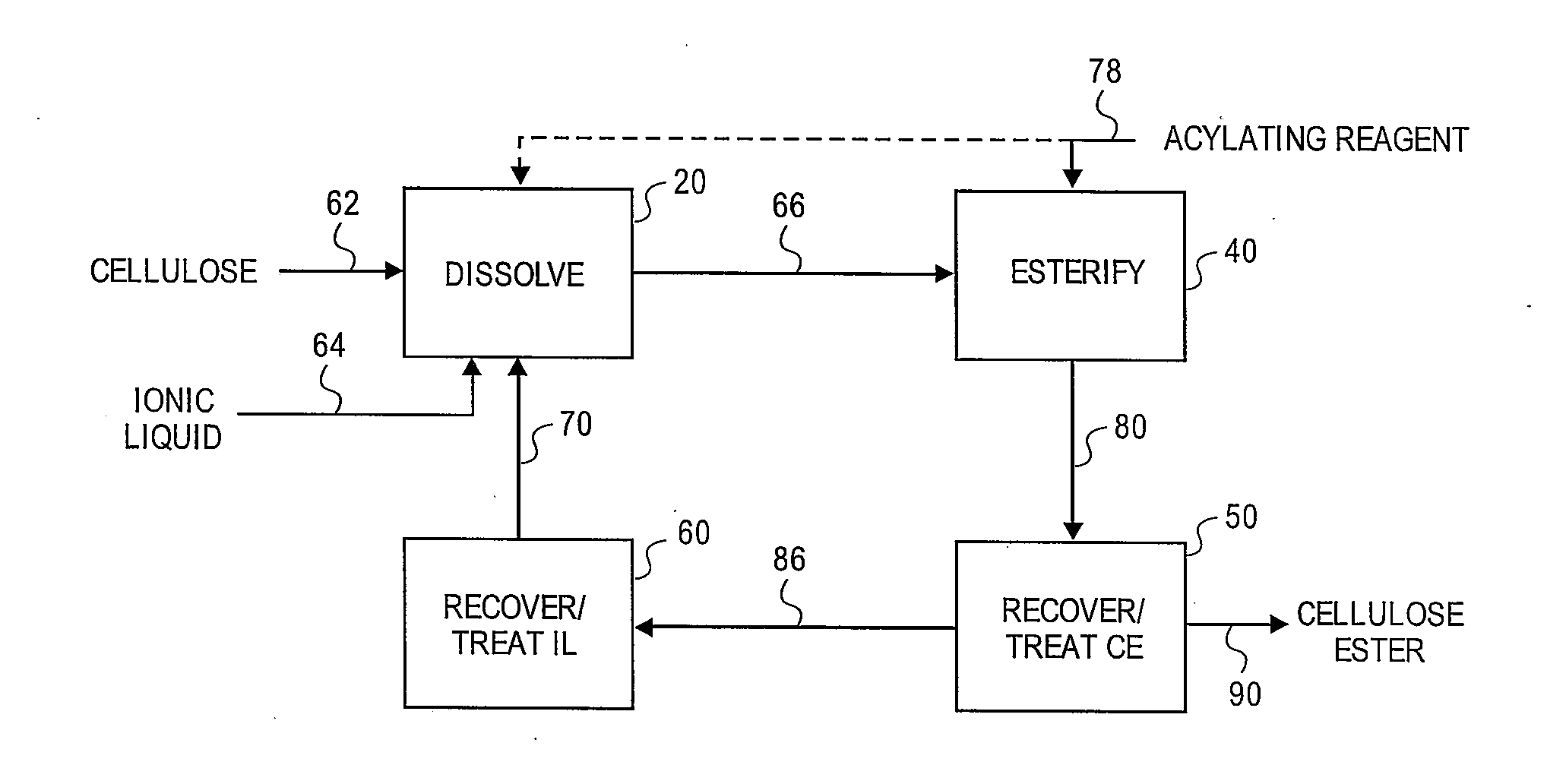
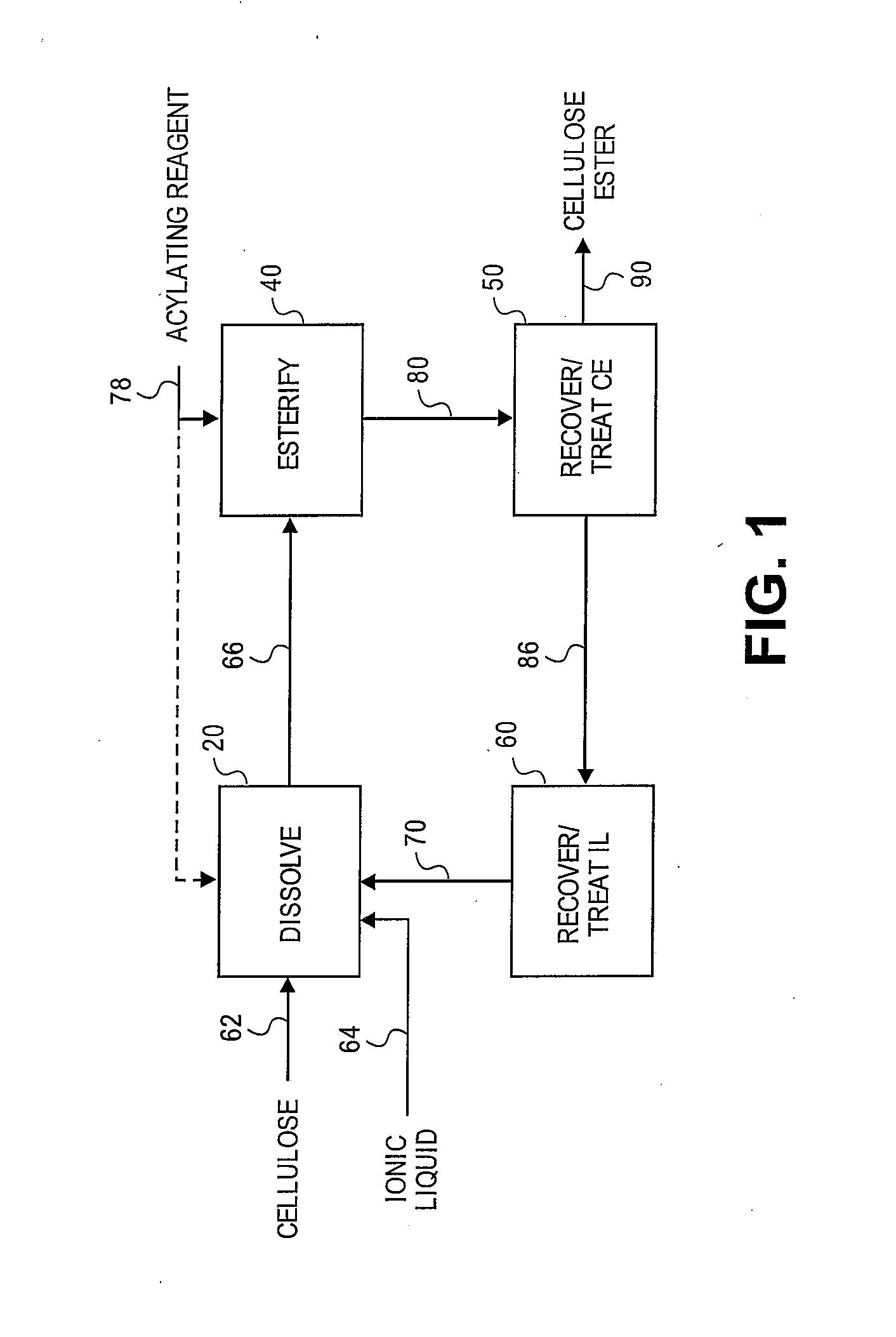
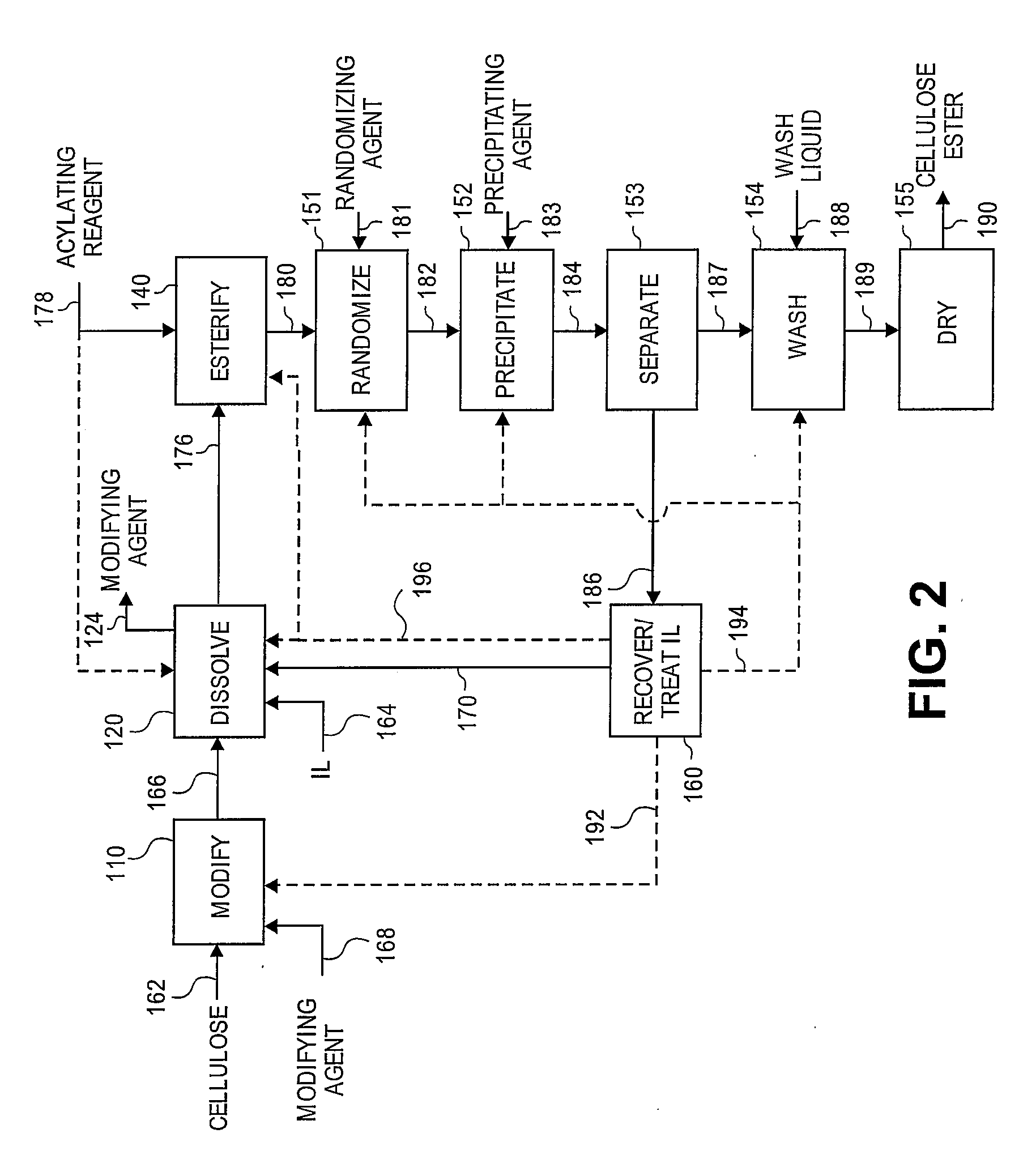
Regioselectively substituted cellulose esters produced in a carboxylated ionic liquid process and products produced therefrom
a technology of cellulose esters and ionic liquids, which is applied in the field of cellulose esters and/or ionic liquid production processes, can solve the problems of insufficient methods and apparatuses for reforming and/or recycling ionic liquids, the inability to use ionic liquid solvents in many processes, and the cost of ionic liquids
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of Cellulose Ester (Comparative)
[0203]A 3-neck 100 mL round bottom flask, fitted with two double neck adapters giving five ports, was equipped for mechanical stirring, with an iC10 diamond tipped IR probe (Mettler-Toledo AutoChem, Inc., Columbia, Md., USA), and with an N2 / vacuum inlet. To the flask was added 61 g of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride. Prior to adding the [BMIm]Cl, the ionic liquid was melted at 90° C. then stored in a desiccator; during storage, the [BMIm]Cl remained a liquid. While stirring rapidly, began adding 3.21 g of previously dried microcrystalline cellulose (DP ca. 335) in small portions (3 min addition). The slurry was stirred for 5 min before applying vacuum. After ca. 3 h 25 min, most of the cellulose had dissolved except for a few small pieces and 1 large piece stuck to the probe. After 5.5 h, the oil bath temperature was increased to 105° C. to speed up dissolution of the remaining cellulose. The solution was maintained at 105° C. for 1.5...
example 2
Modification of Cellulose with Water
[0207]A 3-neck 100 mL round bottom flask, fitted with two double neck adapters giving five ports, was equipped for mechanical stirring, with an iC10 diamond tipped IR probe, and with an N2 / vacuum inlet. To the flask was added 64.3 g of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride. Prior to adding the [BMIm]Cl, the IL was melted at 90° C. then stored in a desiccator; the [BMIm]Cl remained a liquid during storage. To the ionic liquid was added 3.4 g (5 wt %) of microcrystalline cellulose (DP ca. 335) at ambient temperature while stirring rapidly to disperse the cellulose. Approximately 12 min after adding the cellulose, a preheated 80° C. oil bath was raised to the flask. After ca. 17 min in the 80° C. oil bath, visually, all of the cellulose appeared to be dissolved. After ca. 22 min in the 80° C. oil bath, began applying vacuum. To insure complete removal of water, 50 min after applying vacuum, the oil bath setting was increased to 105° C. and the solutio...
example 3
MSA Secondary Component, No Modification with Water
[0212]Cellulose (3.58 g, 5 wt %) was dissolved in 68 g of [BMIm]Cl in a manner similar to Example 2. To the cellulose solution (contact temperature=80° C.) was added a mixture of 433 mg MSA and 6.76 g of Ac2O (3 eq) drop wise (8 min). The reaction was sampled throughout the reaction period by removing 6-10 g aliquots of the reaction mixture and precipitating in 100 mL of MeOH. The solid from each aliquot was washed 2× with 100 mL portions of MeOH then dried at 60° C., 5 mm Hg. The solid samples were snow white. After ca. 2 h, all of the Ac2O appeared to be consumed by IR. The experiment was aborted and the remaining sample was processed as above.
[0213]The precipitation and the wash liquids from each aliquot were combined and concentrated invacuo at 68° C. until the vacuum dropped to 24 mm Hg which provided 64 g of recovered [BMIm]Cl. Unlike Example 2, analysis by 1H NMR revealed that the ionic liquid did not contain any acetic acid ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com