Expansion valve for refrigerating cycle
a technology of expansion valve and refrigerating cycle, which is applied in the direction of gas cycle refrigeration machines, refrigeration machines, lighting and heating apparatus, etc., can solve the problems of increasing cost, low theoretical cycle efficiency, and inability to determine the internal pressure of the temperature-sensing portion, so as to reduce and lessen the influence of temperature of the outside air
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
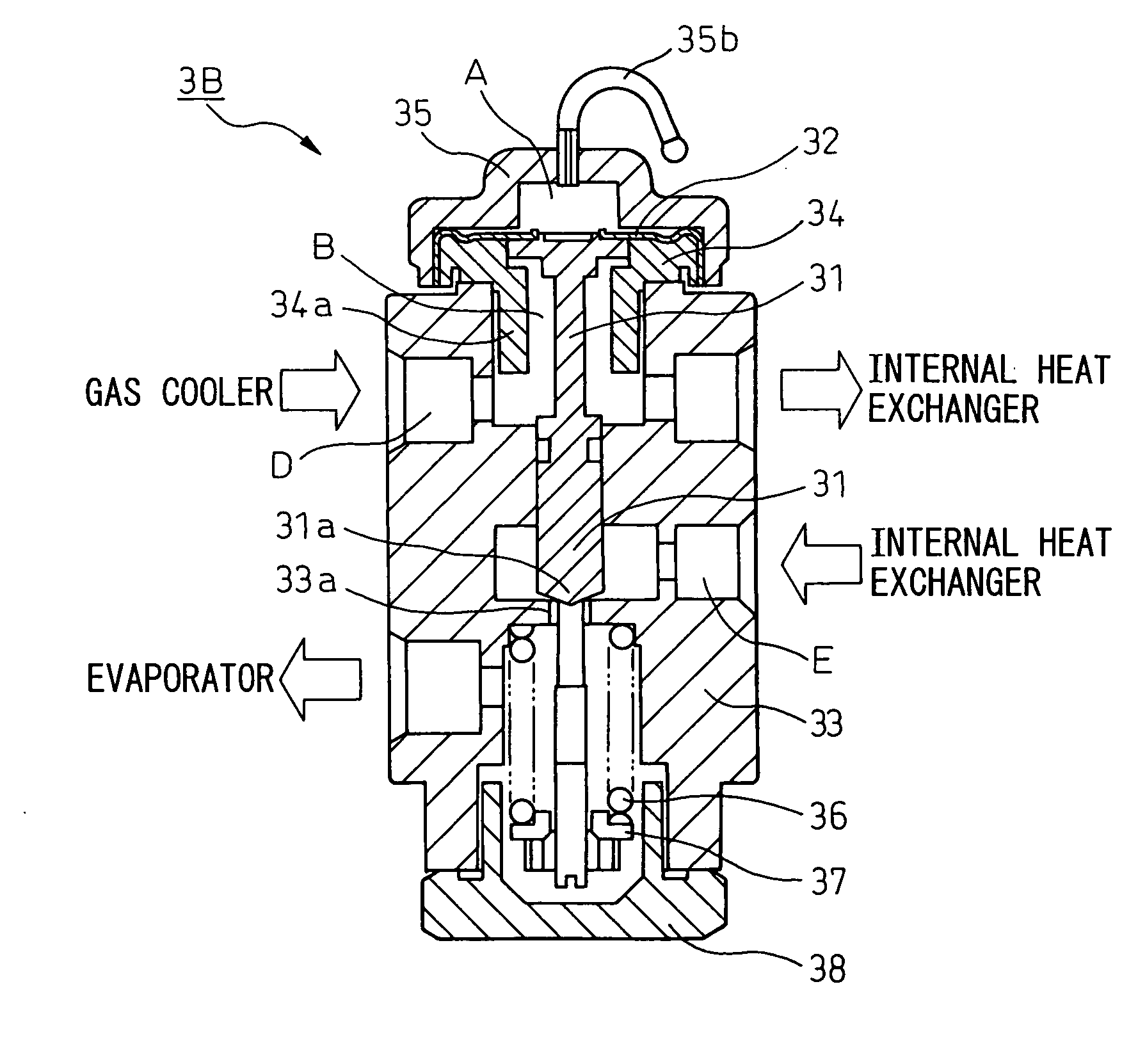
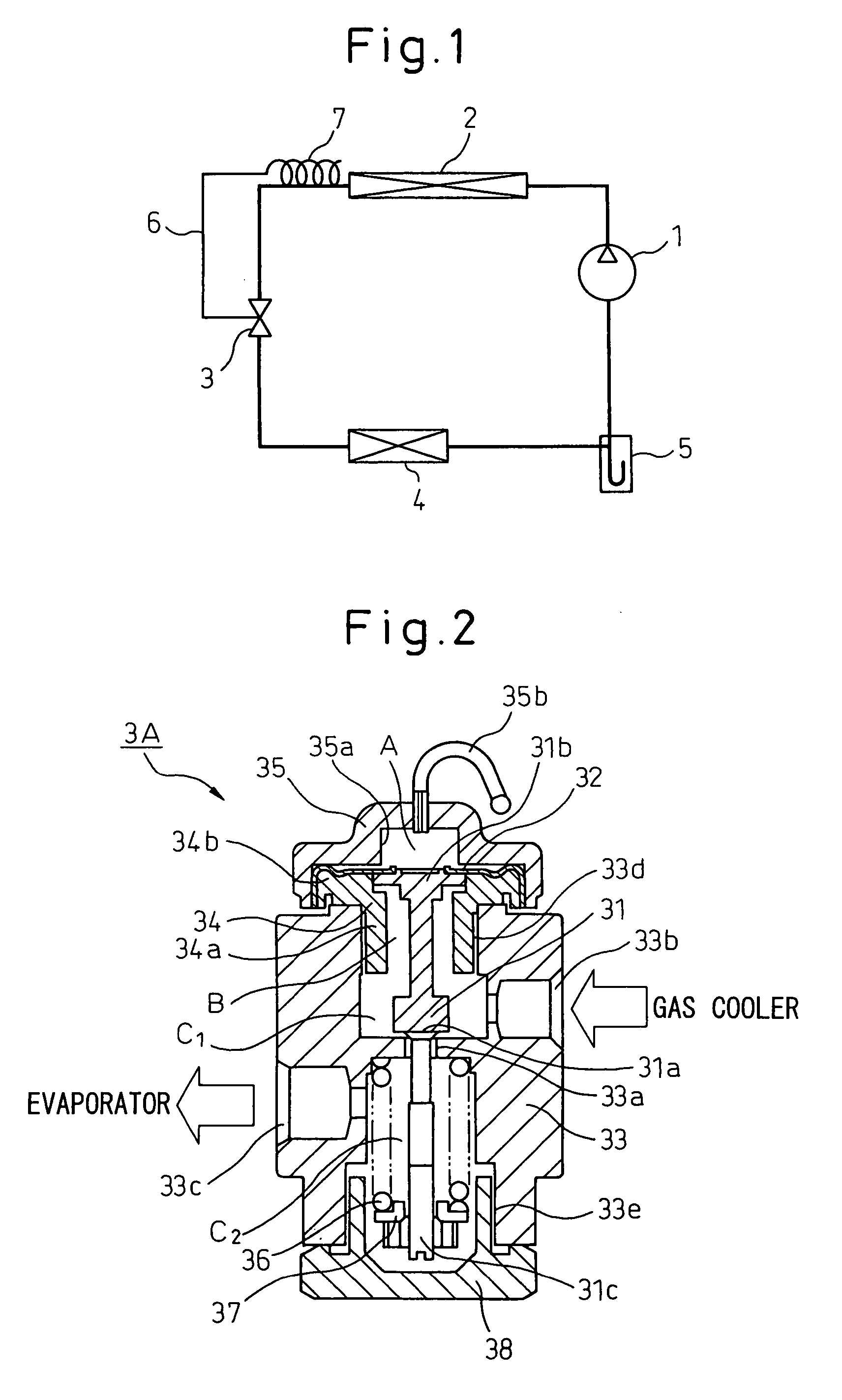
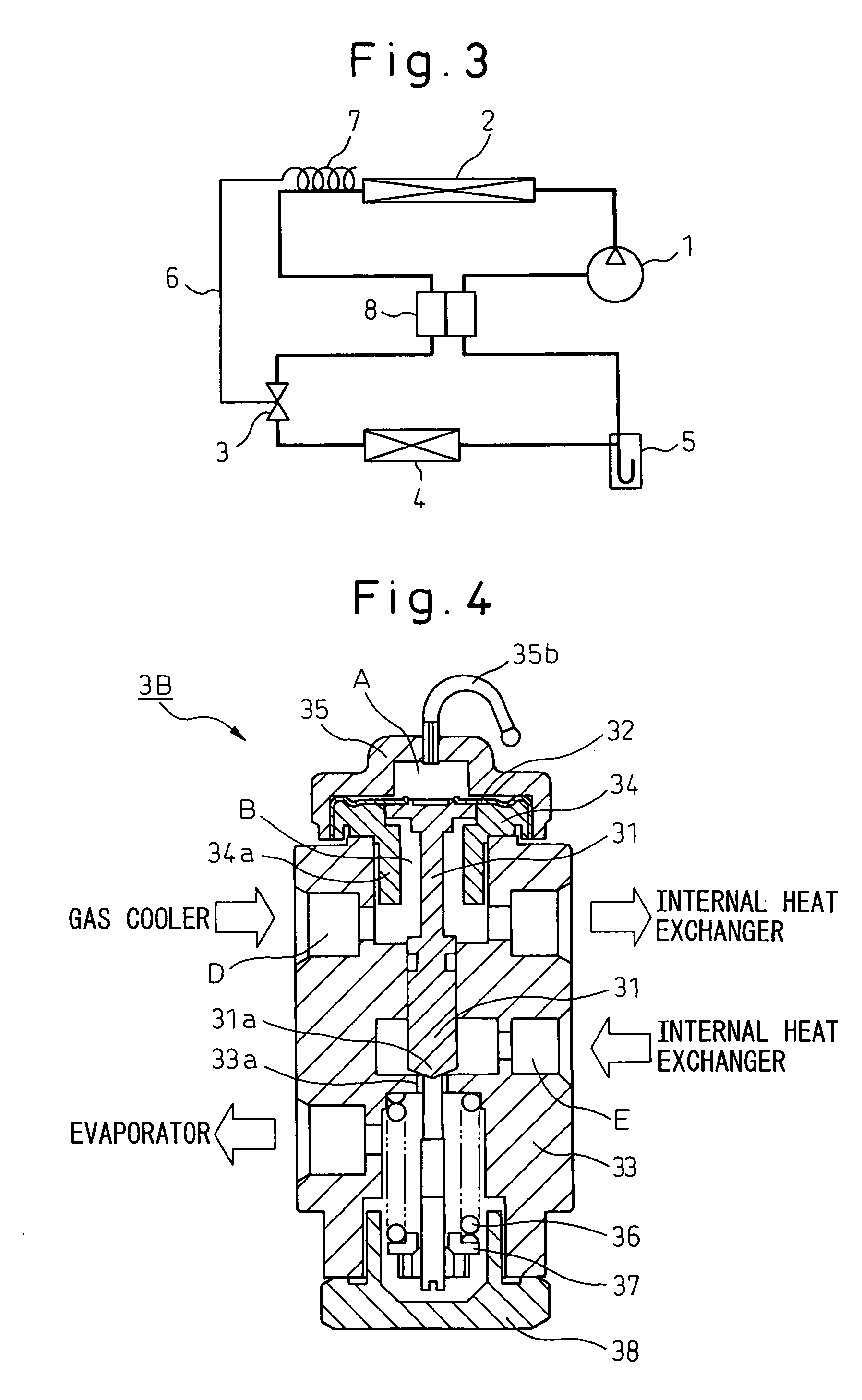
[0053] An expansion valve for a refrigerating cycle according to an embodiment of the invention will be described below with reference to the drawings. FIG. 1 is a view illustrating a vapor compression type refrigerating cycle (supercritical refrigerating cycle), in which CO2 is circulated as a refrigerant, and FIG. 2 is a cross sectional view showing an expansion valve for a refrigerating cycle, according to the invention, applied to the vapor compression type refrigerating cycle illustrated in FIG. 1. In FIG. 1, the reference numeral 1 denotes a compressor that sucks and compresses a refrigerant (CO2), and 2 a gas cooler (radiator) that cools the refrigerant compressed by the compressor 1. An expansion valve 3 is arranged on an outlet side of the gas cooler 2 to control a refrigerant pressure at the outlet side of the gas cooler 2 on the basis of a refrigerant temperature at the outlet side of the gas cooler 2, the expansion valve also functioning as a decompressor that decompress...
ninth embodiment
[0096] Typically, in the expansion valve 3I used in a refrigerating cycle provided with the internal heat exchanger illustrated with reference to FIG. 11, that density, at which a refrigerant is charged into the enclosed space A of the temperature-sensing portion of the expansion valve 3I, is set in the range of about 200 kg / m3 to about 600 kg / m3. In the case where a quantity of superheat is to be increased, an upper limit value of the range of charging density may be made in the order of about 570 kg / m3, and in the case where an elastic member for biasing in a valve closing direction is used in combination, the charging density can be made in the order of about 450 kg / m3. More desirably, that density, at which a refrigerant is charged into the temperature-sensing portion of the expansion valve, is set in the range of about 200 kg / m3 to about 450 kg / m3.
seventh embodiment
[0097] Further, for the expansion valve 3H used in a refrigerating cycle, in which the internal heat exchanger and illustrated with reference to FIG. 10 is used, the expansion valve being provided with no adjustment spring, it is preferable to adopt a charged refrigerant density being the same as that described above. That is, that density, at which a refrigerant is charged into the enclosed space A of the temperature-sensing portion of the expansion valve 3H and the cavity 31d, is set in the range of about 200 kg / m3 to about 600 kg / m3. In the case where a quantity of superheat is to be increased, an upper limit value in the range of charging density may be made in the order of about 570 kg / m3 and, further, in the case where an elastic member for biasing in a valve closing direction is used in combination, the charging density can be in the order of about 450 kg / m3. More desirably, that density, at which a refrigerant is charged into the temperature-sensing portion of the expansion...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com