Method for Providing an Attribute Bounded Network of Computers
a technology of attribute bounded network and computer, applied in the field of providing attribute bounded network of computers, can solve the problems of vegetarians not wanting to use their client computers, user of the client computer has no control over what pages his computer is doing, and many problems, so as to improve the scalability of the network, influence the freshness of urls, and reduce the refresh rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
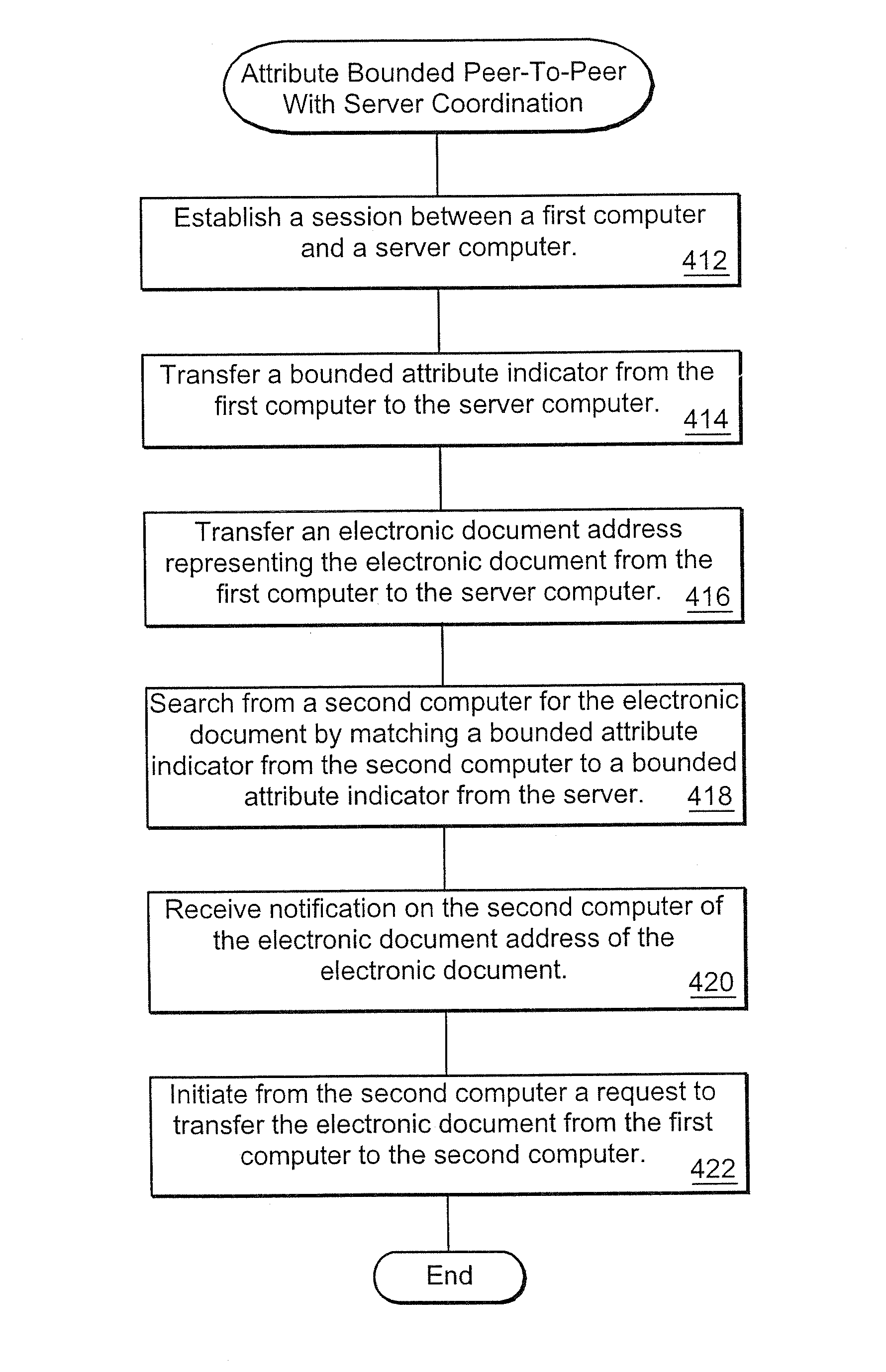
[0065]A description of example embodiments of the invention follows.
Attribute Bounded Network
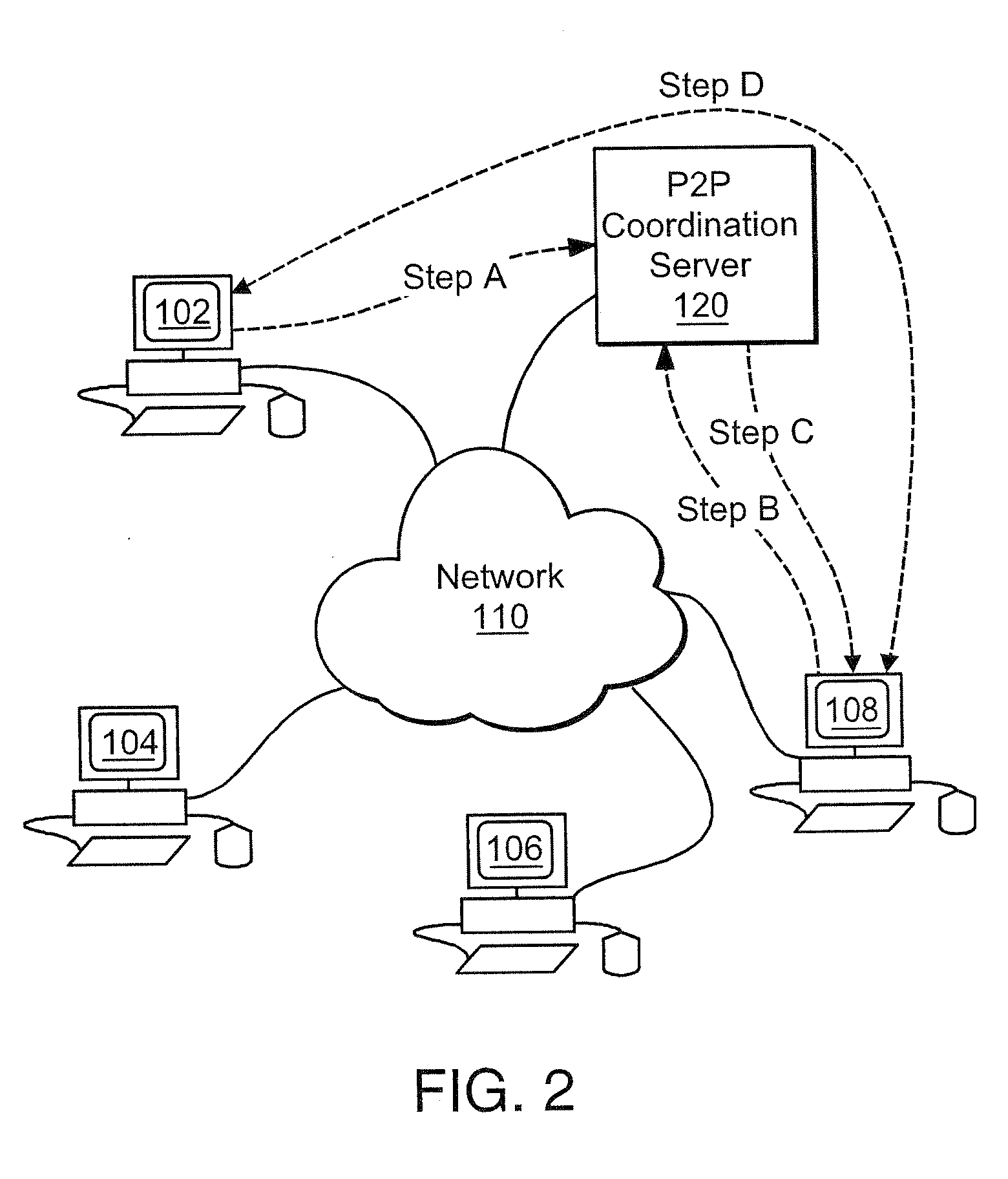
[0066]FIG. 1 illustrates an attribute bounded distributed indexing system using a server coordinated computer network on which an embodiment of the present invention is implemented. Computers 50, 52, 54, 56 are connected to network 110. Web servers 102, 104 are also connected to network 110. In one embodiment computers 50, 52, 54, 56 are personal computers running Web browsers connected to the World Wide Web via network 110. Each computer 50, 52, 54, 56 has a program running that enables the computer to perform distributed processing (e.g., indexing) based upon assignments (e.g., a list of attribute bounded electronic addresses) issued from distributed processing coordination server 100. In this embodiment, distributed processing coordination server 100 contains a list of electronic document addresses representing electronic documents accessible by network 110. The list is attribute bounded ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com