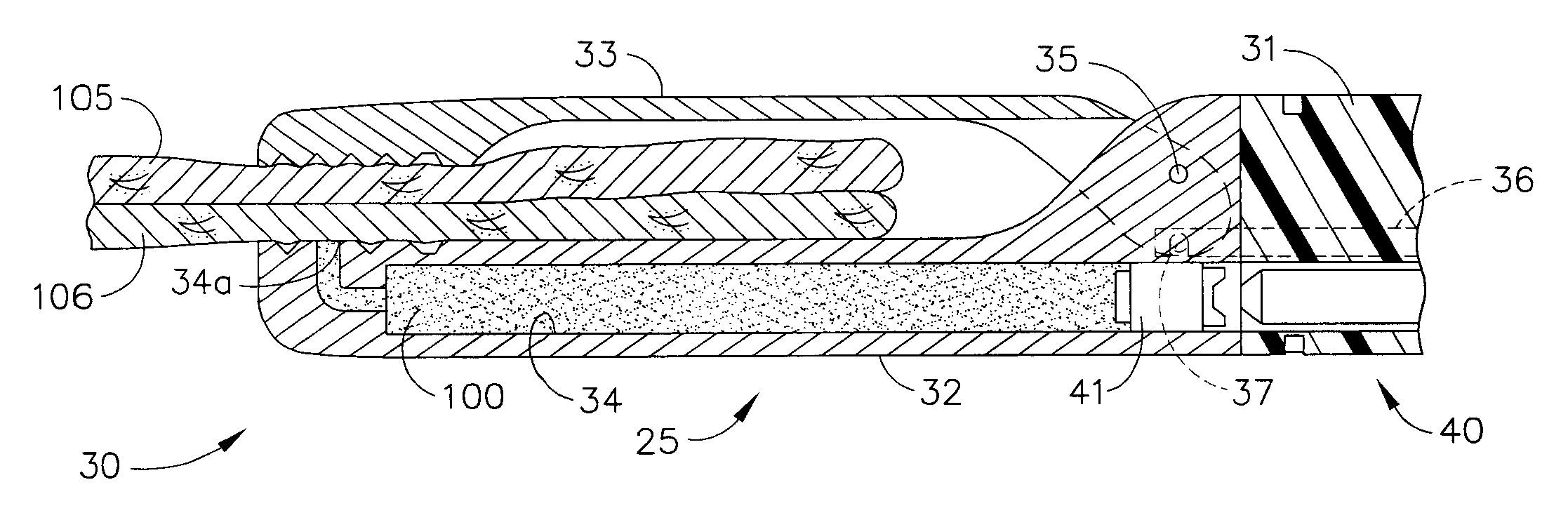
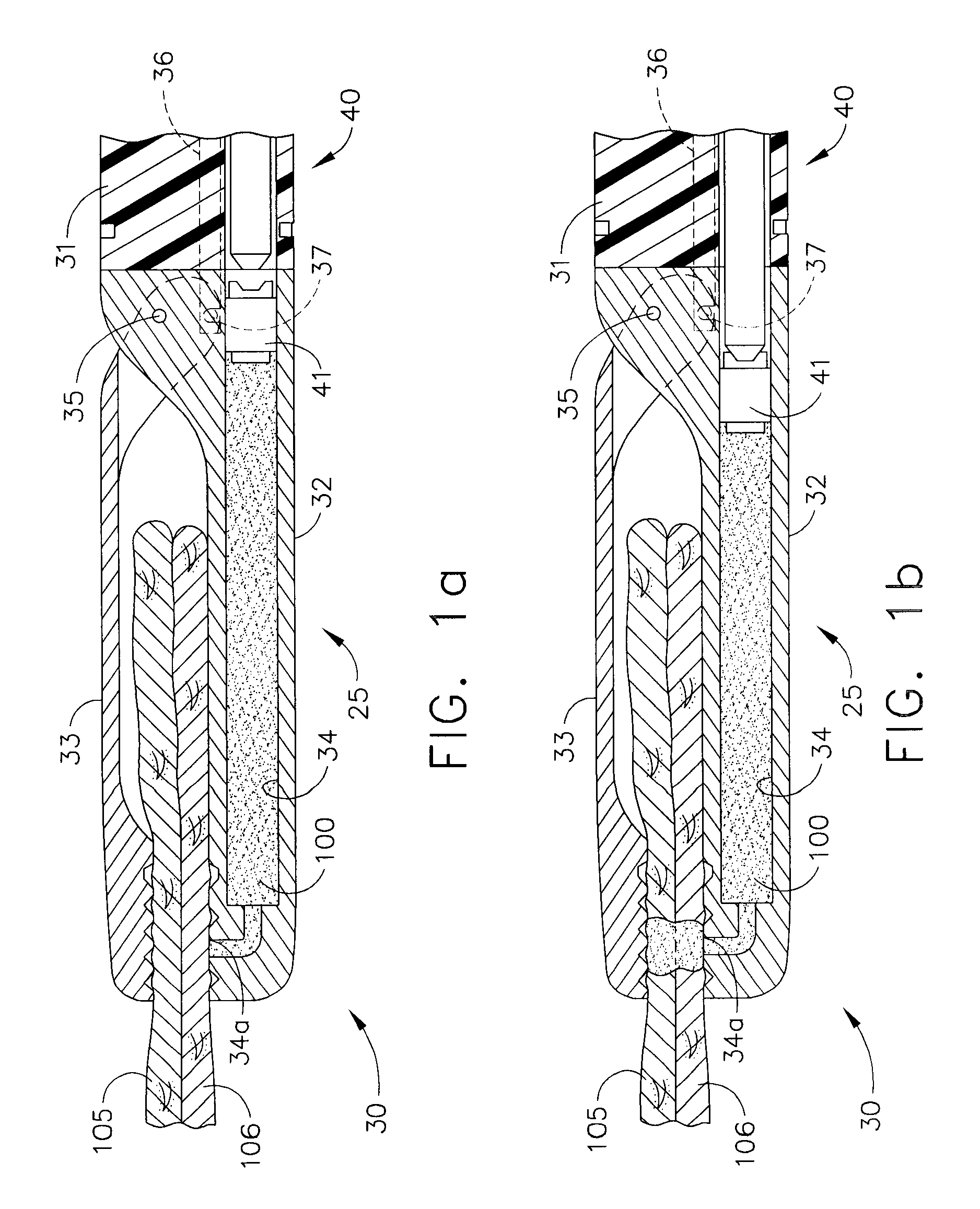
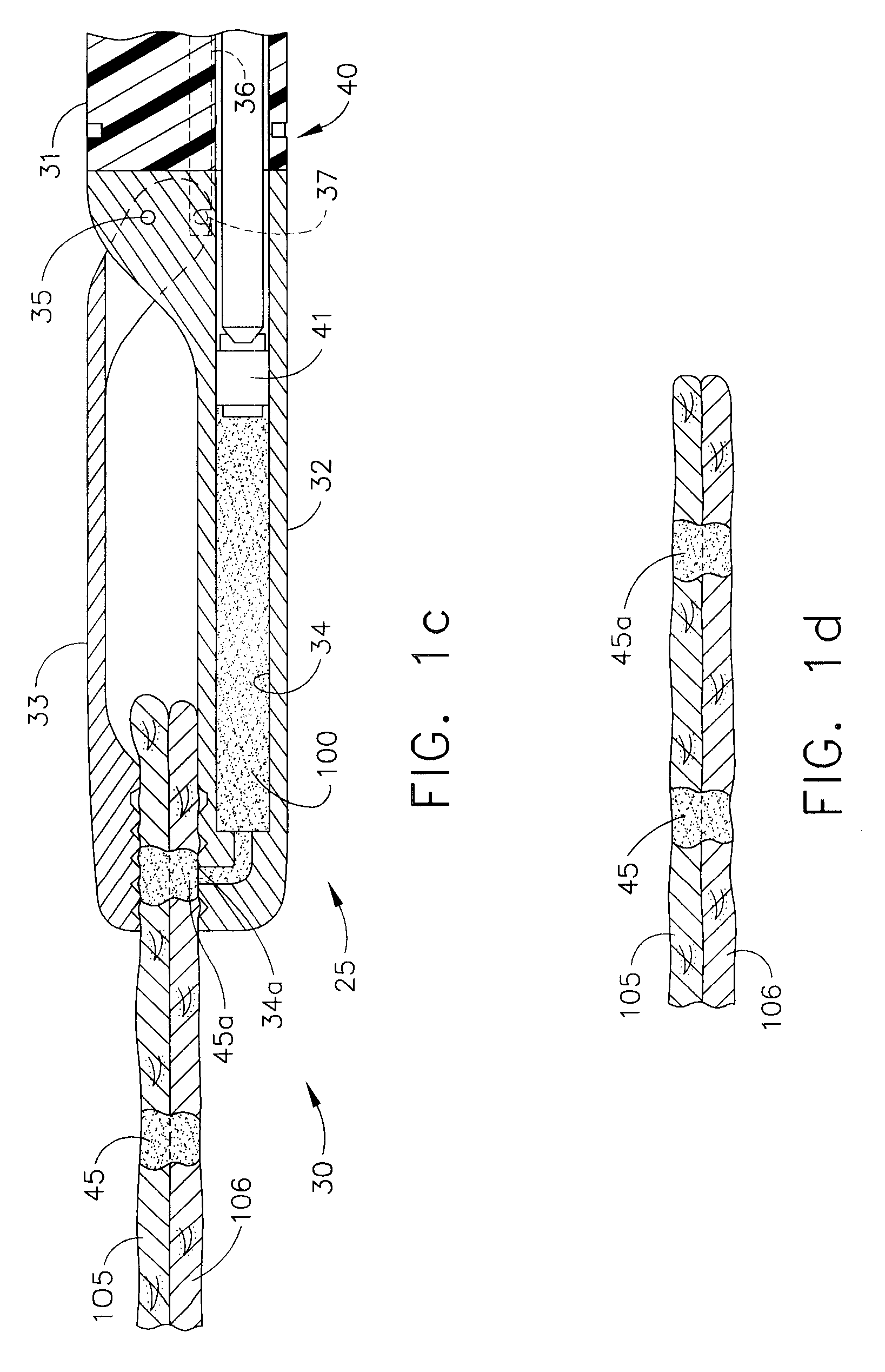
Form in place fasteners
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
twelfth embodiment
[0141]FIGS. 13a-13e show the steps of use of a twelfth embodiment of an alternate embodiment of a surgical form in place fastening device 575 for creating an adhesive fastener 595 about an anatomical vessel. FIGS. 14a to 14c are a series of cross section of the fastening device 575 and vessel as the adhesive fastener 595 is created.
[0142]In FIG. 13a, an end effector 580 of the fastening device 575 is shown next to a vessel 510 that is surrounded by a bandage 511. A pivotable jaw 583 is shown opened relative to a fixed jaw 582. Both the pivotable jaw 583 and fixed jaw 582 contain a pivotable receptacle 585 and a fixed receptacle 586 for the reception of the vessel 510 and bandage 511 therein. Seals 587 are located at either end of receptacle 586 for sealing with the vessel 560 and bandage 561. In FIG. 3b, the vessel 510 and bandage 511 are clamped within the jaws 582 and 583 and the polymerizable adhesive 100 is flooding the receptacles 586 and 587. For thi...
thirteenth embodiment
[0146]FIG. 14d can show an additional embodiment of the surgical fastening device shown in FIGS. 13a-13b including an additional pivot joint 609 to enable pivoting of the end effector as shown. The surgical fastening device 625 has an end effector 630 with a split jaws 632 and 633 that can pivot about a pin 610. A detent 634 (not shown) can be provided to detent the end effector 630 at a series of angles
fourteenth embodiment
[0147]FIGS. 15a-15d show a fourteenth embodiment of a surgical fastening device 675 having an end effector 680 for that uses vacuum to create an adhesive fastener 695 within an anatomical vessel 560. The end effector 680 is attached to shaft 681 and has a pivotable jaw 683 and a fixed jaw 682 and vacuum ports 685. Pivotable jaw 683 is shown closed on vessel 560 and a vacuum is being applied from vacuum ports 685 to expand the vessel 560 within a vacuum chamber 686. A longitudinally movable hollow adhesive needle 670 can be filled with adhesive 100 and can extend through fixed jaw 683 aimed at the vessel 560. As shown in FIG. 15d, distal movement of adhesive needle 670 pierces vessel 560 and enables polymerizable adhesive 100 to be pumped into a lumen 567 of vessel 560 with piston 687. The vessel 560 fills with adhesive 100 which polymerizes to create the fastener 695 within vessel 560 as shown in FIG. 15b. FIG. 15c is a cross section of the severed vessel ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com