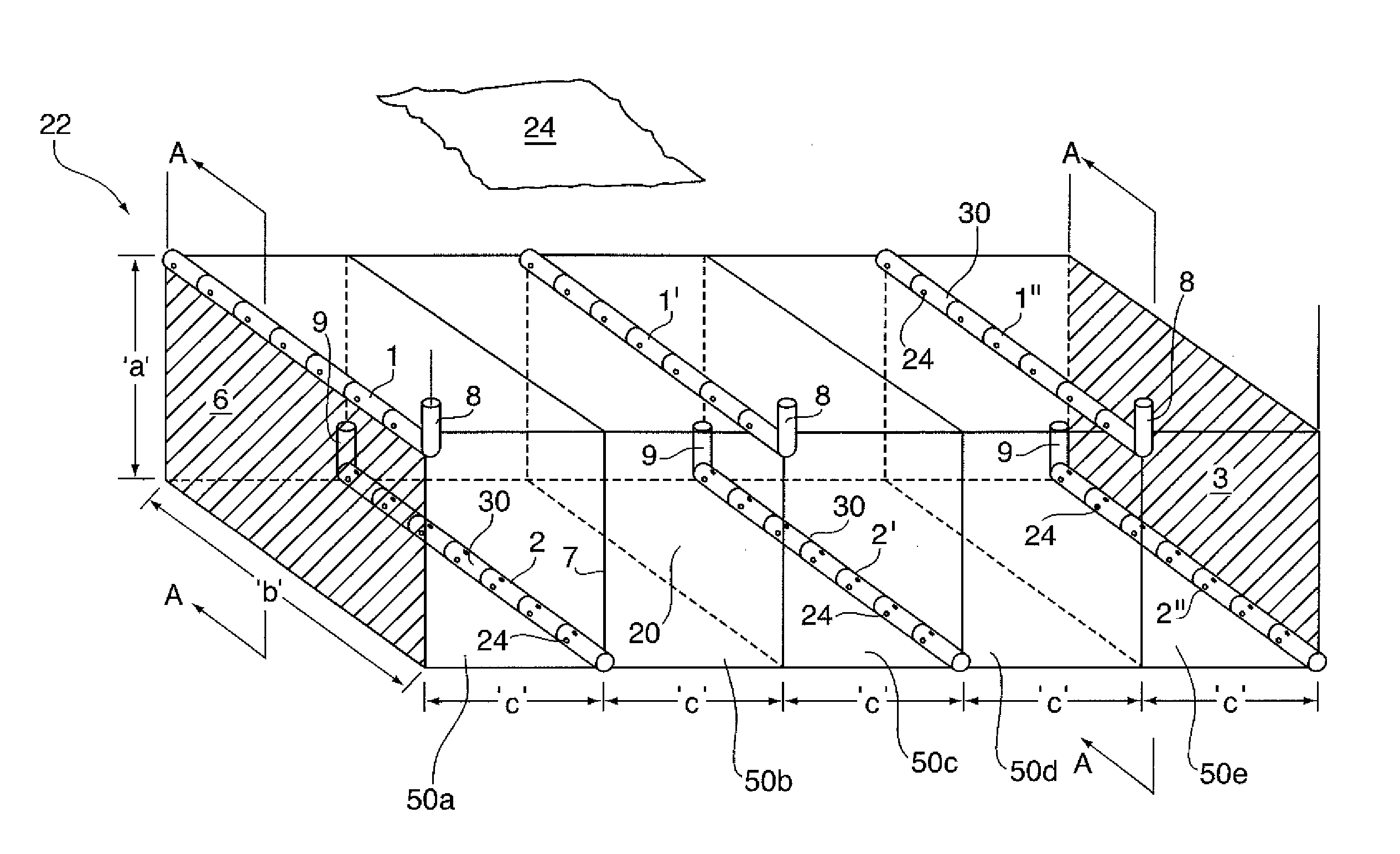
[0101]FIGS. 1 and 4(i)-(iii) depict a method of oil recovery (using air injection and in situ combustion heating) of the present invention, and in particular depict the method used in Example 1 [Staggered Well (Air Injection)], utilizing a total air injection volume of 50,000 m3 / d.
[0102]For the Staggered Well (Air Injection) Method as shown in FIGS. 1, 2.5 injection wells 1, 1′, and 1″, and 2.5 production wells 2, 2′, and 2′ as part of grid blocks 50a-50e, were all simultaneously drilled, for a total of five wells. The reservoir thickness ‘a’ was 20 m and the well offset ‘c’ was 50 m for each grid block 50a-50o. Air injection rates were 10,000 m3 / d for well 1 and 20,000 m3 / d for each of injectors 1′ and 1″, for a total of 50,000 m3 / d for the grid block pattern 50a-50e.
[0103]A summary of results, namely the Oil Recovery Factor over time (1,825 days=5 years) for Example 1, is shown in FIG. 11 as line ‘X’.
example 2
Crossed-Wells Method
[0104]FIG. 10 shows an alternative method of oil recovery from a subterranean reservoir 22, which is not the subject matter of this application but of another patent application of the within inventor and commonly assigned (hereinafter the “crossed wells” method).
[0105]In the crossed-well method depicted in FIG. 10, injector wells 1, 1′ are perpendicularly disposed to the horizontal collection wells 2, 2′, 2″, and 2′″. Specifically in this crossed-well method, parallel horizontal well injection wells 1, 1′ are placed high in reservoir 22, and parallel horizontal production wells 2, 2′, 2″, &2″ are placed low in reservoir 22 perpendicular to injection wells 1, 1′. Horizontal Injection well 1′ is located distance ‘q’ (25 m) from the front edge of the model and injection well 1 is placed distance ‘q’ from the back side of reservoir 22, namely with injectors 1, 1′ separated by a distance ‘2 q’. The well length is “b”. The spacing of the horizontal production wells is...
example 3
Staggered Steam Method
[0108]Example 3 (method of FIG. 1, but with hot steam injection instead of air injection and not employing in situ combustion) is not part of the present invention, and is only provided to illustrate the comparative efficiency with other oil recovery methods (e.g. Example 1 and Example 2).
[0109]Saturated steam was injected continuously at the rate of 150, 300 and 300 m3 / d (water equivalent—for a total of 50,000 m3 / d gaseous equivalent) into injection wells 1, 1′ and 1″ respectively, while production wells 2, 2′ and 2″ were open to production.
[0110]A summary of results of the Staggered Steam method, showing the Oil Recovery Factor over time (1,825 days=5 years) for Example 3, is shown in FIG. 11 as line ‘Y’.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com