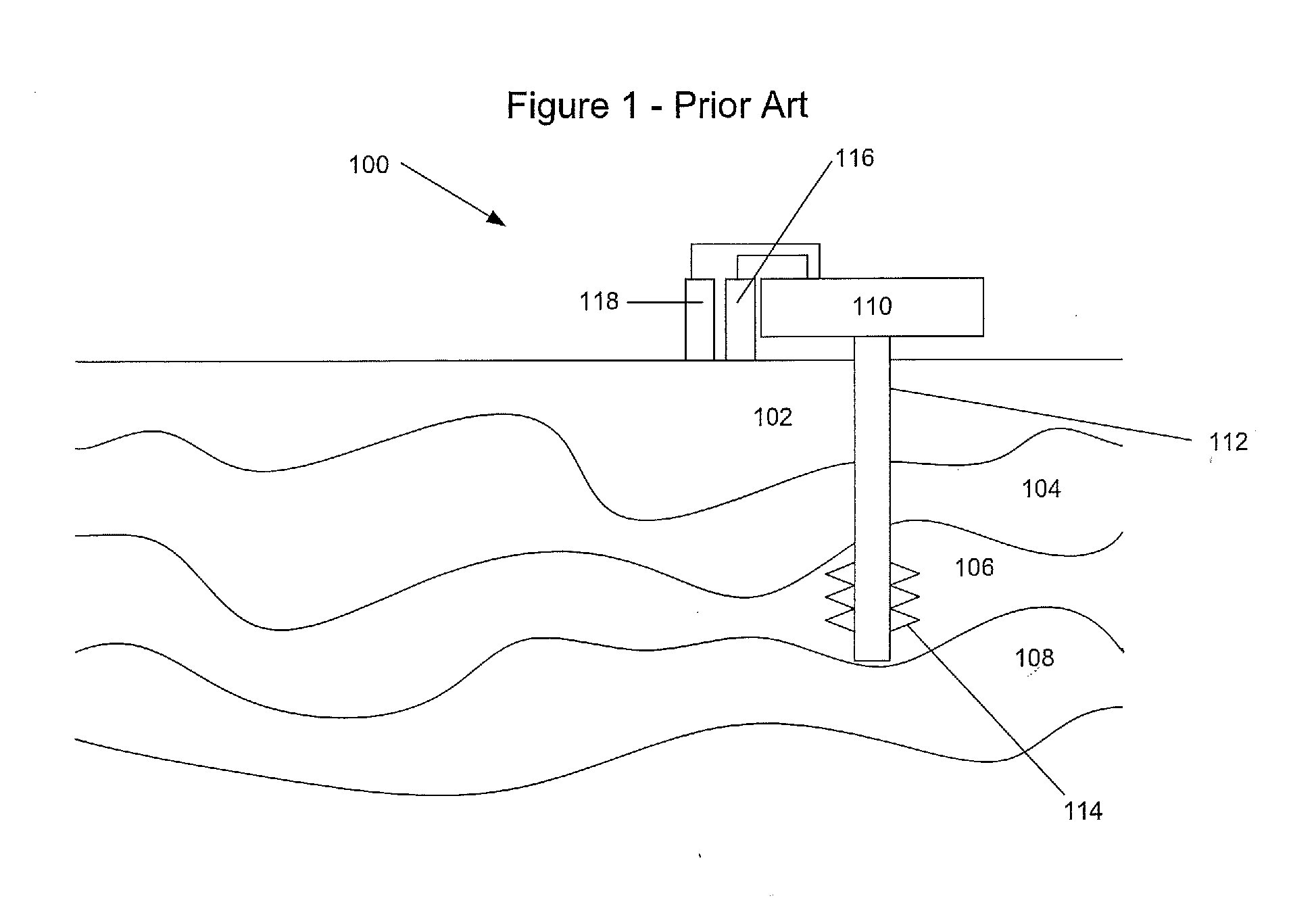
Water injection systems and methods
a technology of water injection system and water injection, applied in the field of systems and methods, can solve the problem that the observed changes cannot explain the potential changes of the surface, and achieve the effect of enhancing crude oil recovery and lowering ionic strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0060]FIG. 5:
[0061]Results from spontaneous imbibition experiments on Middle Eastern limestone core material at 70° C. (Sample1). Dashed line indicates a point in time when change of the brine in the Amott cell took place.
[0062]A spontaneous imbibition test was carried out at 70° C. on Middle Eastern limestone core Sample 1 of about 50 mD permeability and 22% porosity. The oil viscosity was 3.2 mPas. The ionic strength of the formation brine was 4.39 mol / L, while fresh water, used as wettability modifying brine, had ionic strength of 0.32 mol / L. Upon change from the formation water to the fresh water, there was additional oil recovery of 20% indicating wettability change towards more water-wet. Hence, reduction of ionic strength of the brine by a factor of 14 leads to wettability modification.
[0063]FIG. 6:
[0064]Results from spontaneous imbibition experiments on Middle Eastern limestone core material at 70° C. using solution of NaCl as an imbibition brine.
[0065]Second experiment was ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com