Generalized measure of image quality in medical X-ray imaging
a generalized measure and image quality technology, applied in the field of medical x-ray imaging, can solve the problems of poor image resolution, blurring of object image, and high noise level
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
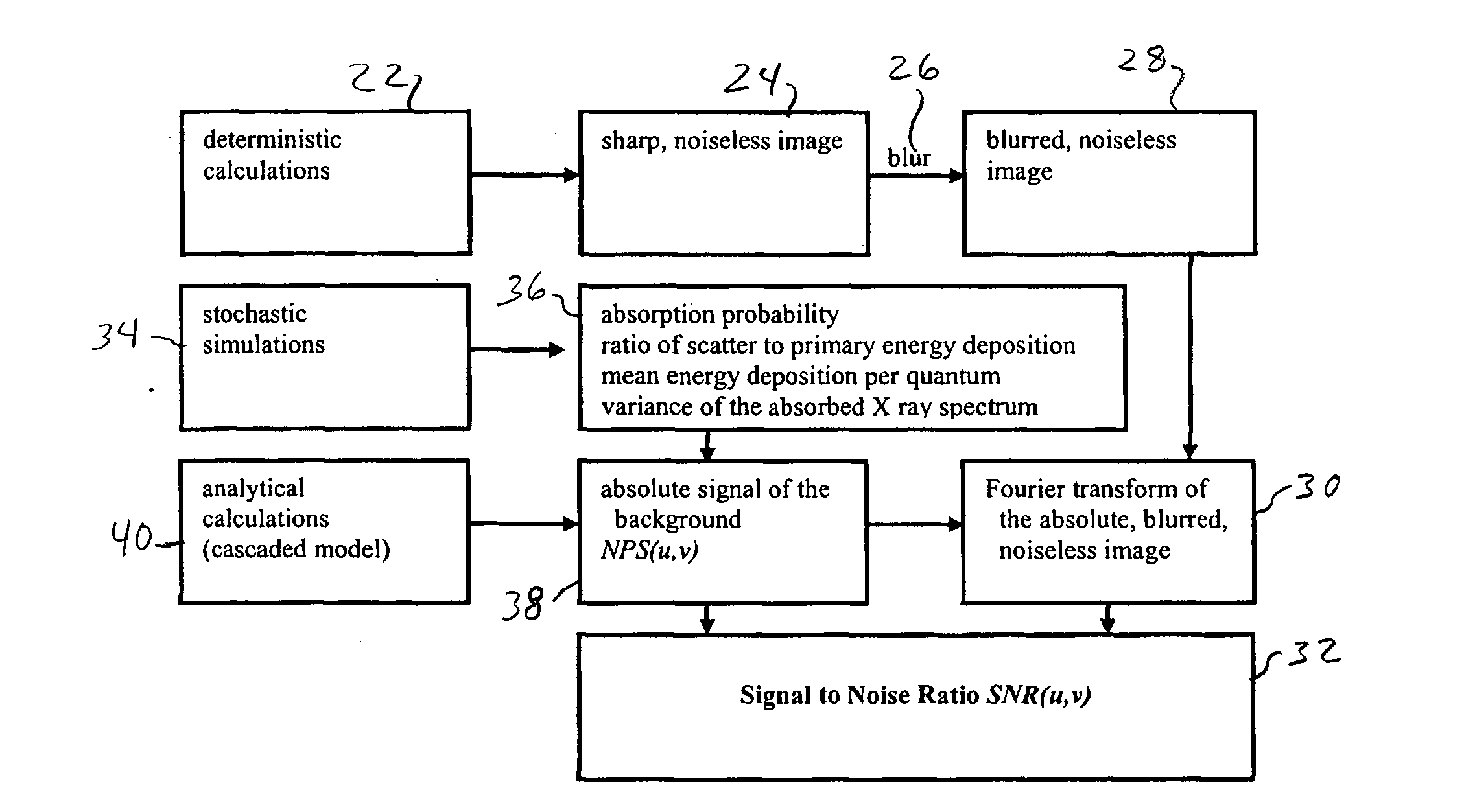
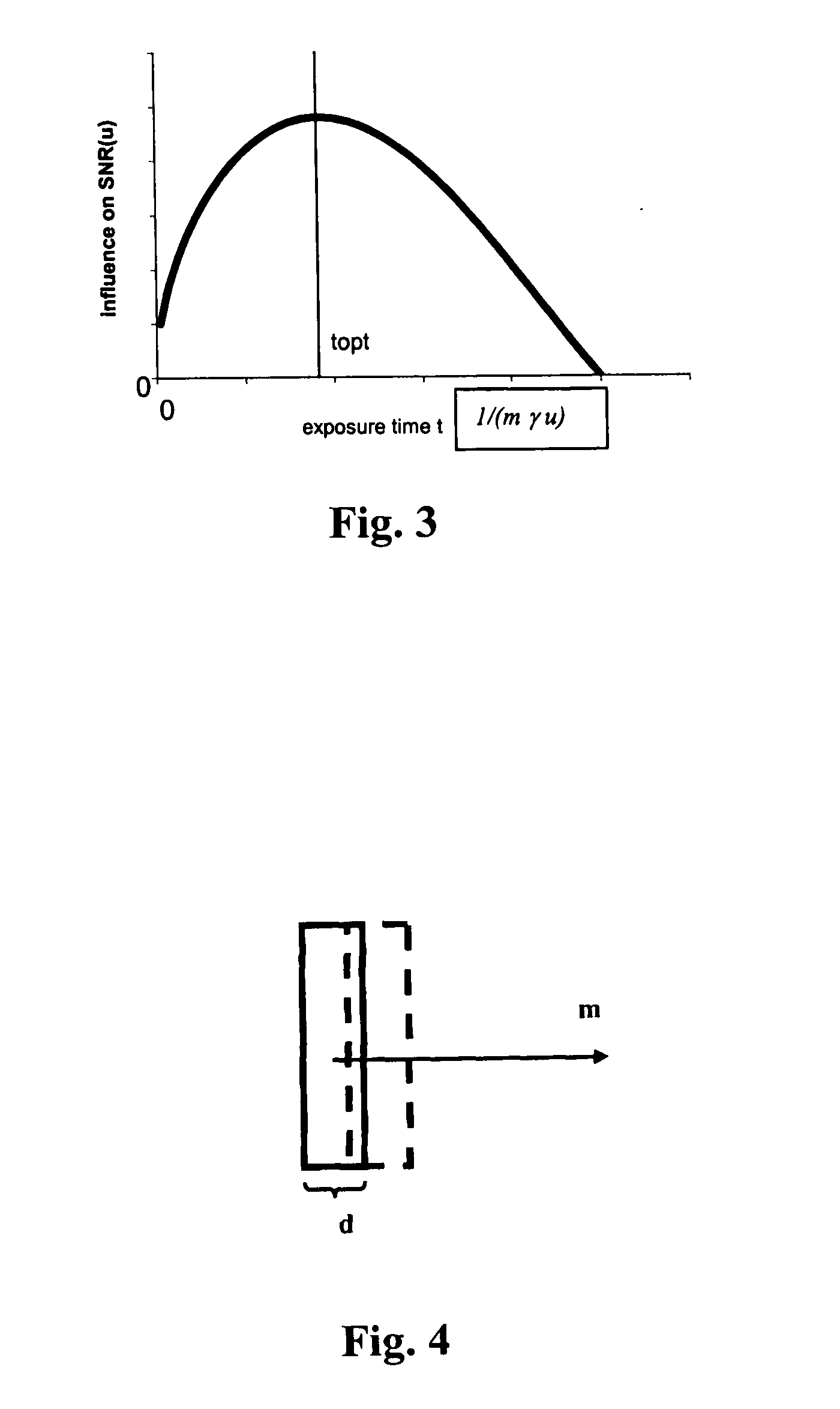
[0025] A method for optimizing a medical projection X-ray imaging device provides a single function, namely the frequency-dependent signal-to-noise ratio SNR which incorporates spatial resolution, contrast and noise. The frequency-dependent signal-to-noise ratio SNR describes the ratio between the signal and noise detected in the X-ray image dependent on two-dimensional spatial frequencies u and v so that SNR=SNR(u,v).
[0026] The calculation of SNR(u,v) utilizes the Fourier transform of the deterministic signal h(x,y) as the value H(u,v) and the noise power spectrum signal NPS(u,v) according to the following formula: SNR(u,v)=H(u,v)NPS(u,v)(1)
[0027] The noise power spectrum is only defined if the underlying signal is spatially invariant. An object of interest which is being imaged by the X-ray, however, absorbs either more or less radiation than the background. As such, the noise power spectrum is different at the location of the object of interest. Assuming that the object of i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com