Raman spectroscopic monitoring of hemodialysis
a raman spectroscopy and hemodialysis technology, applied in the field of raman spectroscopy monitoring of hemodialysis, can solve the problems of urea buildup in the body and particularly in the blood, not allowing continuous evaluation of effectiveness, and requiring time-consuming chemical analyses, so as to reduce the time a patient has to spend, monitor and/or control hemodialysis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
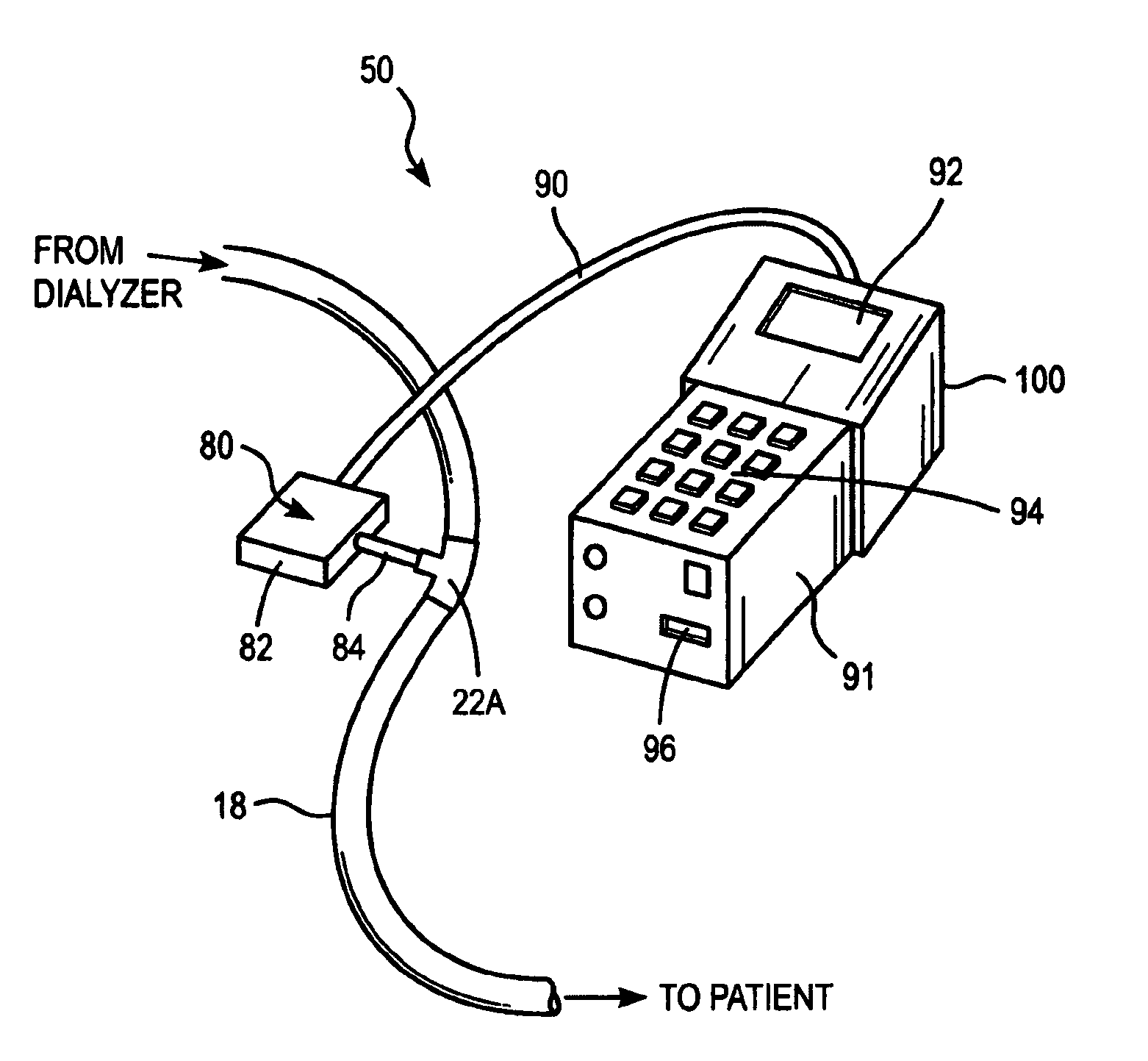
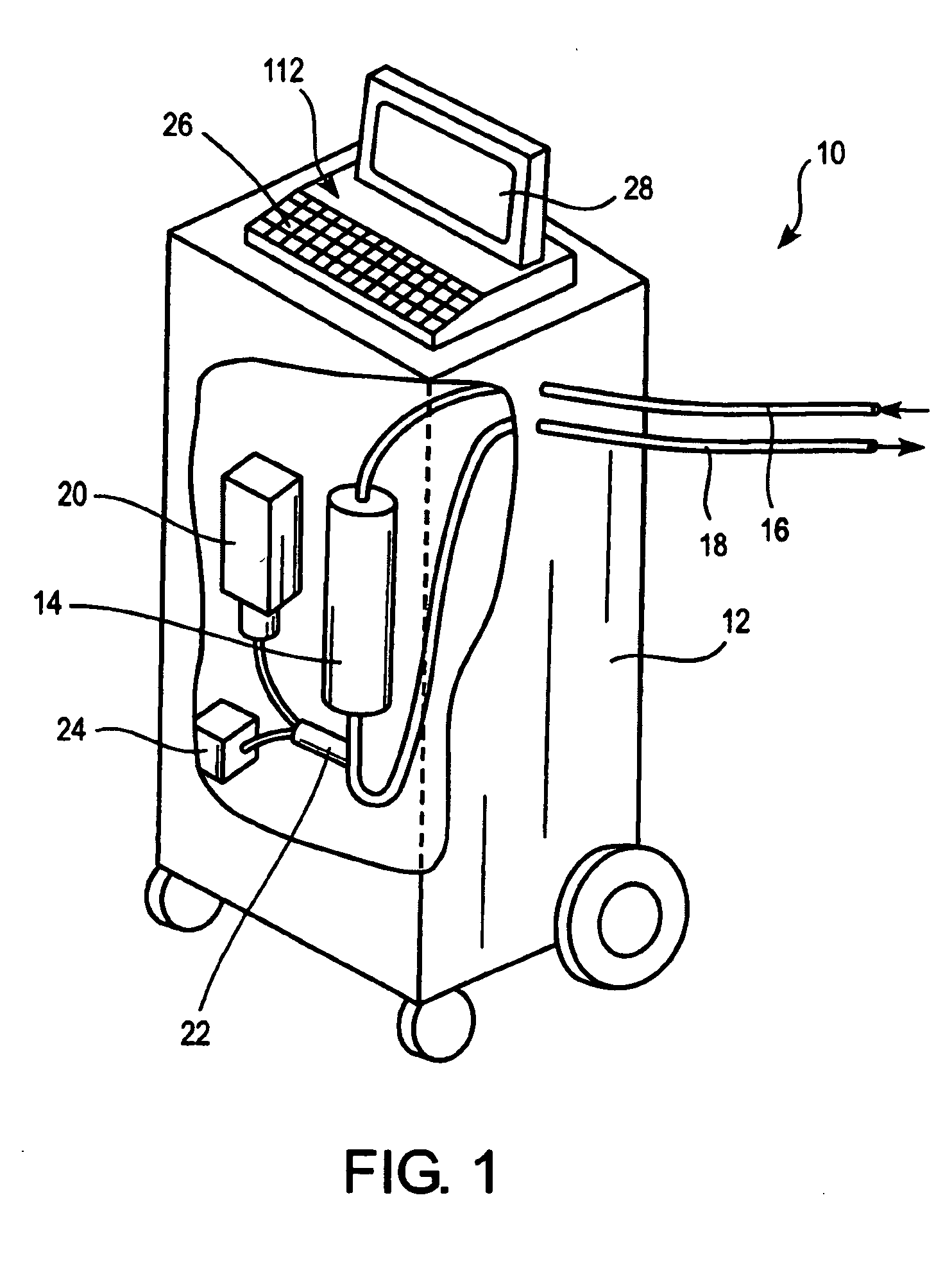
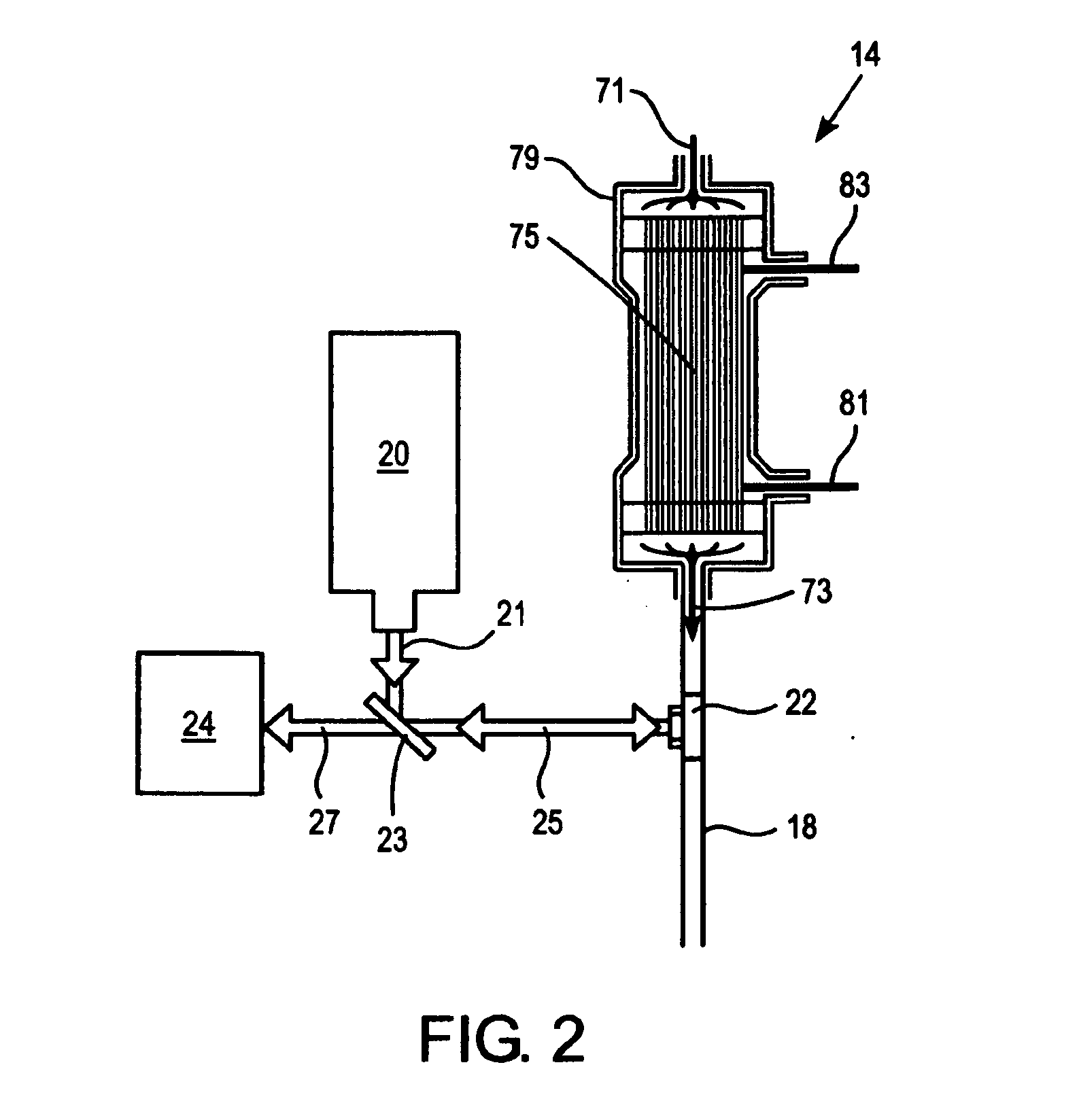
[0020]Without being bound by any particular embodiment, the following discussion is offered to facilitate understanding of the invention. The present invention provides methods for monitoring levels of at least one analyte in blood of a patient undergoing hemodialysis using Raman spectroscopy, taking advantage of the optical access afforded through the clear delivery tubing connecting the patient's blood flow to the dialyzer. Unique Raman spectroscopic signature of an analyte can be identified and quantified against a whole blood background utilizing the Raman spectroscopy-based systems.
[0021]The analytes of particular interest in the present invention are the products of metabolic activity within the body of the patient. The term “analyte” as employed herein, however, can encompass any chemical composition released in the bloodstream (e.g., toxins released by microorganisms or a compound imbibed by an individual). The analyte contained in the blood may be a specific analyte or a co...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| excitation wavelengths | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| power | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameters | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com