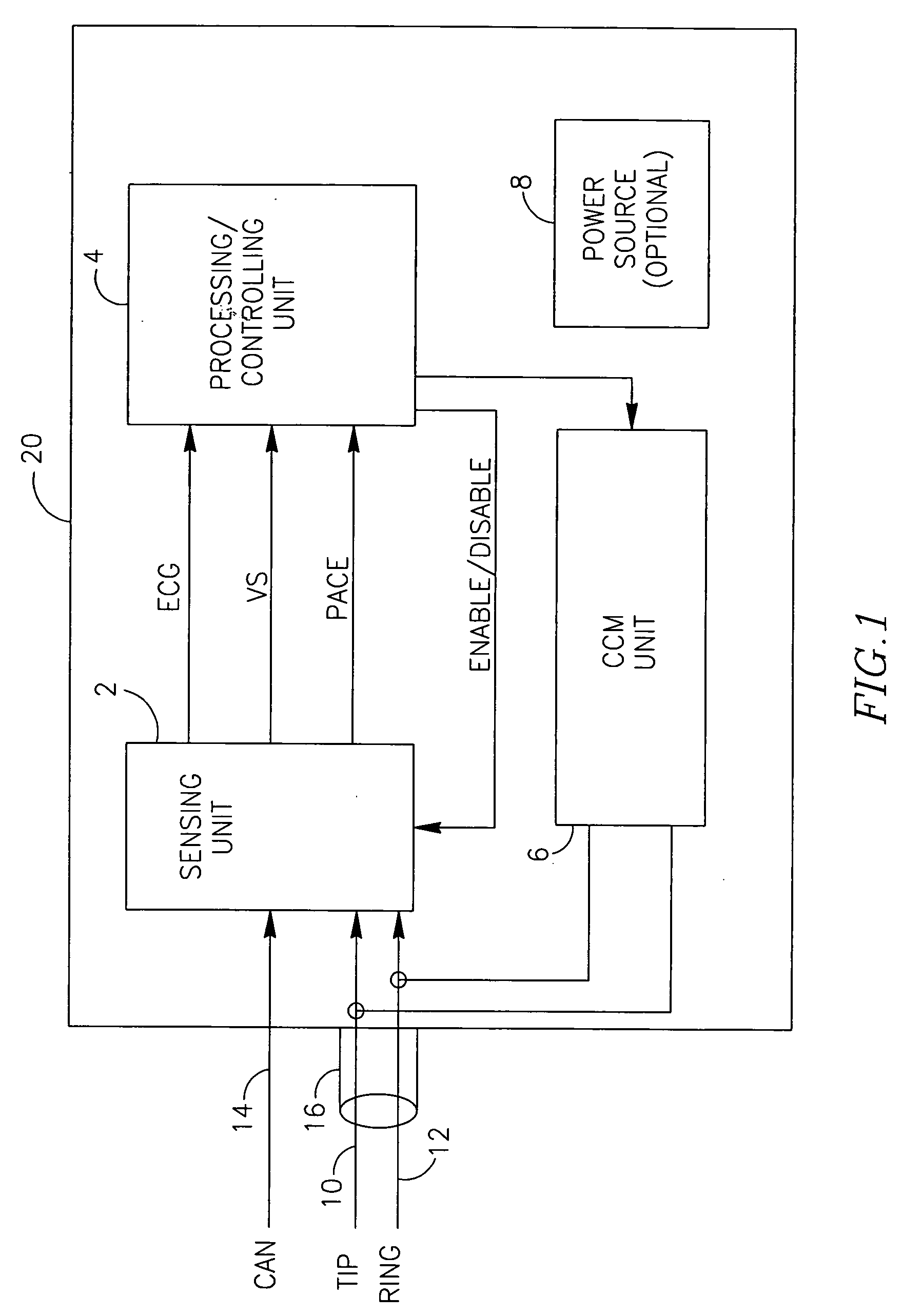
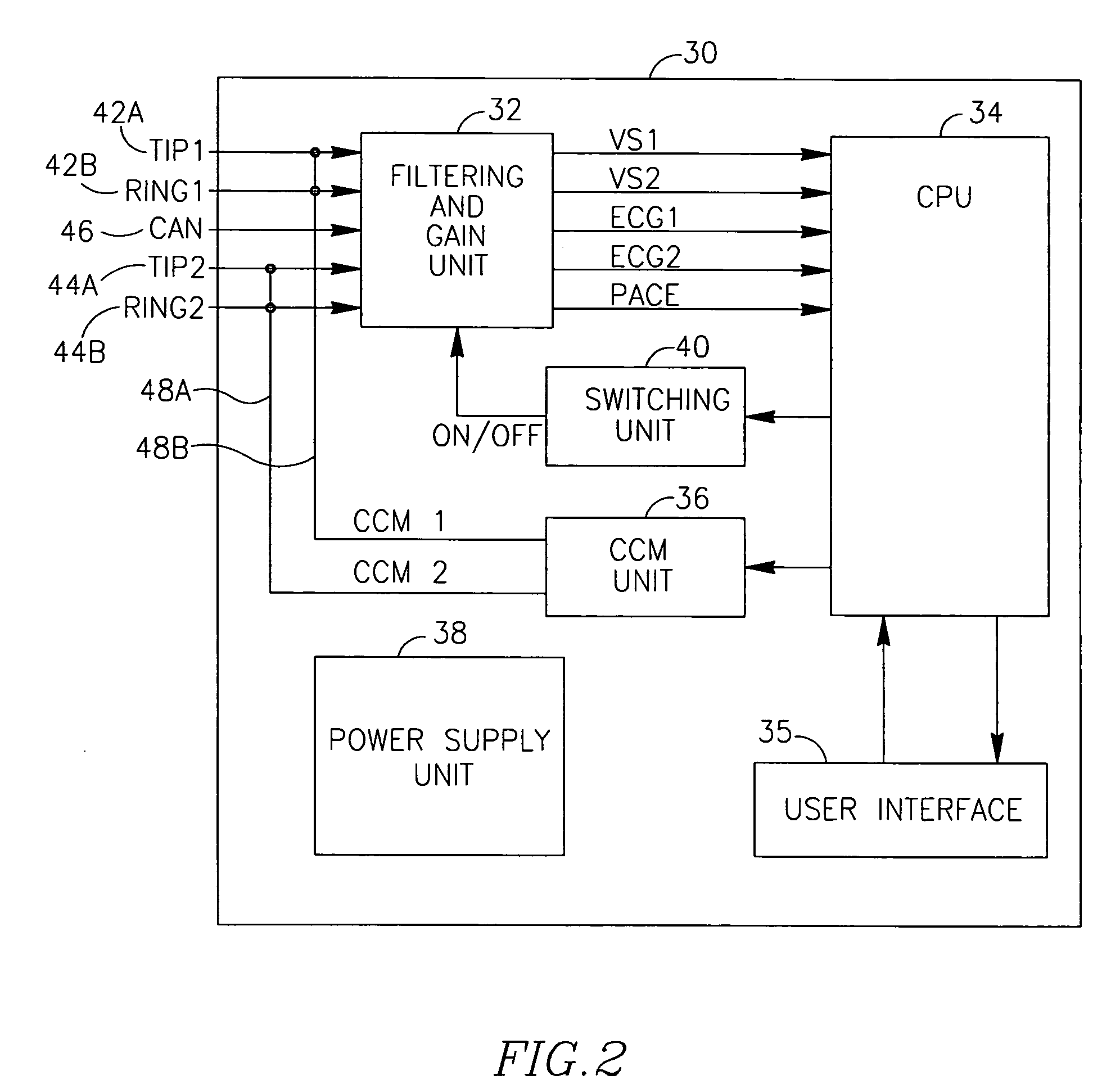
[0017]Another aspect of the present invention is that the recording of the global
ECG signal enables the use of a simplified
lead system in which there is no need for a sensing atrial lead. In such a simplified
system, preferably (but not obligatorily) only one or two ventricular leads are used (and, preferably, the can of the
implanted device), obviating the need for an atrial lead.
[0018]In accordance with another aspect of the present invention, the
ECG signal (global
signal) is used to differentiate between an electrical event due to an arrythmogenic atrium and an electrical event due to a distant ventricular ectopic beat. This is made possible due to an increased effective sensing range of unipolar differential recording performed between the distant
electrode (preferably, but not obligatorily, the can of the CCM device) and one or more of the ventricular
electrode(s), as compared to the very limited effective sensing range obtainable when recording locally sensed events (for example by using differential recording between two narrowly spaced
electrode tip and ring, as is known in the art, or the like) using a ventricular electrode. This is enabled by the much larger distance between the can and the ventricular electrode(s). The probability of detecting a distant ectopic activity (such as, for example an ectopic event generated in the lateral part of a
ventricular wall) is much larger using such globally recorded IECG than the probability of detecting such an event using ventricular local sensing with it's limited effective sensing range.
[0021]In accordance with another aspect of the present invention, the template may be a dynamic template which may be based on data continuously acquired from the patient and continuously adapting to time varying changes occurring in the heart of the patient. Such variations may include, inter alia,
drug induced changes in cardiac electrical properties and activity, and changes in cardiac electrical waveforms due to a change in the
physiological condition of the patient. Such changes may also include but are not limited to,
physical stress related changes in
heart rate or changes in electrical properties of
cardiac muscle cell or in the properties of other electrically excitable cardiac tissues and / or pathways, hormonally induced changes due to intrinsic
adrenergic or
cholinergic effects, long term changes due to electrode movements or resistivity changes caused by deposition of extraneous material on the electrodes, changes in
heart rate, changes in recorded waveforms due to artificial pacing by a pacemaker, or other such effects).
[0037]It is noted, that the devices and methods of the present invention provide the ability to sense and process signals within a single heart cycle almost immediately (or within a few milliseconds from the local sense event), enabling the identification of remote ectopic activity. It is not necessary to sense and process a whole QRS complex, allowing the making of a real-time decision within the current
heart beat cycle (in other words, the devices and methods of the present invention enable real time
decision making within each individual beat cycle). This is different from known ICD devices and methods, which normally take a decision whether or not to provide electrical therapy several seconds after sensing and
processing multiple
heart beat cycles.
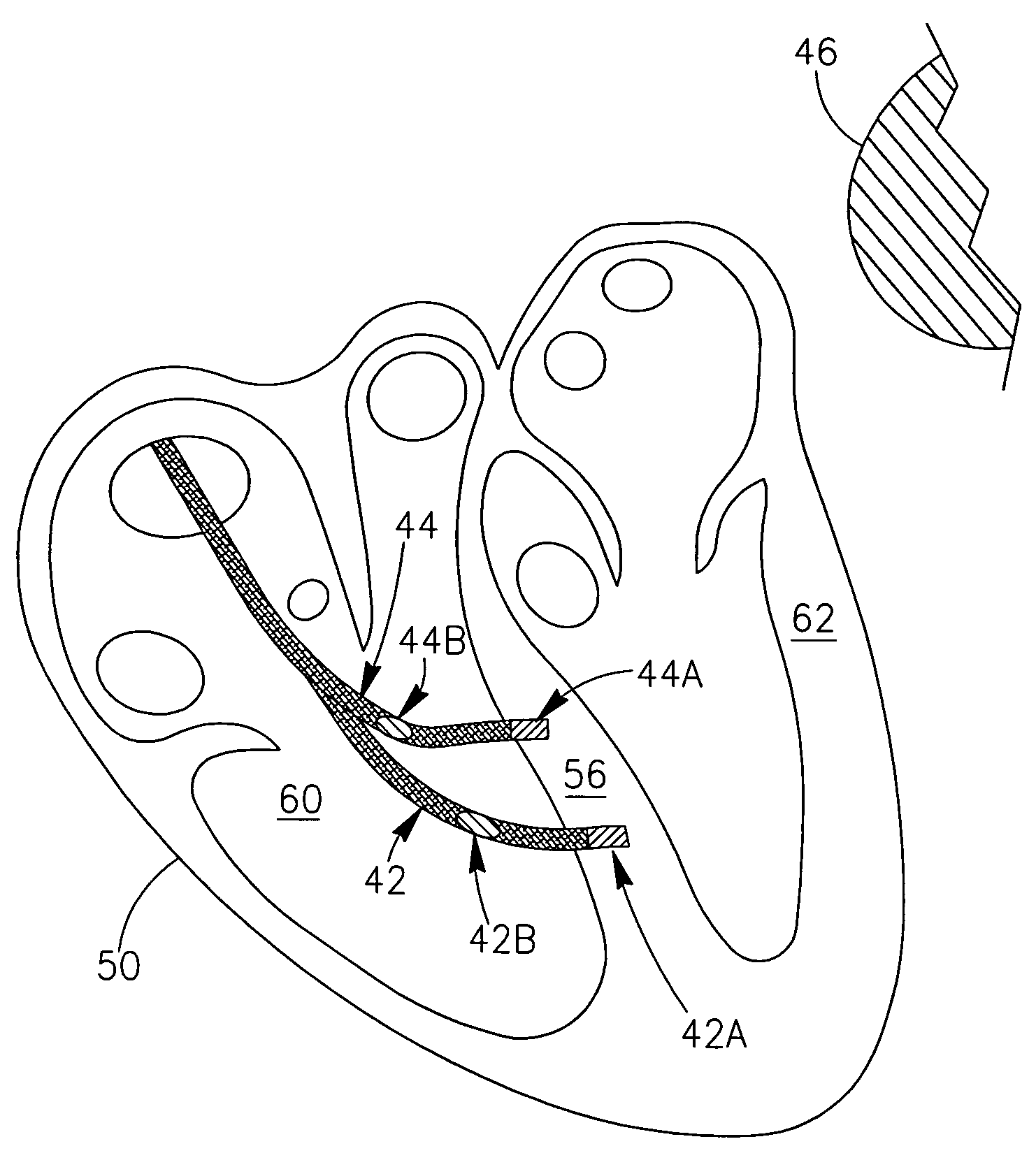
[0039]It is noted that, in accordance with embodiments of the present invention, the devices and systems described herein may use other leads in the heart with a dedicated electrode or with an electrode that simultaneously serves for other purposes. Examples may include but are not limited to, a separate pacemaker lead or
ICD lead, or a
coronary sinus lead which may allow (possibly in parallel to its original function)
connectivity to an electrode that provides signal(s) from outside the RV or LV, and thus allows better measurement of RV and LV remote ectopic activity. Such signals may be sensed and / or recorded between electrodes positioned outside the LV or RV chamber, or between one or more of such electrodes and the device's can, or between one or more such electrodes and an electrode positioned inside the RV or LV chambers.
 Login to View More
Login to View More  Login to View More
Login to View More