Method of processing crustaceans
a crustacean and processing method technology, applied in the field of seafood processing, can solve the problems of reducing the shelf life of products, difficult to extract uncooked meat, time-consuming and often frustrating, etc., and achieves the effect of reducing time and pressure, reducing product shelf life, and reducing product textural qualities
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
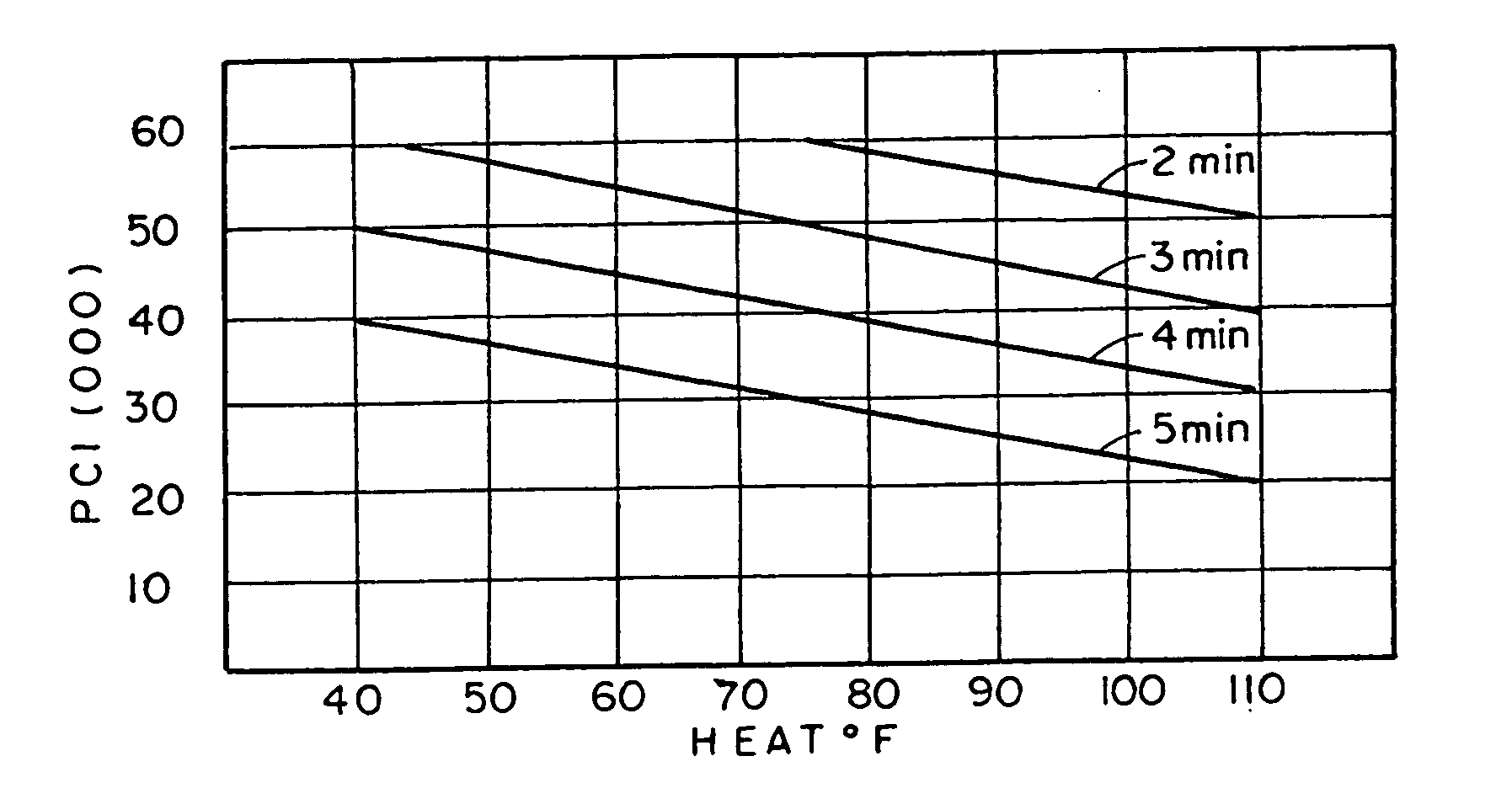
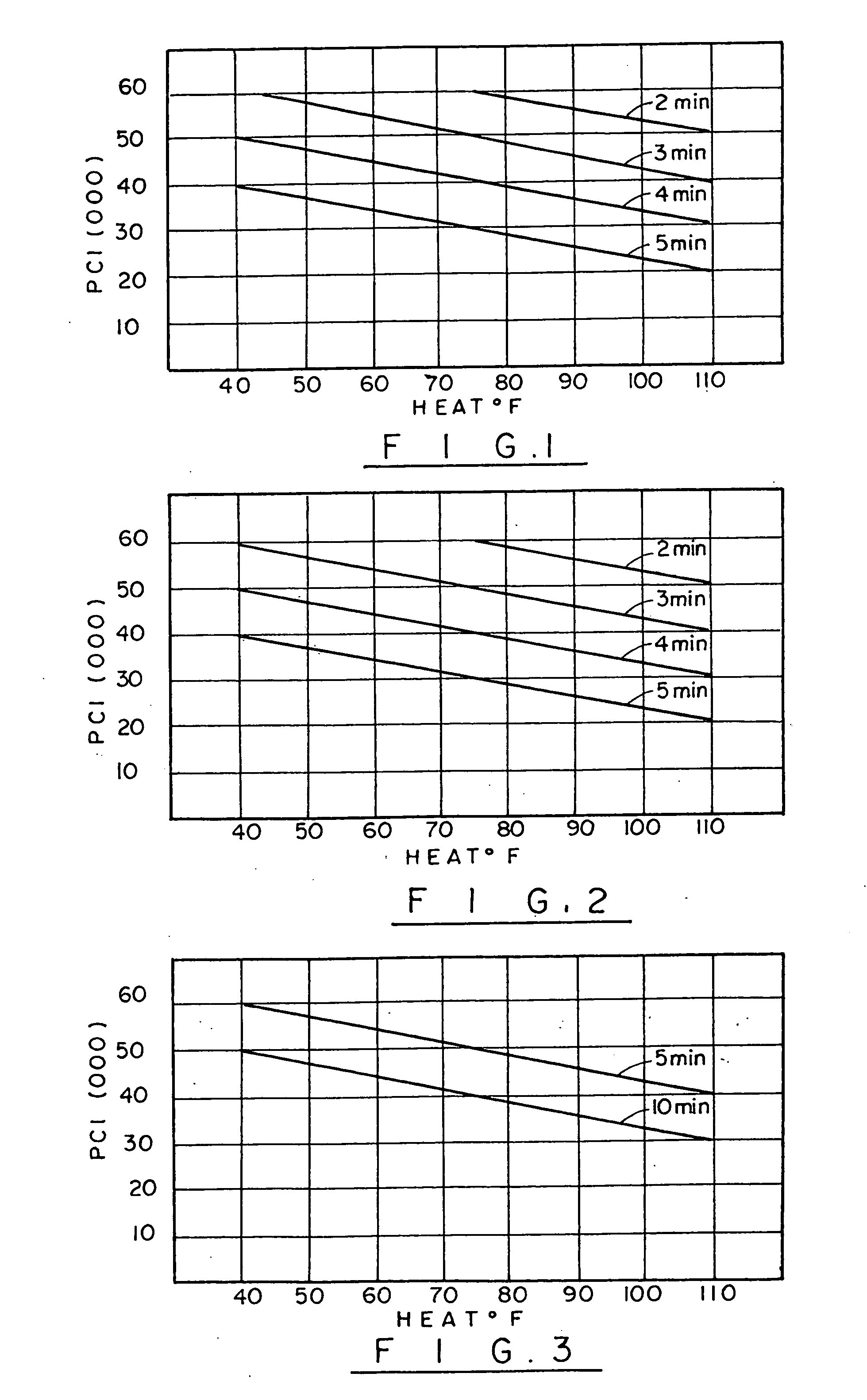
[0016] The new process for the treatment of raw shelled product according to the present invention will now be described in more detail. According to this process, the raw shelled product, such as crustacean, crab, crawfish and the like are treated in a high-pressure environment with minimal application of heat.
[0017] It is well known that shellfish, such as crab, crawfish and lobster deteriorate in quality immediately upon death. For this reason, one of the more expensive methods of introducing these products to the market involves shipping the product either live in refrigerated containers, or fresh frozen. The consumer is then challenged to cook the fresh or fresh frozen product and hand pick the cooked product to extract edible meat.
[0018] According to the present invention, crustaceans, or other shellfish, are placed in a pressure vessel that contains a pressure transmitting fluid, for example, water. If desired, the shellfish can be prepackaged in pouches and then loaded int...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com