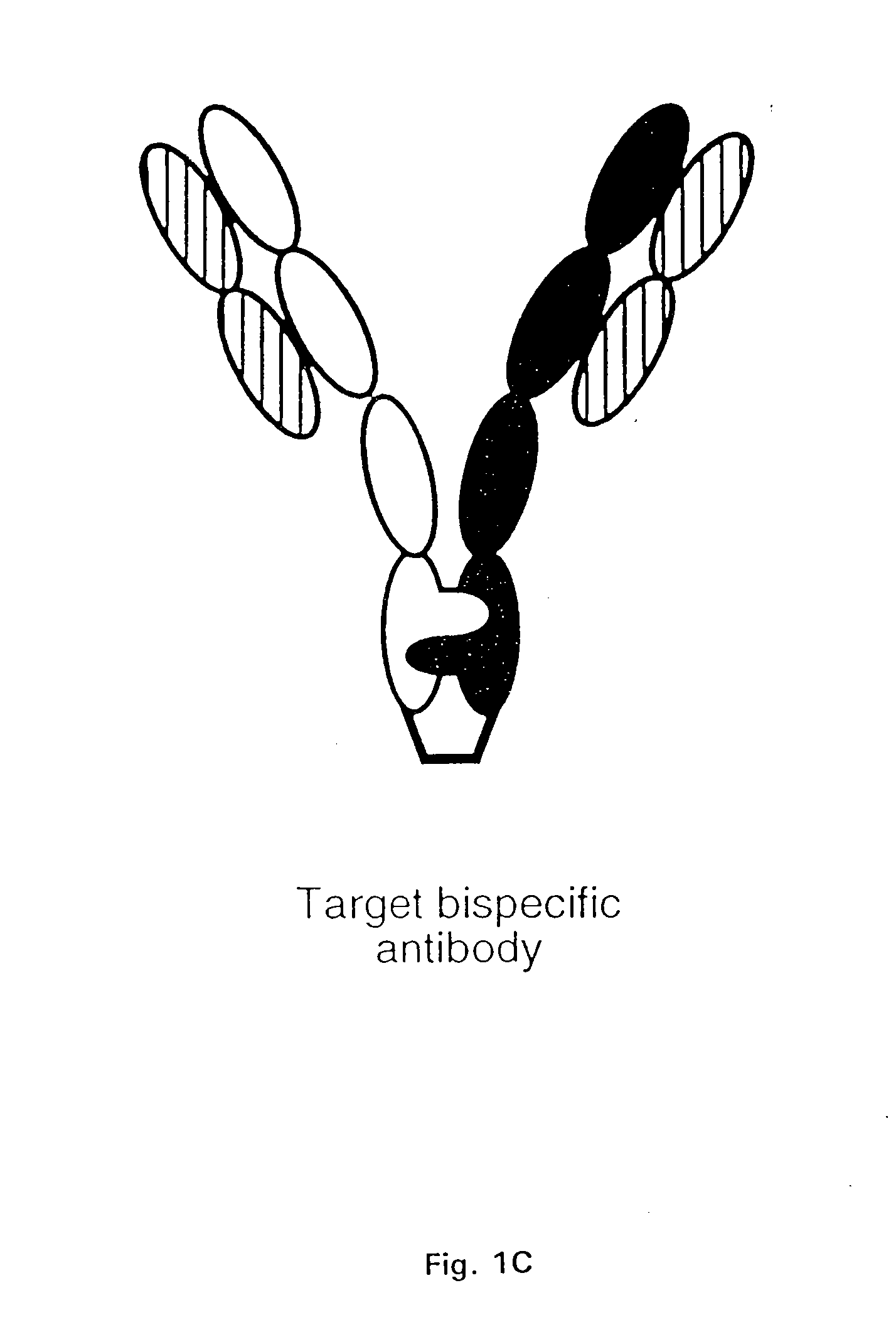
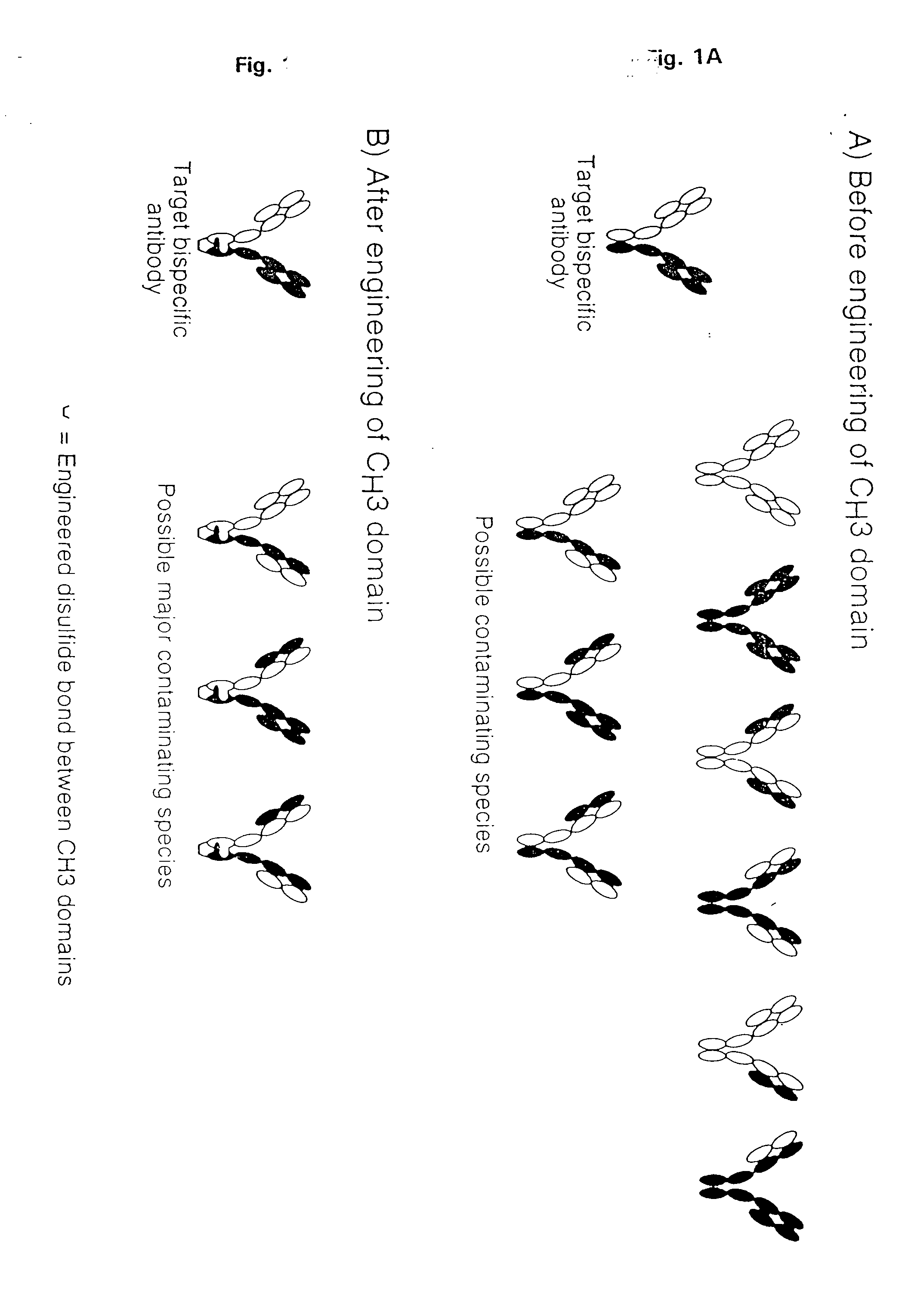
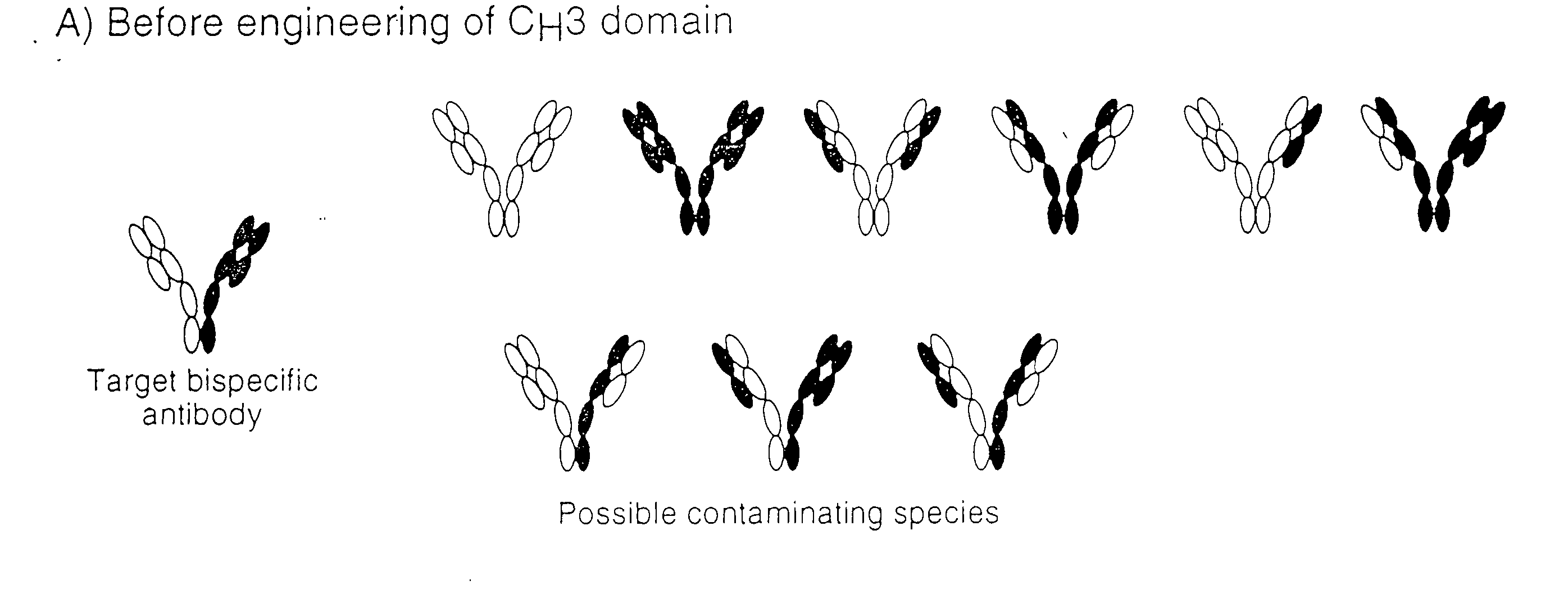Method for Making Multispecific Antibodies Having Heteromultimeric and Common Components
a multi-specific antibody and heteromultimeric technology, applied in the direction of antibodies, fused cells, peptides, etc., can solve the problems of low product yield, low yield of bsab, and ineffective hinderance of bsab use, so as to enhance the formation of desired heteromultimeric, and enhance the yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Generation of Protuberance-into-Cavity Heteromultimer Immunoadhesins
[0184] The CH3 interface between the humanized anti-CD3 / CD4-IgG chimera previously described by Chamow et al. J. Immunol. 153:4268 (1994) was engineered to maximize the percentage of heteromultimers which could be recovered. Protuberance-into-cavity and wild-type CH3 variants were compared in their ability to direct the formation of a humanized antibody-immunoadhesin chimera (Ab / Ia) anti-CD3 / CD4-IgG.
[0185] Thus, mutations were constructed in the CH3 domain of the humanized anti-CD3 antibody heavy chain and in CD4-IgG by site-directed mutagenesis using mismatched oligonucleotides (Kunkel et al., Methods Enzymol. 154:367 (1987) and P. Carter, in Mutagenesis: a Practical Approach, M. J. McPherson, Ed., IRL Press, Oxford, UK, pp. 1-25 (1991)) and verified by dideoxynucleotide sequencing (Sanger et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 74:5463 (1977)). See Table 3 below.
TABLE 3CH3 of anti-CD3CH3 of CD4-IgGMost Preferred Mu...
example 2
Generation of Non-Naturally Occurring Disulfide Linkages in Heteromultimeric Immunoadhesins
[0193] A. Design of CH3 inter-chain disulfide bonds.
[0194] Three criteria were used to identify pairs of residues for engineering a disulfide bond between partner CH3 domains: i) The Cα separation preferably is similar to those found in natural disulfide bonds (5.0 to 6.8 Å) (Srinivasan, N., et al., Int. J. Peptides Protein Res. 36:147-155 (1990)). Distances of up to 7.6 Å were permitted to allow for main chain movement and to take into account the uncertainty of atomic positions in the low resolution crystal structure (Deisenhofer, Biochemistry 20:2361-2370 (1981)). ii) The Cα atoms should be on different residues on the two CH3 domains. iii) The residues are positioned to permit disulfide bonding (Srinivasan, N., et al., (1990) supra).
[0195] B. Modeling of disulfide bonds. Disulfide bonds were modeled into the human IgG1 Fc (Deisenhofer, supra) as described for humAb4D5-Fv (Rodrigues et a...
example 3
Structure-Guided Phase Display Selection for Complementary Mutations That Enhance Protein-Protein Interaction in Heteromultimers
[0201] The following strategy is useful in the selection of complementary mutations in polypeptides that interact at an interface via a multimerization domain. The strategy is illustrated below as it applies to the selection of complementary protuberance-into-cavity mutations. However, the example is not meant to be limiting and the strategy may be similarly applied to the selection of mutations appropriate for the formation of non-naturally occurring disulfide bonds, leucine zipper motifs, hydrophobic interactions, hydrophilic interactions, and the like.
[0202] A. Phage display selection. A phage display strategy was developed for the selection of stable CH3 heterodimers and is diagrammed in FIG. 2. The selection uses a protuberance mutant, T366W (Ridgway et al., supra (1996)), fused to a peptide flag (gD peptide flag, for example, Lasky, L. A. and Dowben...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com