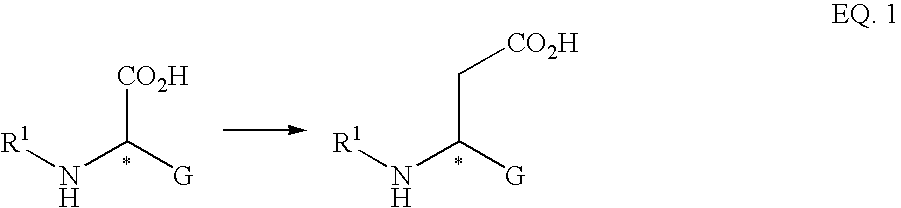
Process for synthesizing aspartic and glutamic acid derivatives especially useful as intermediates in the manufacture of a caspase inhibitor
a technology of aspartic and glutamic acid and intermediates, which is applied in the preparation of carbamic acid derivatives, amino-carboxyl compound preparations, organic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of poor cellular penetration and cellular activity, unsatisfactory pharmacological properties, and poor oral absorption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
N-Carboxybenzyloxy-(2S,3S)-4-fluorothreonine (102)
[0291]To a stirred solution of (2S,3S)-4-fluorothreonine 101 (0.1009, 0.82 mmol) in THF / H2O (1:1, 5 ml) adjusted to pH 9 using sodium carbonate was added N-carboxybenzyloxysuccinimide (0.308 g, 1.24 mmol). After stirring the solution for 18 hours at room temperature, the solvent was removed in vacuo to give a white residue. The residue was partitioned between ethyl acetate (5 ml) and water (10 ml). The organic layer was separated and aqueous layer further extracted with ethyl acetate (2×5 ml), this organic phase was discarded. The pH of the aqueous layer was adjusted to 3 using 1N HCl. The aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl acetate (4×10 ml), the combined organic layers were dried (MgSO4) and the solvent removed in vacuo to afford N-carboxybenzyloxy-(2S,3S)-4-fluorothreonine 102 as a pale yellow oil (110 mg, 70% yield); 1H (400 MHz, CDCl3) 8.20 (1H, bs, OH, exchange with CH3OD), 6.46, 6.45 and 6.07 (1H, 3×d, J 8.9), 5.10-4.85 (2H...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| enantiomeric excess | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com