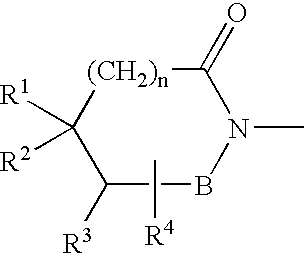
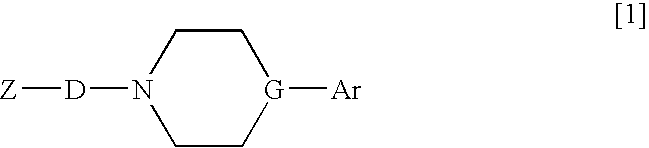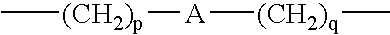In vivo screening method of therapeutic agent for memory/learning dysfunctions by schizophrenia
a technology for schizophrenia and memory/learning dysfunction, applied in the field of in vivo screening of therapeutic agents, can solve the problems of selective and serious damage to certain memory functions, insufficient drug efficacy of these existing drugs, and most serious damage to reference memory, so as to improve cognitive dysfunction activity, improve cognitive dysfunction, and improve cognitive function.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
(Method)
[0027] Wistar male rats (7 weeks old) were used. Haloperidol (a typical anti-psychotic agent), clozapine, quetiapine, risperidon, olanzapine or aripiprazole (atypical anti-psychotic agent), or lurasidone being under development as a novel anti-psychotic agent was suspended in a 0.5% methyl cellulose (MC) and the resultant suspension was used as a test compound. Serotonin 5-HT 1A receptor antagonist WAY-100635 or noradrenaline α2 receptor antagonist 1-PP was dissolved in a physiological saline solution (Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.) and used as a test compound. As an NMDA type receptor antagonist, MK-801 hydrogen maleate (SIGMA-ALDRICH M-107) was dissolved in a physiological saline solution (Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.). A test compound (0.3 to 10 mg / kg) or a 0.5% MC or a physiological saline solution as a control was orally or interperitoneally administered to the animals one hour prior to the training session of the passive avoidance task, and MK-801 (0.05 mg / kg) o...
example 2
[0034] In the procedures of Example 1, PCP HCl (0.75 mg / kg) was subcutaneously administered instead of MK-801 (0.05 mg / kg) to animals prior to both of the training session and the testing session of the memory / learning task to induce memory / learning dysfunctions, and the memory / learning dysfunction improving activity of a test compound can be evaluated.
example 3
[0035] The memory / learning dysfunction improving activity of a test compound can be evaluated under the exactly same conditions as those in Examples 1 and 2, except that ketamine is used instead of MK-801 or PCP HCl.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| acid addition | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| drug efficacy strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com