Three-dimensional textile composite structure and manufacture and use thereof
a textile composite and three-dimensional technology, applied in the direction of pedestrian/occupant safety arrangement, packaging foodstuffs, packaged goods, etc., can solve the problems of time-consuming process of spraying and curing thermoset resin onto fabrics, unsatisfactory energy absorption performance, etc., to achieve a faster and convenient process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
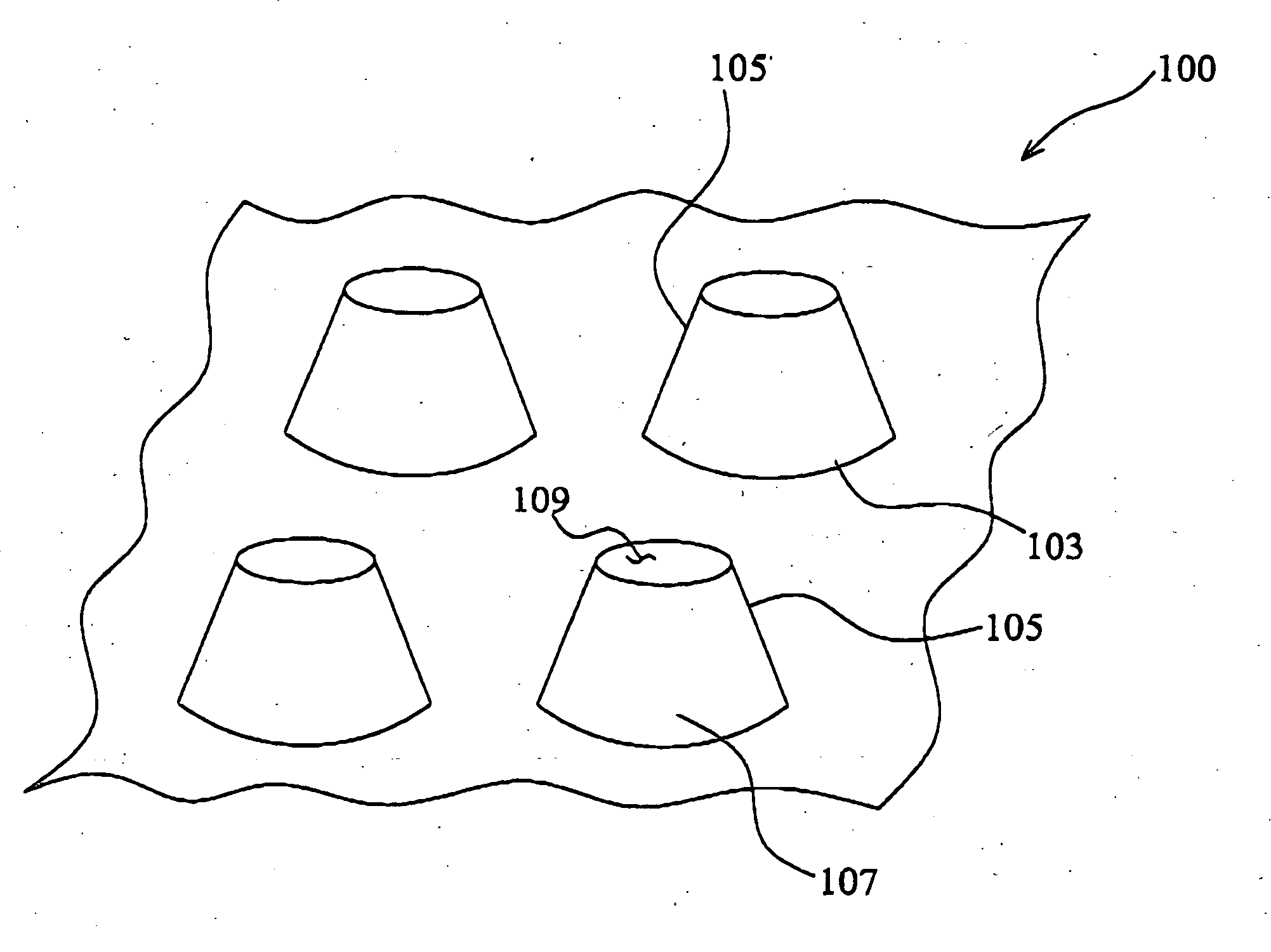
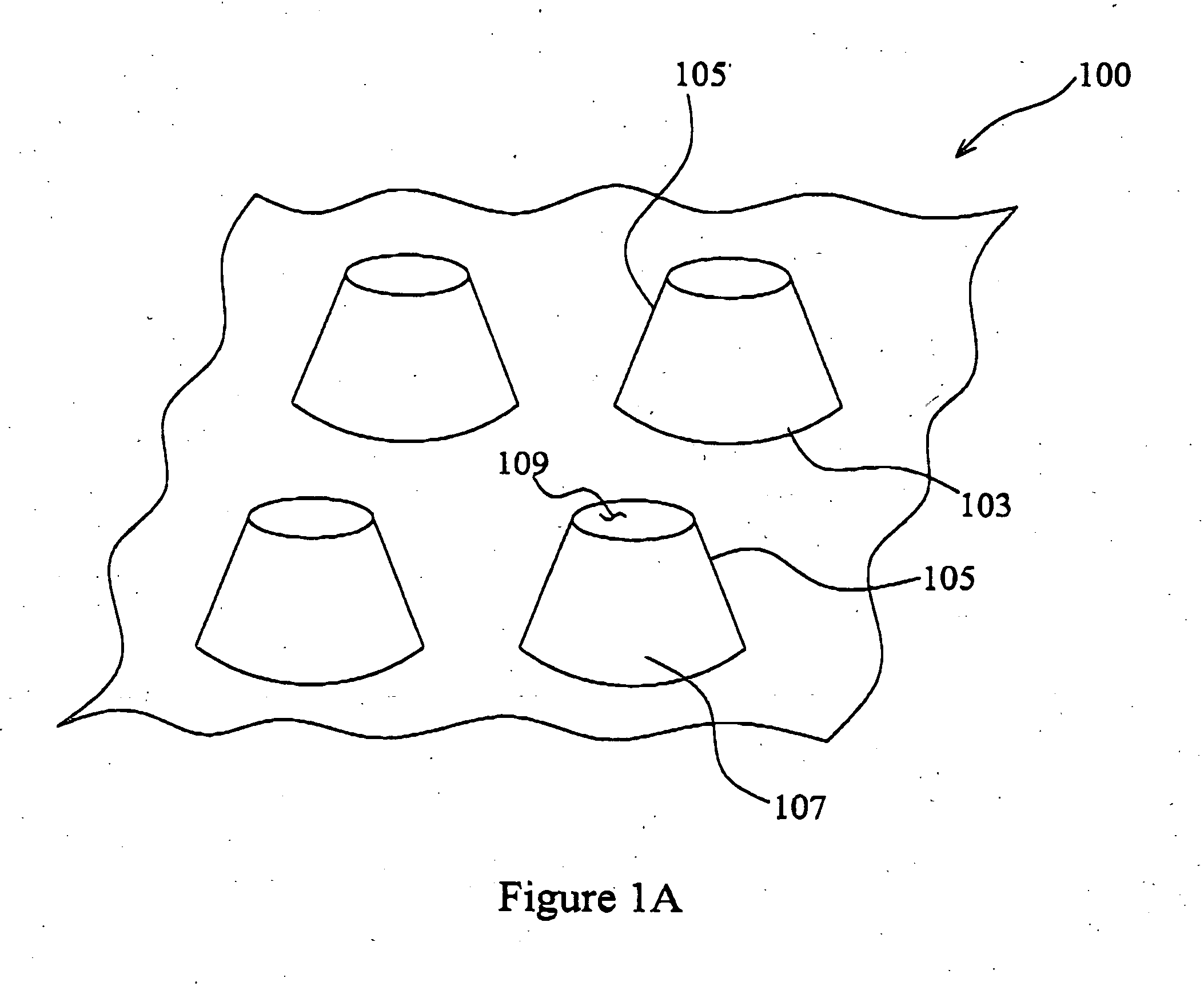
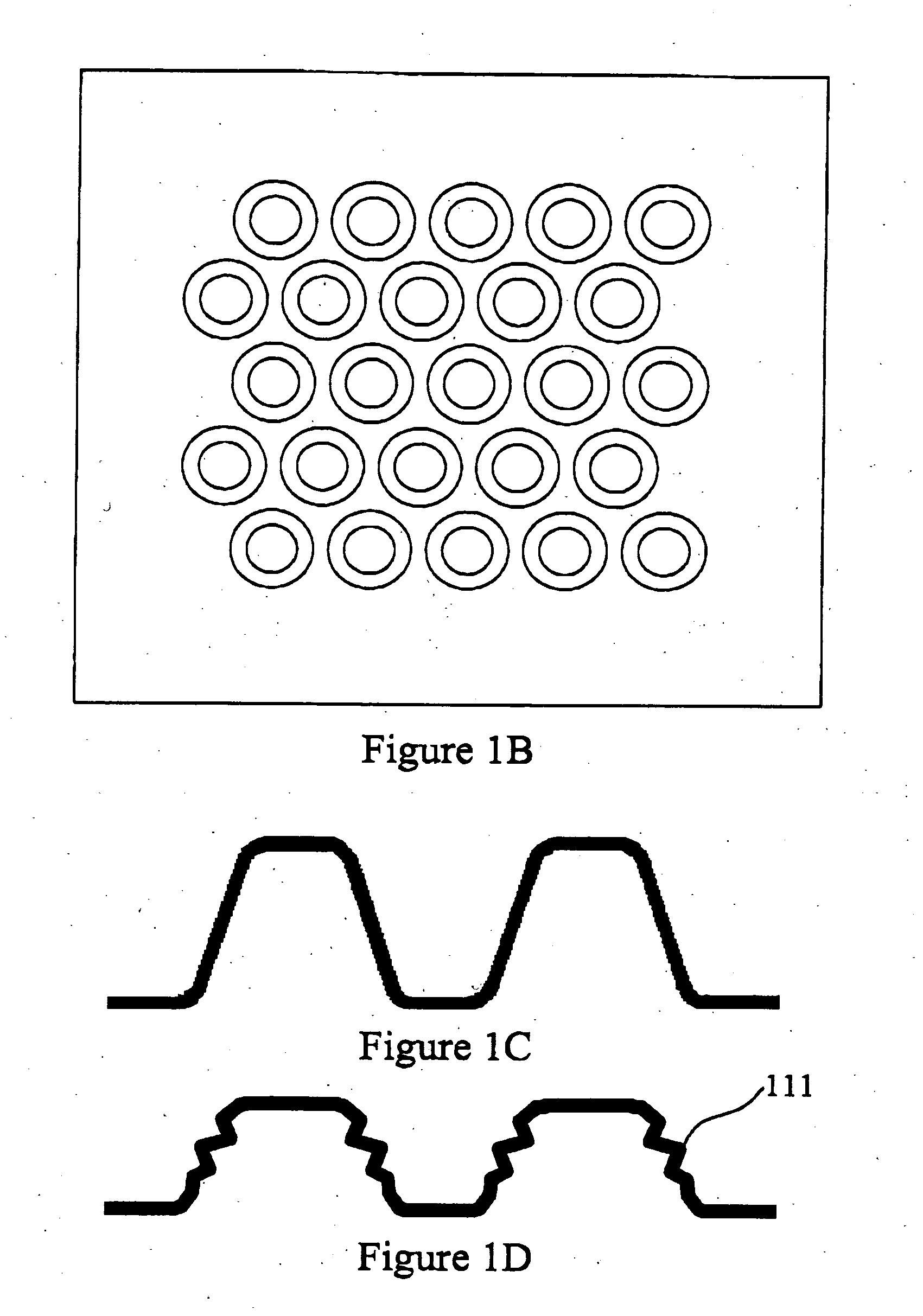
[0045]FIG. 1 illustrates an exemplary three-dimensional sheet-like textile composite structure 100 with energy-absorbing capacities under multiple impacts. The textile composite structure 100 has a generally planar base 103 and a plurality of projections 105 extending from the base 103. In the exemplary embodiment, each projection 105 has a grid-domed shape with a conical sidewall 107 and a generally flat top 109. Furthermore, each projection 105 defines a space (not shown) where the sidewall 107 and / or the top 109 may collapse under impacts. FIGS. 1B and 1C are respective top plan view and cross sectional view of the textile composite structure of FIG. 1A.
[0046] The textile composite structure 100, at least the projections 105, includes a textile and a matrix material. More specifically, in the exemplary embodiment, the textile structure 100 is made from non-woven fabric materials impregnated with thermoplastic matrix materials.
[0047] Materials for producing the non-woven fabric ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| energy-absorbing capacities | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com