Complement C3 precursor biopolymer markers indicative of insulin resistance
a technology of precursor biopolymer and insulin resistance, which is applied in the field of complement c3 precursor biopolymer markers indicative of insulin resistance, can solve the problems of not working, eam when used as free chemicals to embed analyte molecules, and complex structure, and achieve rapid and accurate diagnosis of acute syndrome x events, effective disease management and preventative medicine, and facilitate treatment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
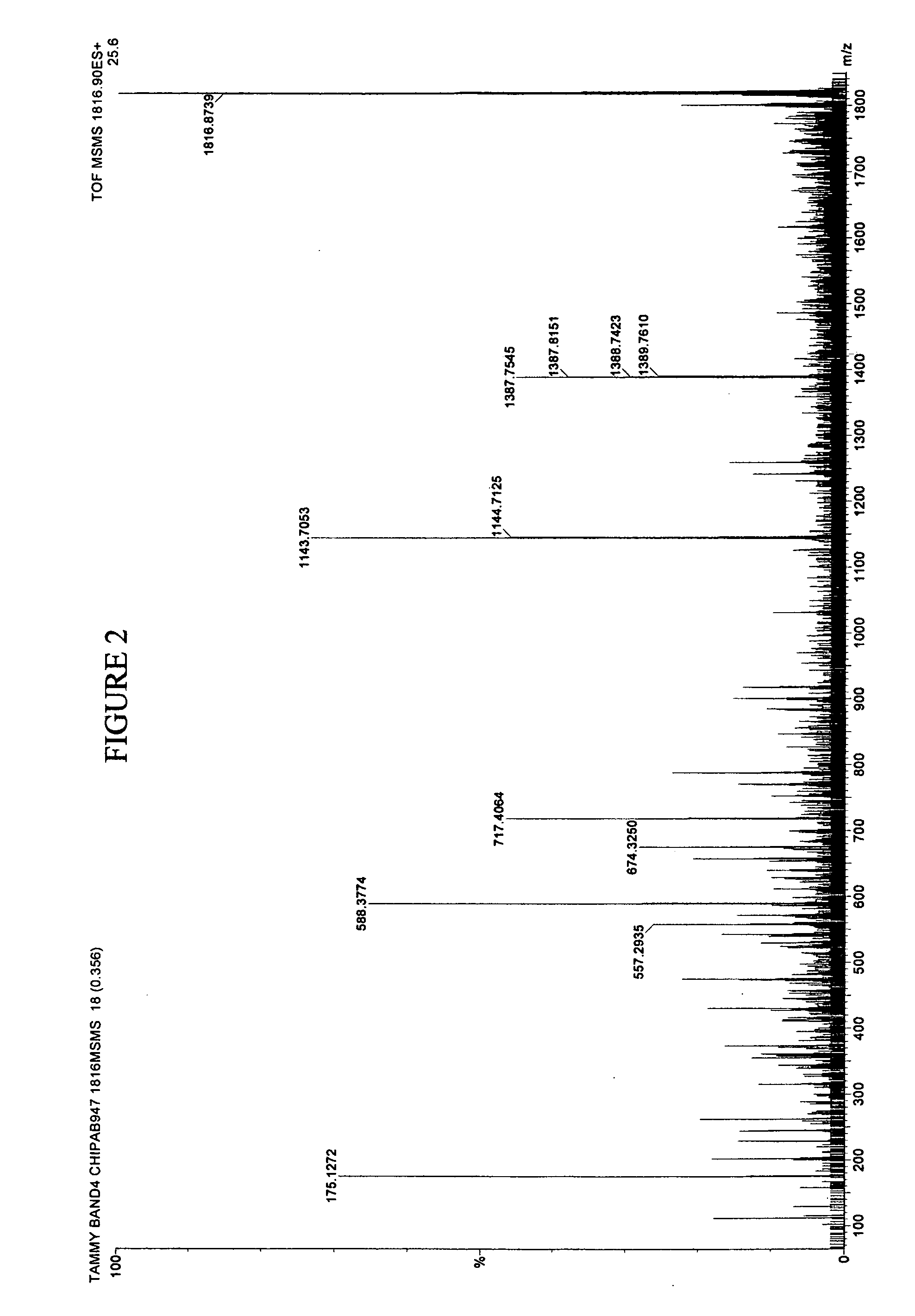
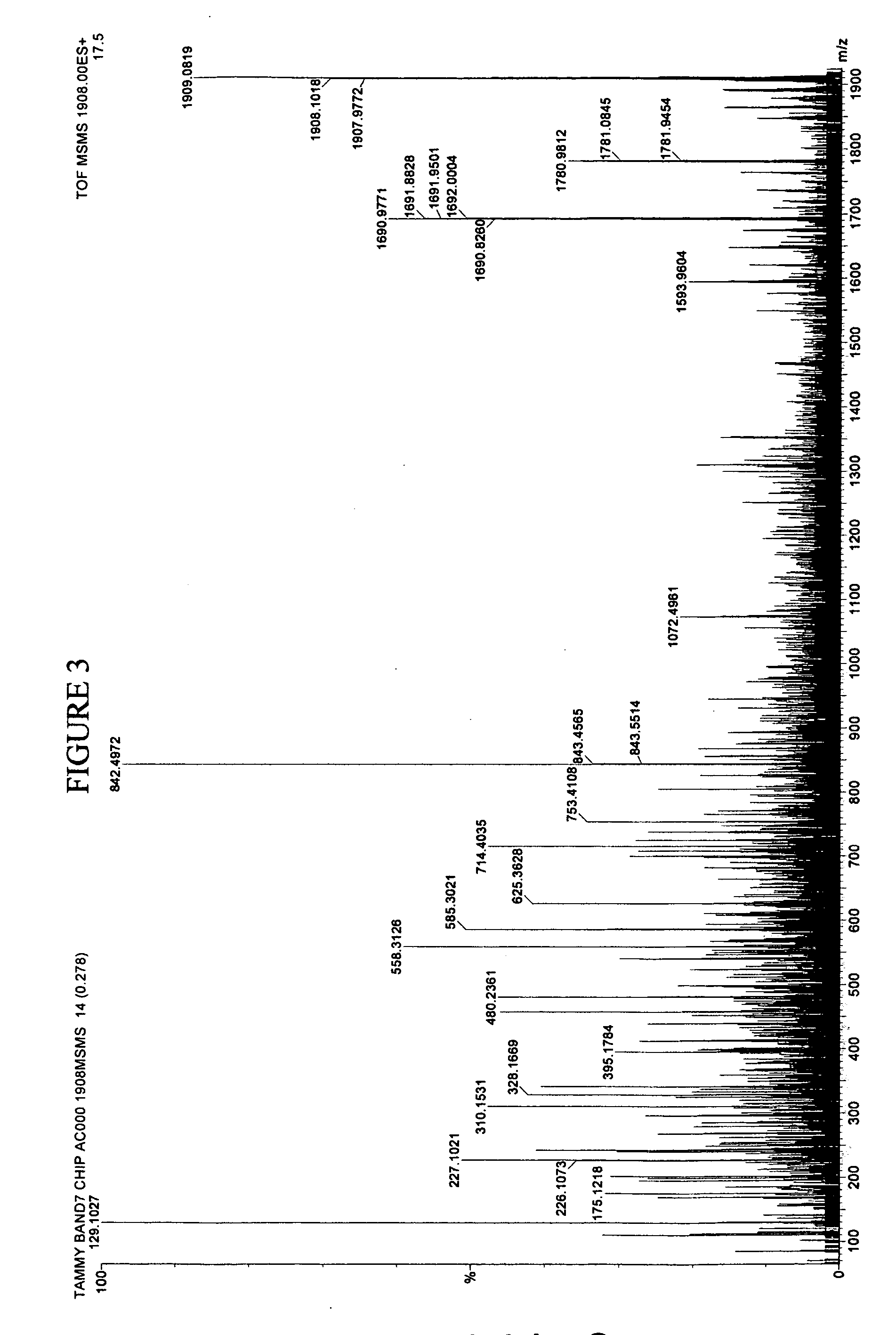
[0094] In earlier work, for example in U.S. patent application Ser. No. 09 / 846330 filed Apr. 30, 2000, the contents of which is herein incorporated by reference, raw sera was obtained and mixed with formic acid and extracted the peptides with C18 reversed phase ZIPTIPs.
[0095] In the instantly disclosed invention, we deal with proteins generally having a molecular weight of about 20 kD or more. In general, proteins of greater than 20 kD can reliably be fragmented by trypsin or other enzymes. The instant technology incorporates sufficient sensitivity to deal with even the low production of peptides from proteins less than 20 kD clipped from gel.
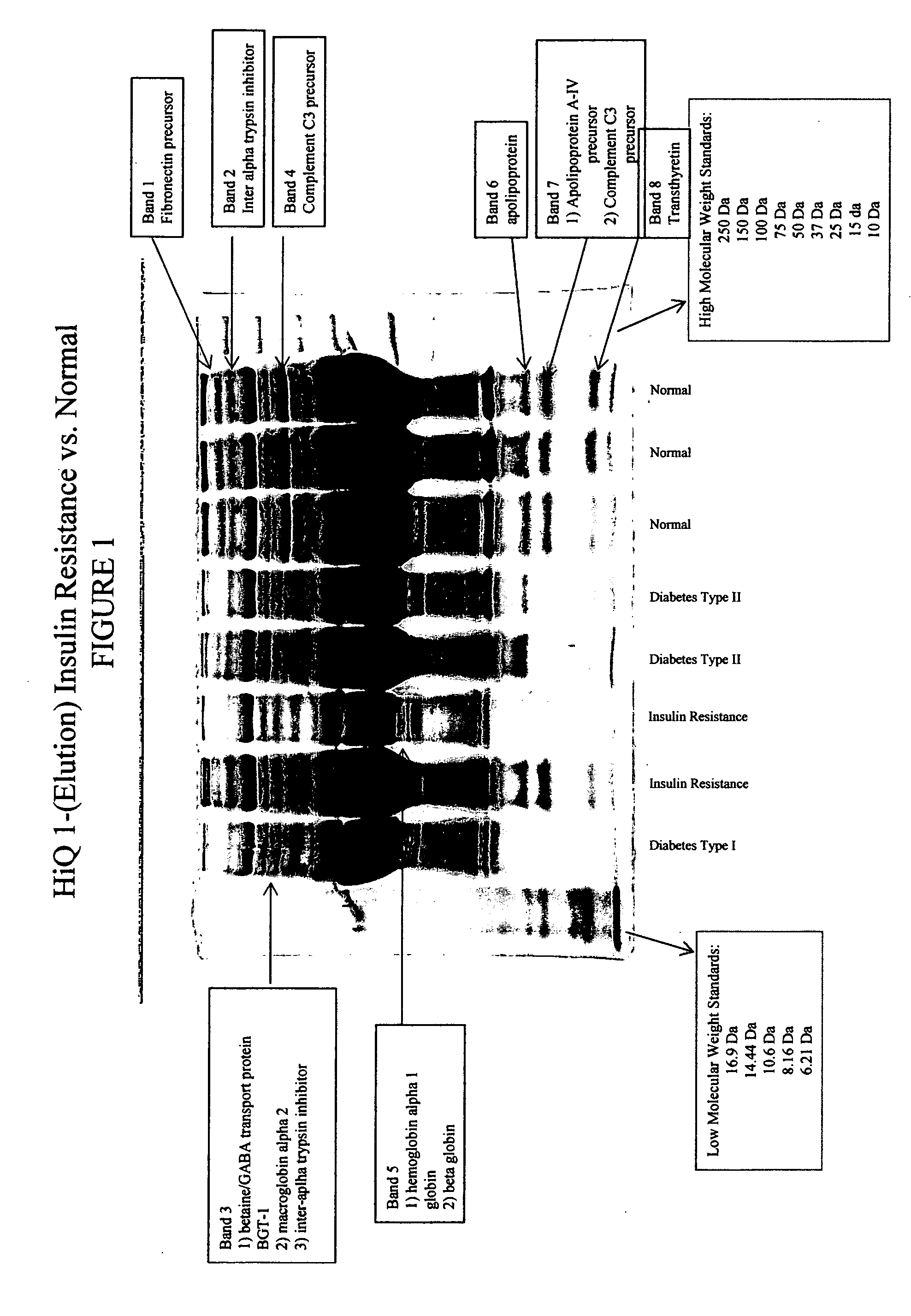
[0096] Proteins differ from peptides in that they cannot be effectively resolved by time of flight MS and they are too large (>3 kD) to be effectively fragmented by collision with gases. The most commonly used solution to these problems is to resolve the proteins by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis followed by staining with silver, or cooma...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com