Antimicrobial hand wash
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
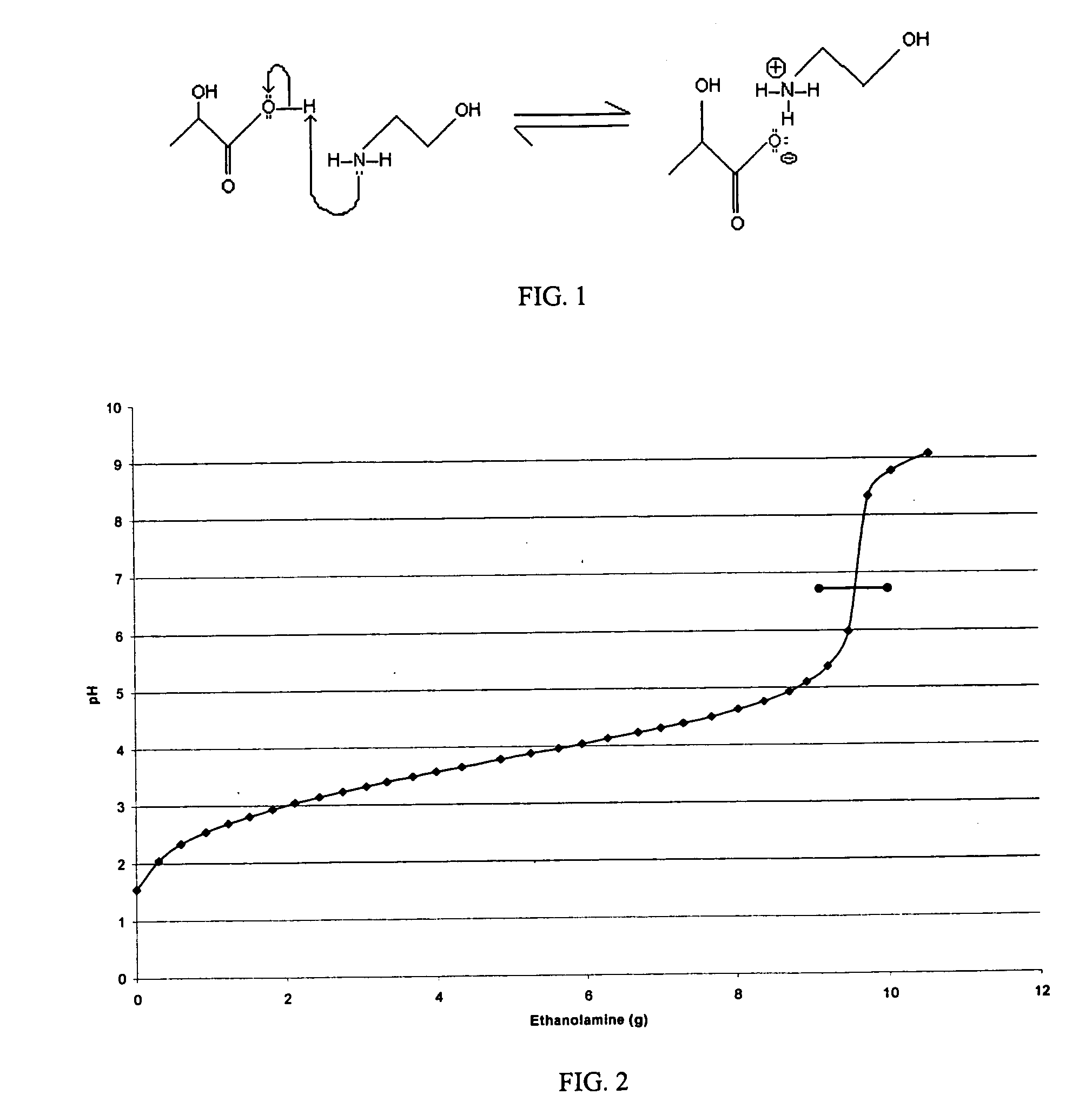
[0045]While making soap through a saponification reaction of a primary nitrogenous base with a primary fatty acid, the addition of excess base was examined. Because the high pH resulting from excess base would be irritating and detrimental to the skin care properties of the hand wash, the excess base was neutralized with a second water soluble acid. For a first control (Control 1), a hand wash made without excess base was tested along side the hand wash containing excess base neutralized with the second acid. A second control (Control 2) excess base is present, but is not subsequently neutralized with the second acid. The hand washes included antimicrobial agent, namely triclosan. The base was monoethanolamine. The first acid was lauric acid, and the second was lactic acid.
[0046]The triclosan was dissolved in dipropylene glycol, to make an “active premix.” The monoethanolamine was added to the water and then the lauric acid was added. After allowing the saponification process to com...
example 2
[0047]Because there is a boost in the efficacy of the product due to the use of excess primary nitrogenous base and a secondary neutralizing acid, alternate bases were tested. The focus was to find suitable weaker bases that might be used, because weaker bases should further reduce the degree of skin irritation experienced when using a resultant antimicrobial hand wash. Samples were made using the same procedure as in Example 1, but with alternate bases. Because the bases had different molecular masses, the percentage used in each sample was different. This was done in order to ensure that the same number of moles were present in each sample, thus allowing for the same concentration of amine salt in the final hand wash. As mentioned the same formulation was used as in Example 1, but with the base, monoethanolamine, replaced with the following:
Alternate BasesTriethanolamine9.355 gEquistar, USAAminomethylpropanol5.525 gANGUS Chemical, USA(AMP-95)Tetrahydroxypropyl10.29 gBASF, USAethyl...
example 3
[0048]In this example, alternate acids were considered for use in neutralizing excess base present after the saponification reaction, i.e, to replace the lactic acid specifically used in Example 1. The samples were made in accordance with Example 1, except that the lactic acid was replaced with alternate acids. A sample was also created having excess base and no second acid addition. The samples were adjusted to pH: 9.2±0.10 with each acid, and then tested for log reduction properties. The acids tested were as follows:
AcidAmountpHLog ReductionNoneN / A10.151.6Hydrochloric acid47.66 g 9.193.1Phosphoric acid1.52 g9.173.5Sulfuric acid12.20 g 9.183.4Ascorbic acid4.68 g9.174.4Malic acid*1.87 g9.122.8Succinic acid1.75 g9.172.8Glycolic acid2.04 g9.163.0Acetic acid43.68 g 9.192.2
[0049]From the high pH sample, it is plain to see the amine salt is important for the efficacious properties of the hand wash. Of the different acids tested, all drastically improved the log reduction values for the h...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Acidity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Acidity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com