Adjustable brace
a brace and adjustable technology, applied in the field of adjustable braces, can solve the problems of not being able to adjust the size of the cast to compensate for the reduced size, and achieve the effects of reducing weight, improving comfort and hygiene, and simplifying the design and construction of the bra
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
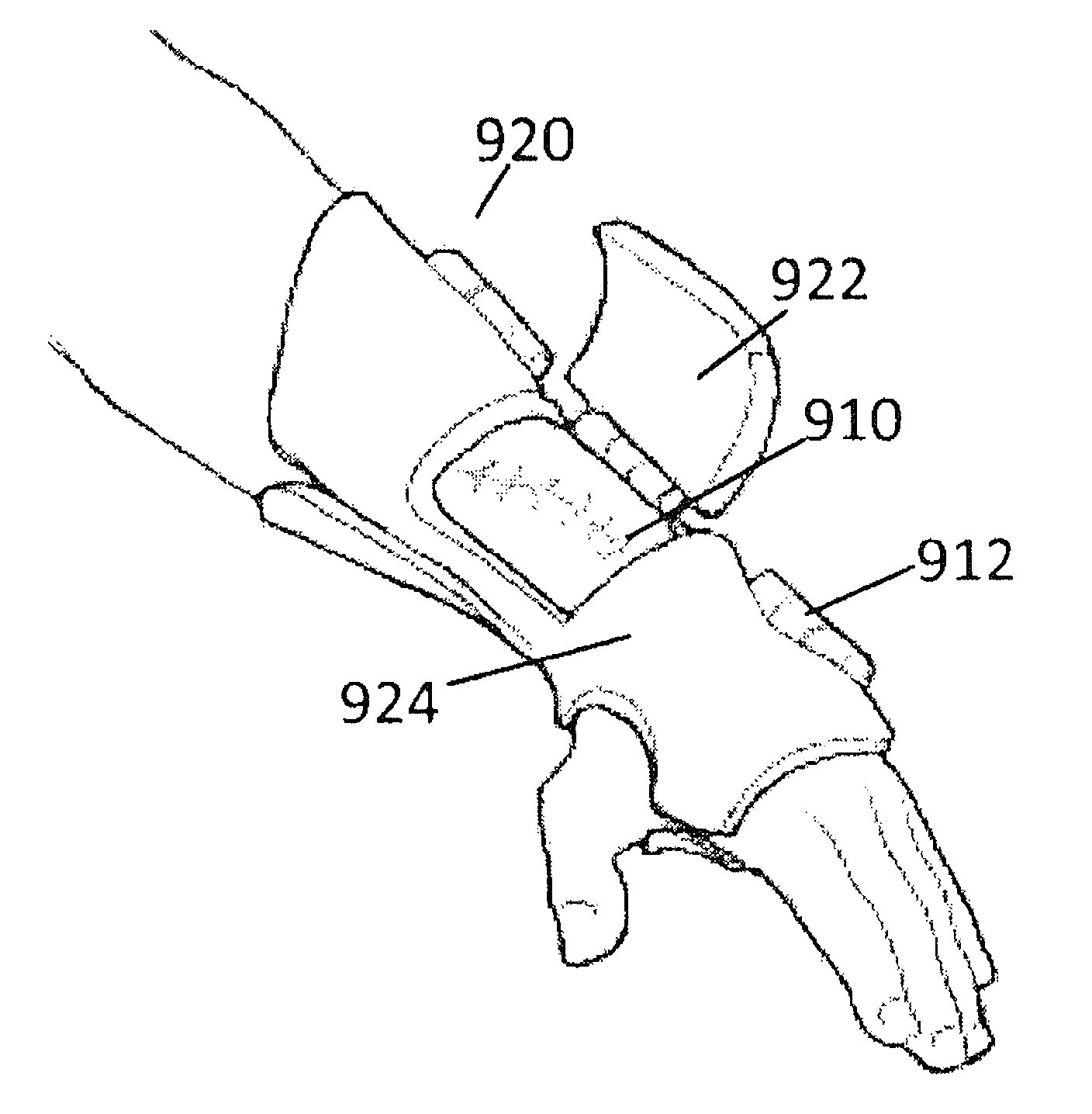
[0025]The present invention is a custom designed and adjustable cast or brace having a interior surfaces that corresponds closely to a body. When a patient injures a limb, such as a broken bone, there can be a swollen area around the injury. The adjustable brace can be designed to closely fit around the limb when it is initially injured. As the injured limb heals, the swelling can go down which results in an open volume between the limb and the cast or brace. This open volume reduces the support for the bone and the limb. When an open space is detected, the adjustable brace can adjusted to reduce the cross section of the brace at the region that surrounds the portion or portions of the limb that are now smaller in size. Thus, the adjustable brace can be adjusted to accurately fit the patient's anatomy as the surface changes.
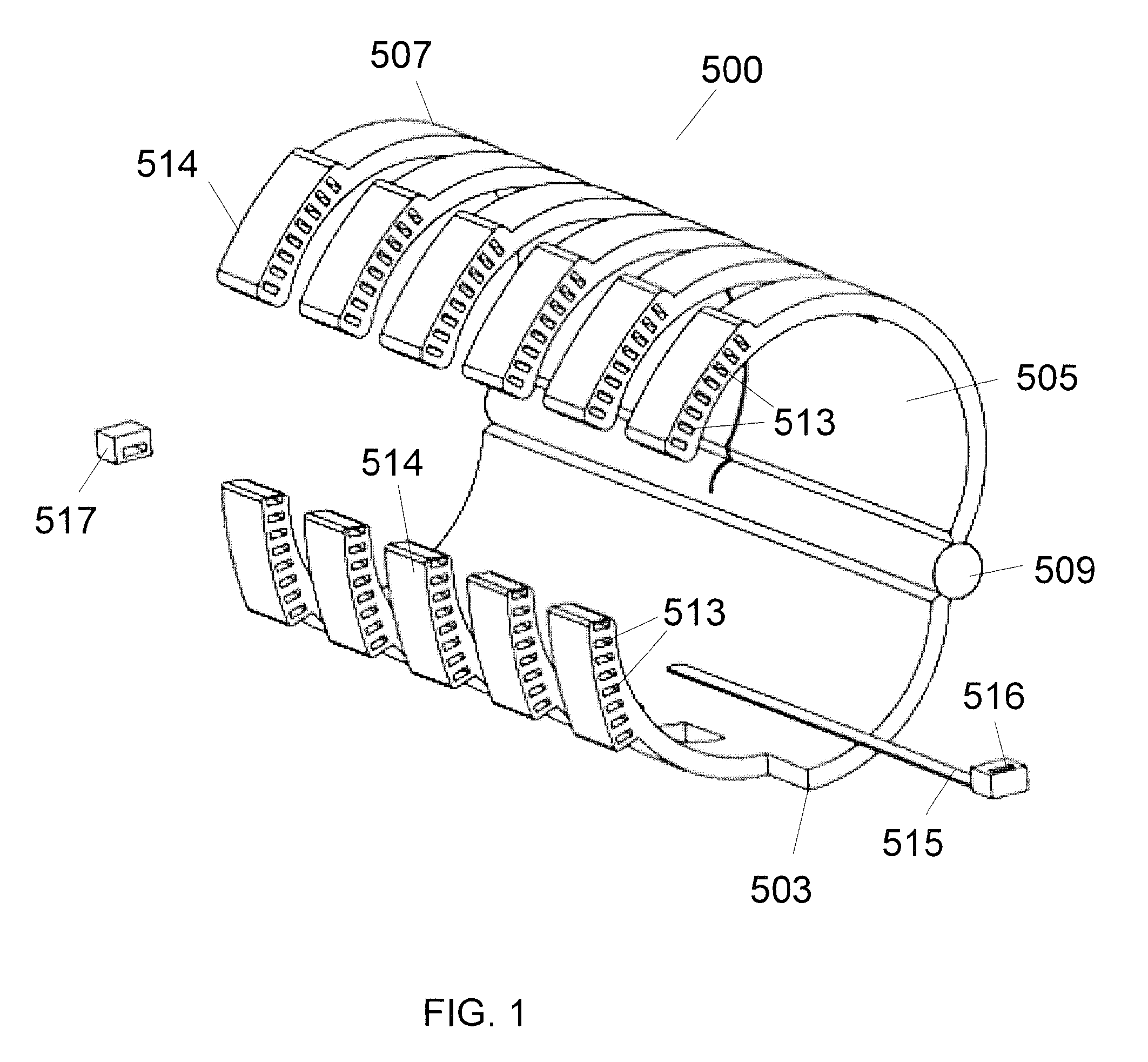
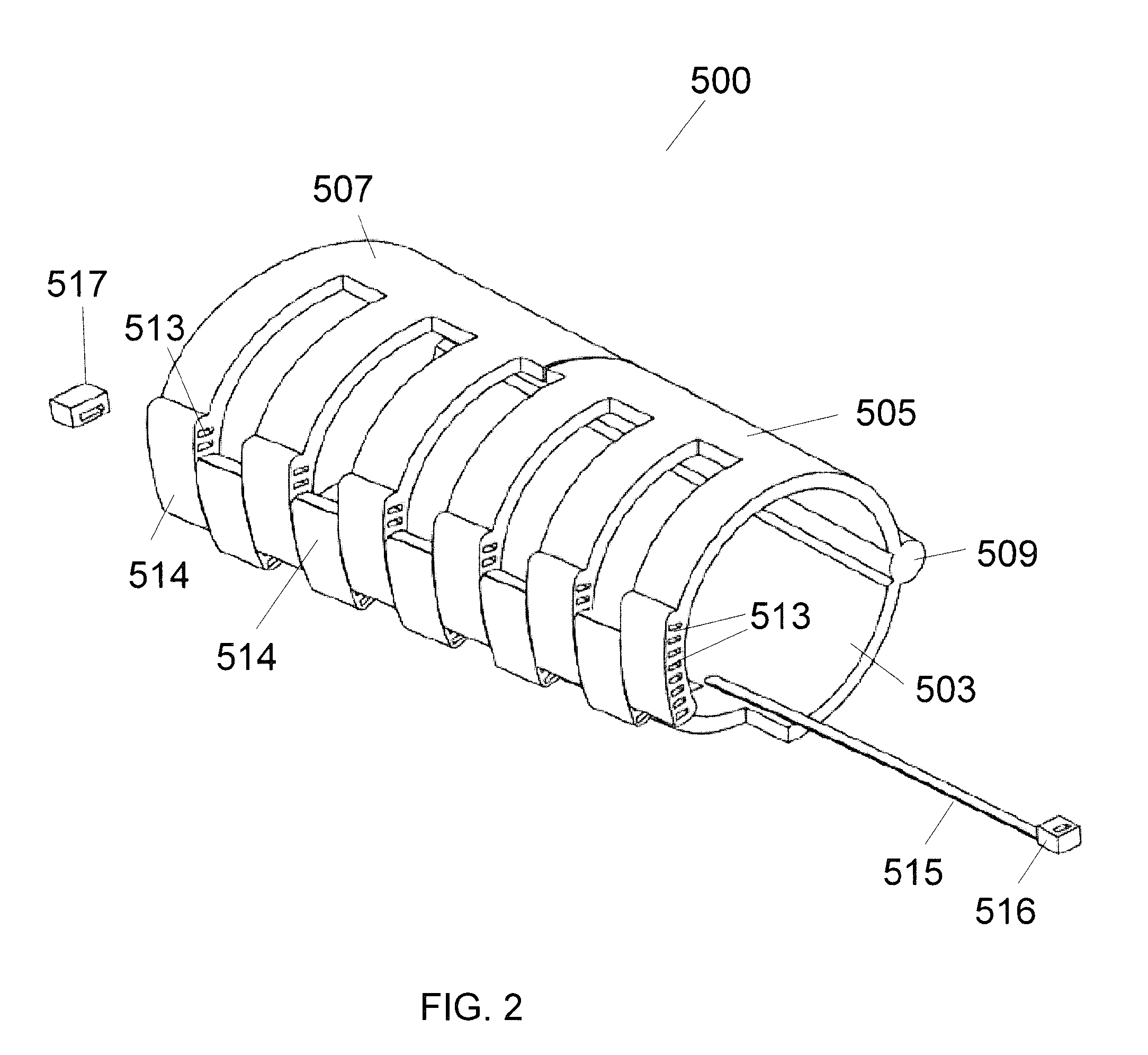
[0026]With reference to FIG. 1, an embodiment of an adjustable brace 500 is illustrated having a first lower portion 503 and a first upper adjustable portion 505...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com