Tissue-Engineered Endothelial and Epithelial Implants Differentially and Synergistically Regulate Tissue Repair
a tissue engineering and epithelial technology, applied in the field of tissue engineering endothelial and epithelial implants differentially and synergistically regulate tissue repair, can solve the problems of tight association between functional imbalance and airway structure remodeling, limited current treatment options for airway disorders and other tubular structures, and often adverse effects, so as to reduce or inhibit abnormal or pathological tissue remodeling typified
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Endothelial and Epithelial Cell Implants Differentially Regulate Airway Repair
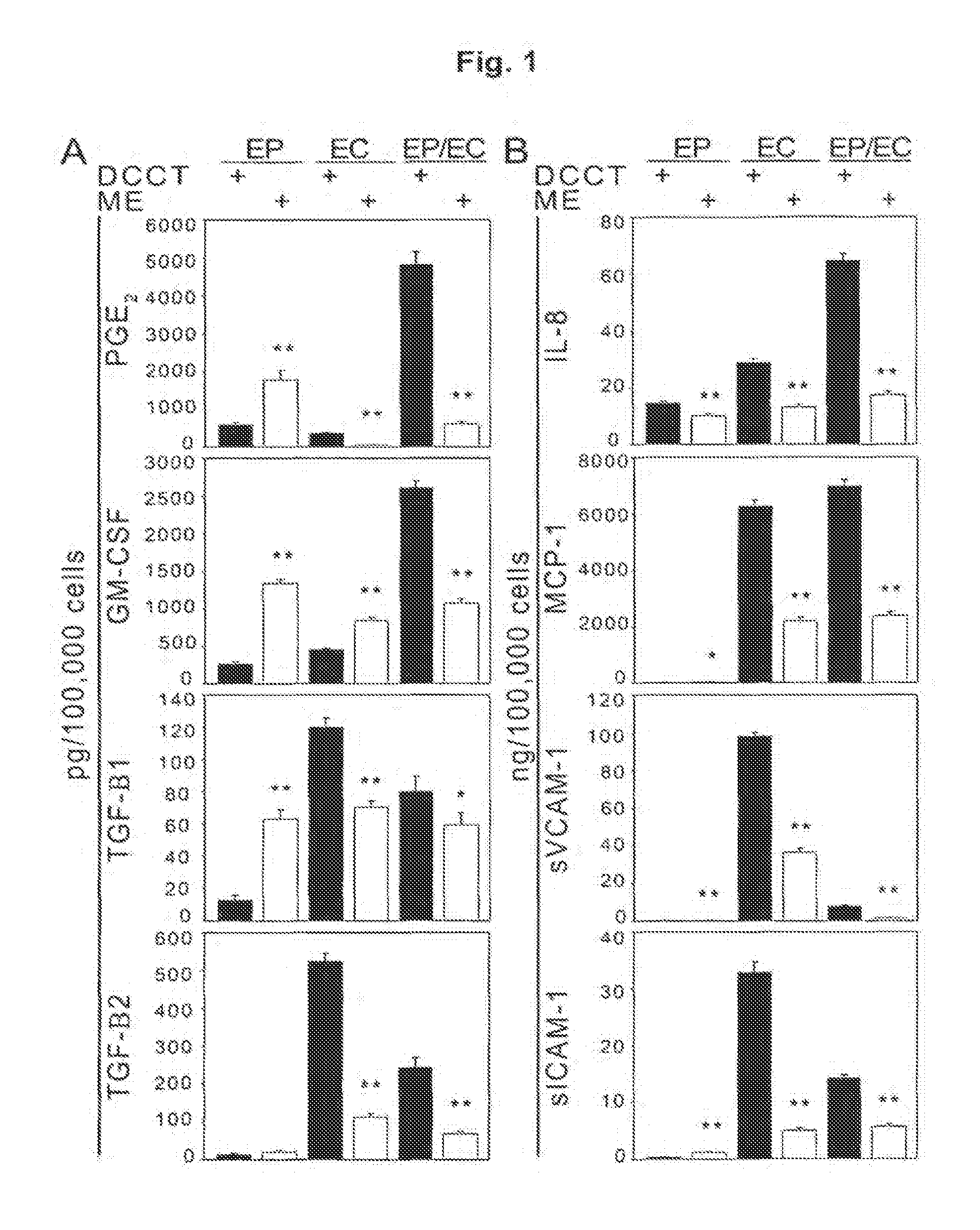
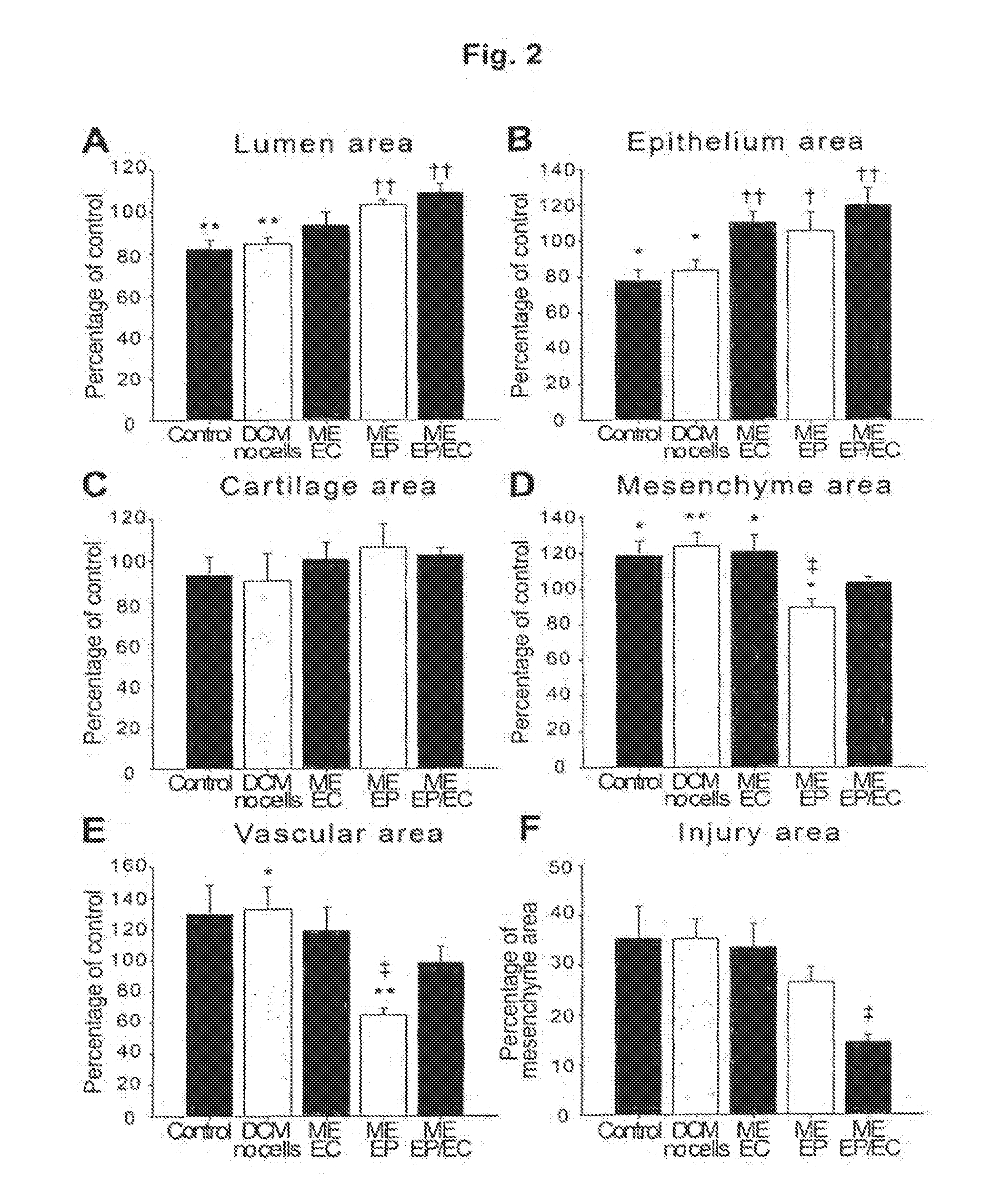
[0094]In the present study, an in vivo airway injury model was employed to understand whether injury and repair of the airway is mediated by the first line sensor—the airway epithelium—or by the endothelial cells of the perfusing vasculature. Tissue engineered implants of the bronchial epithelium and endothelium promoted specific and synergistic repair of the airway through biochemical regulation of the airway microenvironment. While epithelial cells modulate local tissue composition and reaction, endothelial cells preserve the epithelium and perfusing microvasculature; together their relative impact was enhanced suggesting both cell types together increase airway repair. From these findings it may be inferred that in vascular injury, engineered endothelial cells implants recapitulate aspects of endothelial cells from both the epithelium and the perfusing microvasculature, while airways and other tubular o...
example 2
Fibroblast Growth Inhibited by Matrix-Embedded Cells
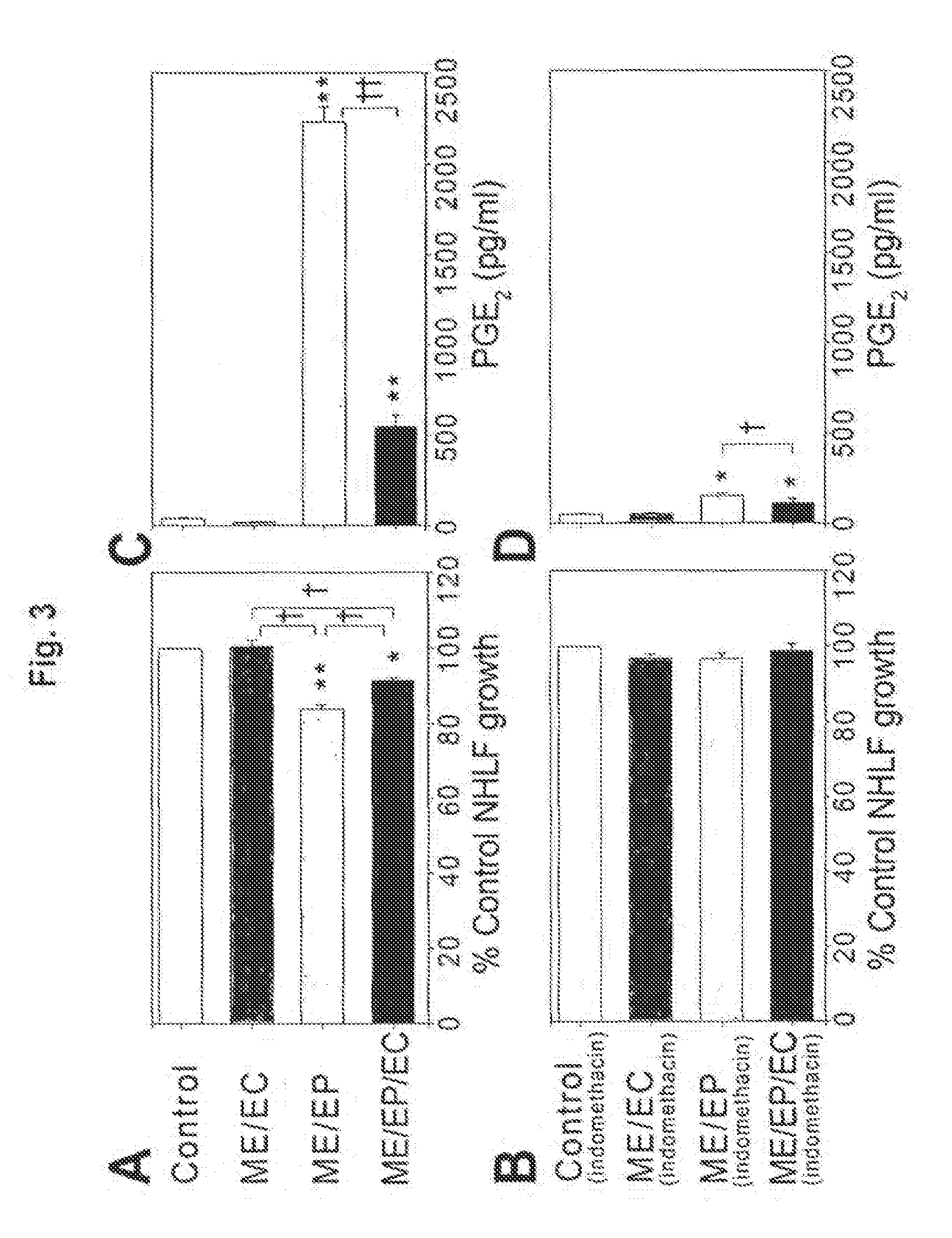
[0101]Fibroblasts are essential supporting cells of the airway and of the mesenchymal hyperplastic lesion. To determine the effect of matrix-embedded cells on fibroblast proliferation, normal human long fibroblasts (NHLF) were seeded at 5×104 cells / well and grown for 48 hours on 6-well transwell plates (Costar). Fresh medium (5 ml / well of BEGM:EGM-2, 1:1) was then added with or without 5 μM indomethacin (Sigma) and 24 mm inserts (0.4 μm membrane) with matrices (engrafted with endothelial cells, epithelial cells, or co-cultures of epithelial cells and endothelial cells) placed on top of the NHLF. After an additional 48 hours, NHLF were trypsinized and total cell number for each well was determined with a cell counter (Coulter Counter). Medium was collected and analysed using commercially available ELISA kits.
[0102]NHLF proliferation was maximally reduced when cocultured with matrices containing epithelial cells alone, modestly by em...
example 3
Tube Formation Inhibited by Matrix-Embedded Cells
[0104]The effect of matrix-embedded cells on angiogenesis in vitro was examined by tube formation of human umbilical vein epithelial cells (HUVEC) cultured with conditioned medium (CM). This process involved migration, invasion, and differentiation of HUVEC in the formation of the tubular network. A CAS™ HT tube formation kit (Trevigen) was used. Reduced growth factor basement membrane extract purified from Engelbreth-Holm-Swarm (EHS) tumor was pipetted into wells of a 48-well plate (100 μl / well) and incubated at 37° C. for 1 hours to allow the extract to solidify. HUVEC were plated at a density of 2×104 cells / well and incubated at 37° C. for 8 hours with either BEGM:EGM-2 (1:1) medium unconditioned (incubated at 37° C. without cells for 48 h) or conditioned for 48 hours from matrices engrafted with endothelial cells, epithelial cells, or epithelial cells / endothelial cells.
[0105]Eight hours after seeding, images of tube formation were...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| emission current | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com