Method and apparatus for shifting speeds in a fluid-actuated motor
a technology of fluid-actuated motors and shifting speeds, which is applied in the direction of bends, sealing/packing, and borehole/well accessories to achieve the effect of changing the rotational speed of the drill bi
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
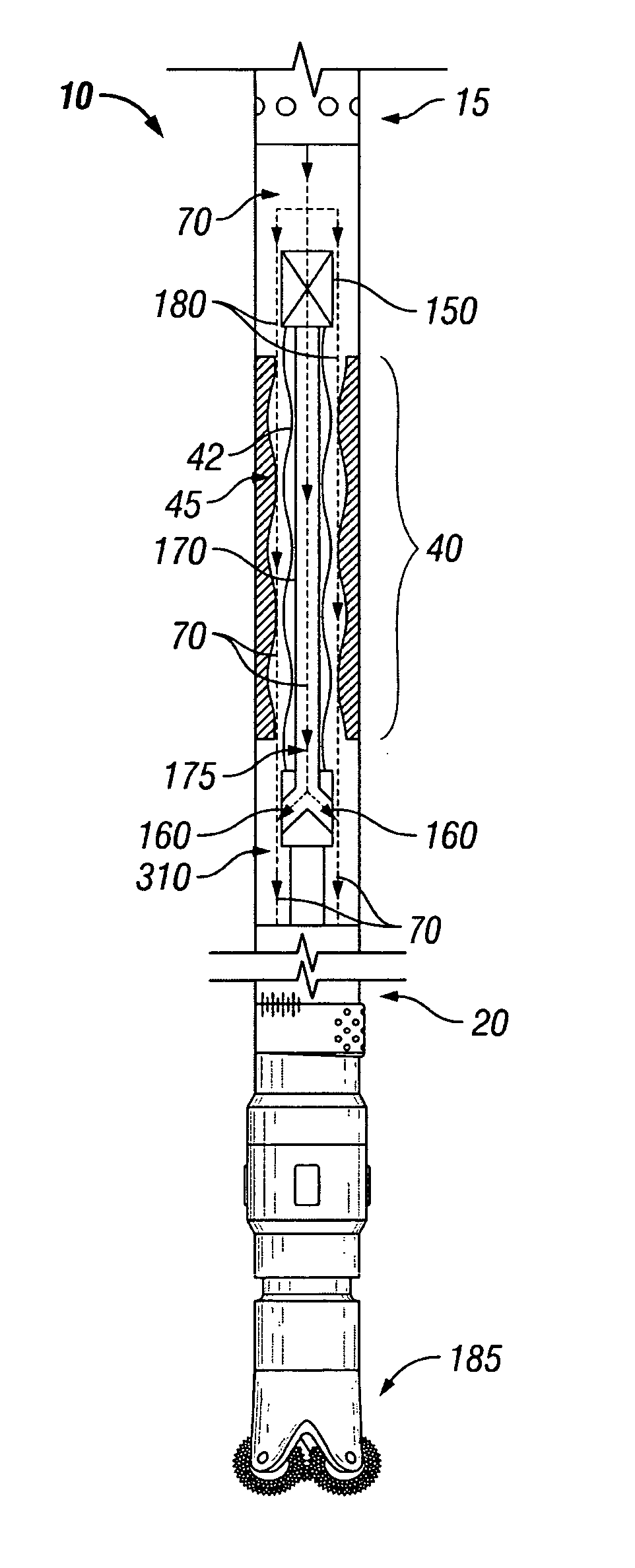
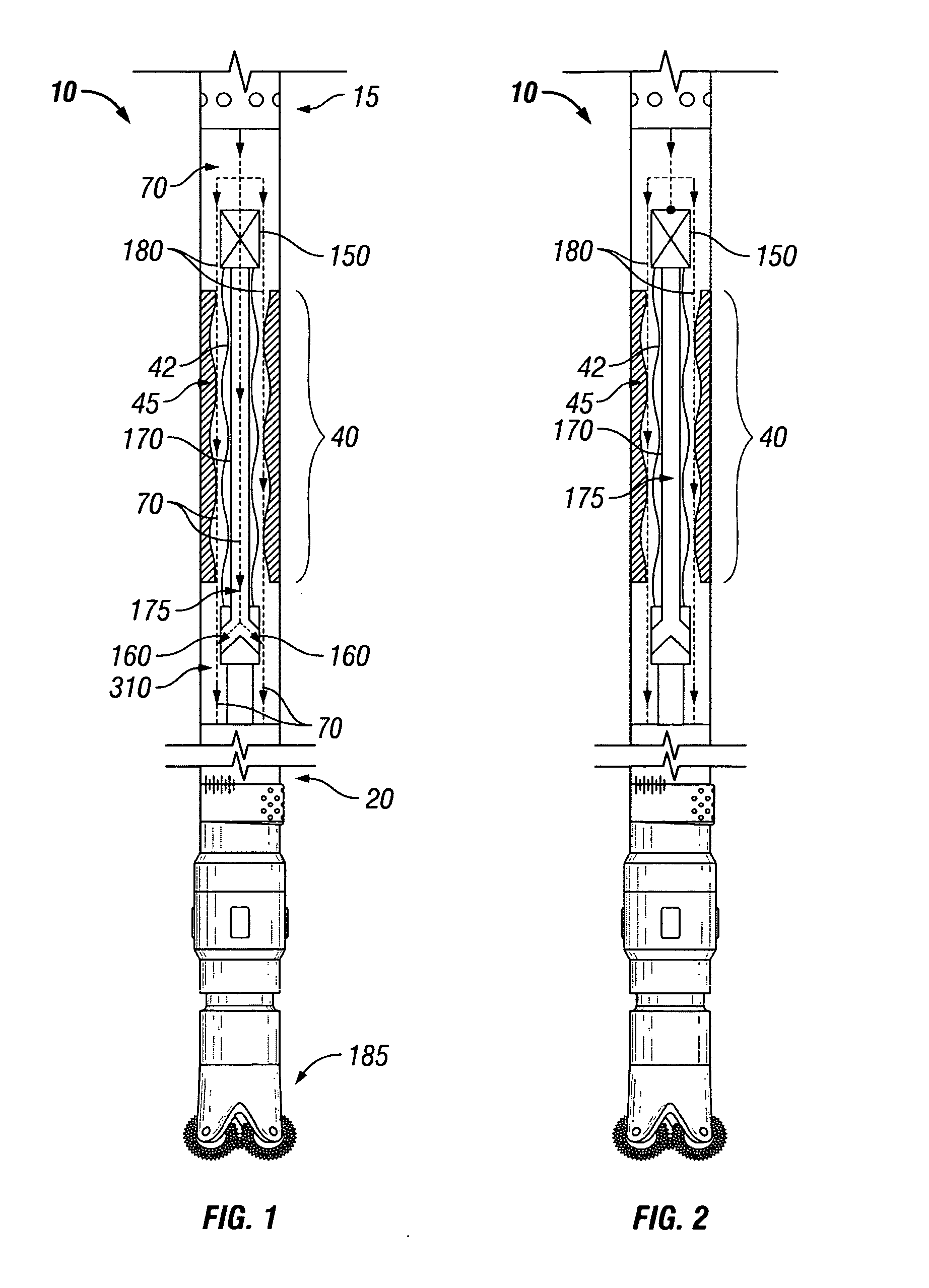
[0035]FIG. 1 is a diagram of an exemplary embodiment of a typical positive displacement motor 10 (“PDM”), or mud motor. The top side 15 of the motor connects to a drill string (not shown). The bottom side 20 connects to a drill bit 185. The power section 40 comprises a rotor 42 and stator 45. When a mud pump is turned on, fluid 70 enters the drill string, flows through the power section 40 and exits the bottom side 20 of the motor.
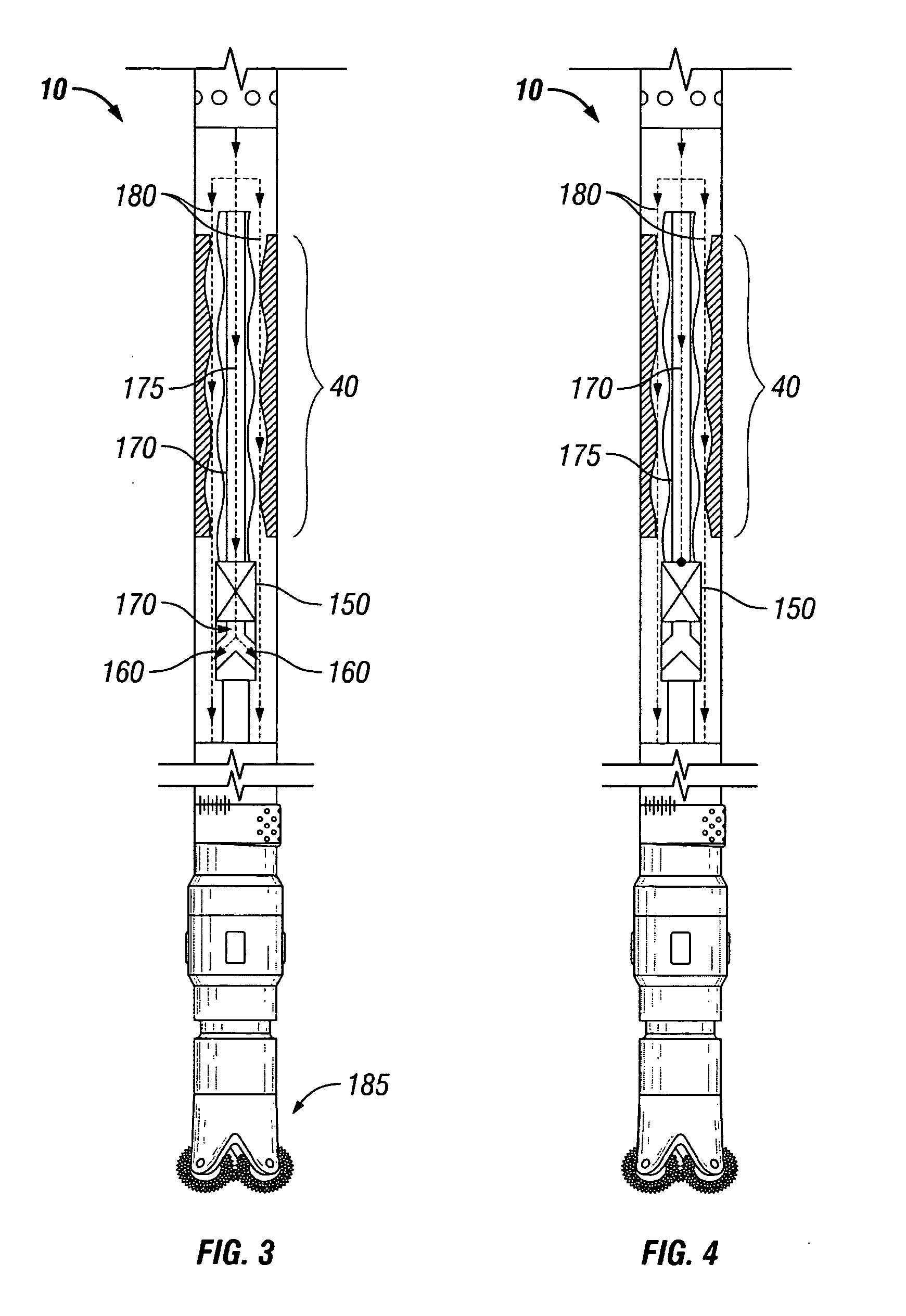
[0036]FIG. 2 is a diagram of an exemplary embodiment of a typical positive displacement motor 10 having a bypass valve 150 attached above the power section 40 of the motor 10; FIGS. 3 and 4 show the bypass valve 150 attached below the power section 40 of the motor 10; and FIGS. 5 and 6 show the bypass valve 150 attached inside the power section 40 of the motor. Because operation of the bypass valve is similar regardless of whether it attaches above, below, or inside the power section of a motor, only the operation of the bypass valve of FIGS. 1 and 2 need...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com