Treatment method for optically transmissive body
a treatment method and optical transmissive body technology, applied in the field of optical elements and methods for treating optical elements, can solve the problems of increasing the cost of treatment and high price of platinum, and achieve the effect of improving the optical properties of the transmissive body
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
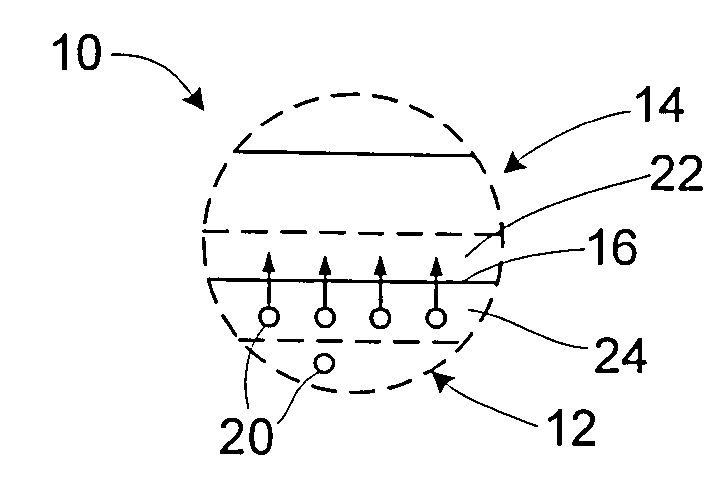
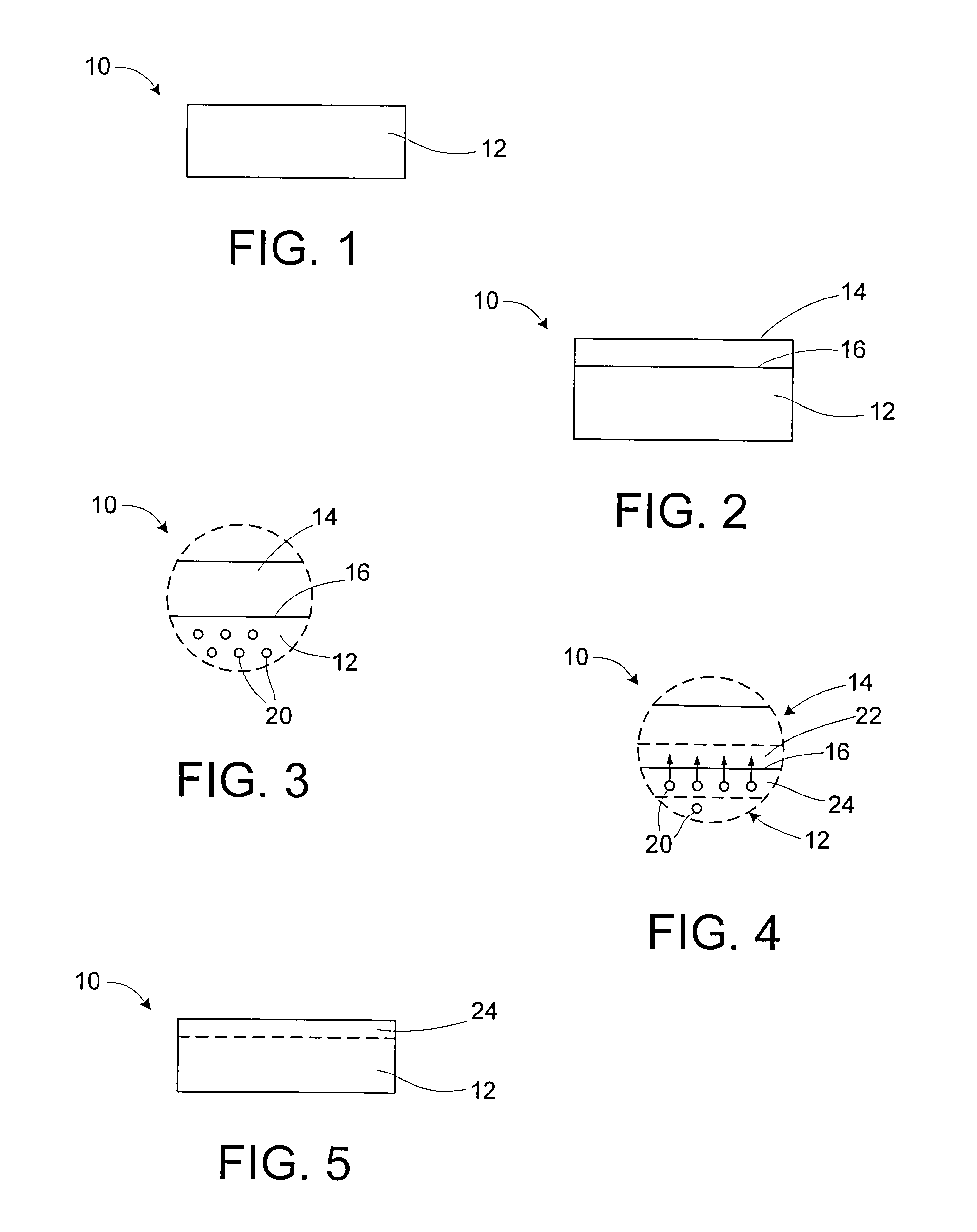
[0017]A method of treating a transmissive body of zinc sulfide or zinc selenide includes placing a non-platinum metal layer, such as a layer of cobalt, silver, or iron, on a surface of the transmissive body, and improving the optical properties of the transmissive body by subjecting the body and the layer to an elevated temperature and elevated pressure. The zinc sulfide or zinc selenide may be chemical vapor deposited material. The non-platinum metal of the non-platinum metal layer is a non-platinum metal selected to advantageously affect the optical properties of the transmissive material in a subsequent heating at elevated pressure. In particular, the reduction of free sulfur or free selenium (or other species) in the transmissive body portion may improve optical properties for visible and near infrared (NIR) wavelengths. Of particular interest may be wavelengths of about 1064 nm or 1 micron, which are wavelengths that are utilized by semi-active laser (SAL) seekers. Transmission...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com