Semiconductor memory device and method of manufacturing the same
a memory device and semiconductor technology, applied in the direction of semiconductor devices, electrical appliances, transistors, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to improve the manufacturing yield, difficult to achieve good embedding characteristics, and difficult to improve the withstand voltag
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
(First Embodiment)
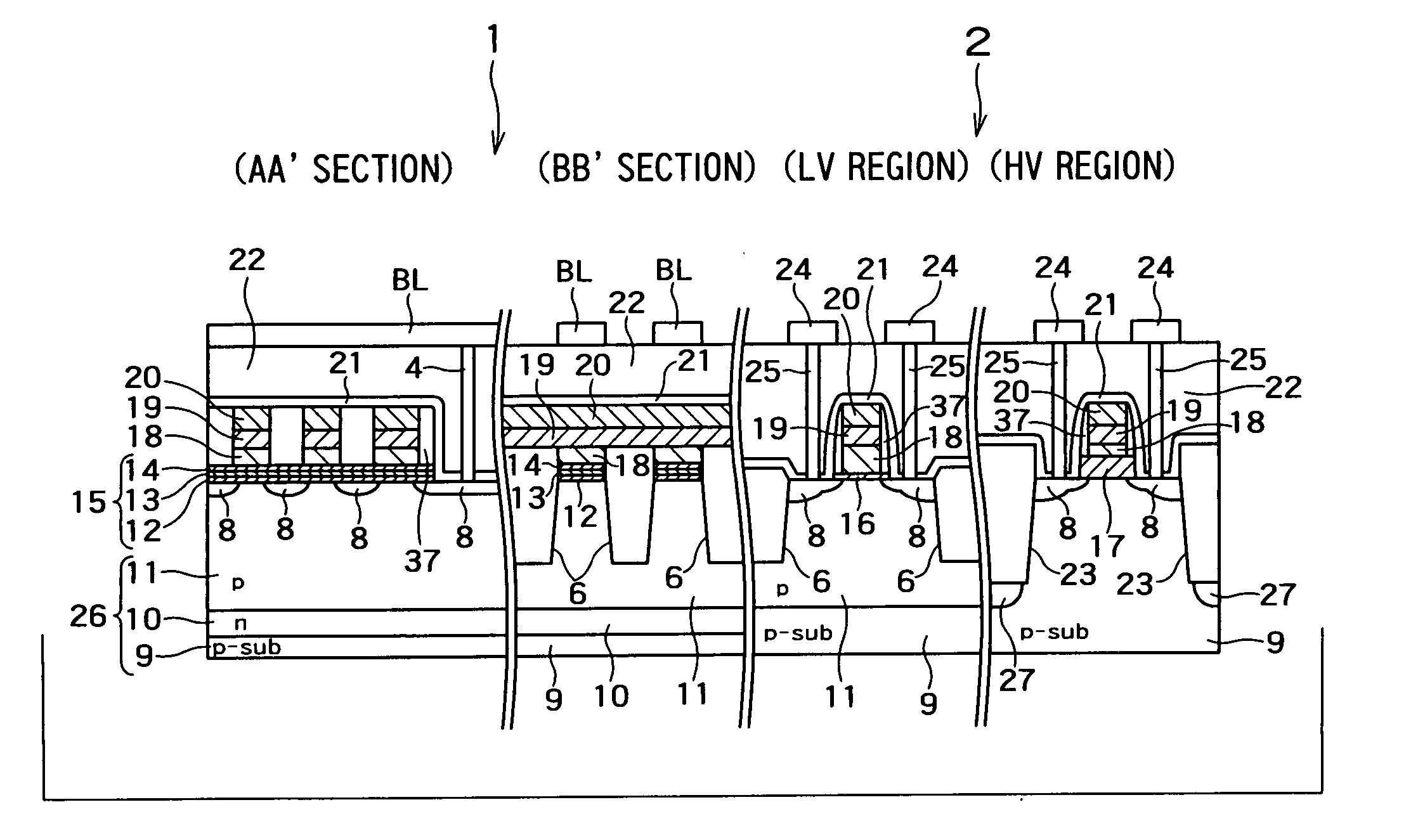
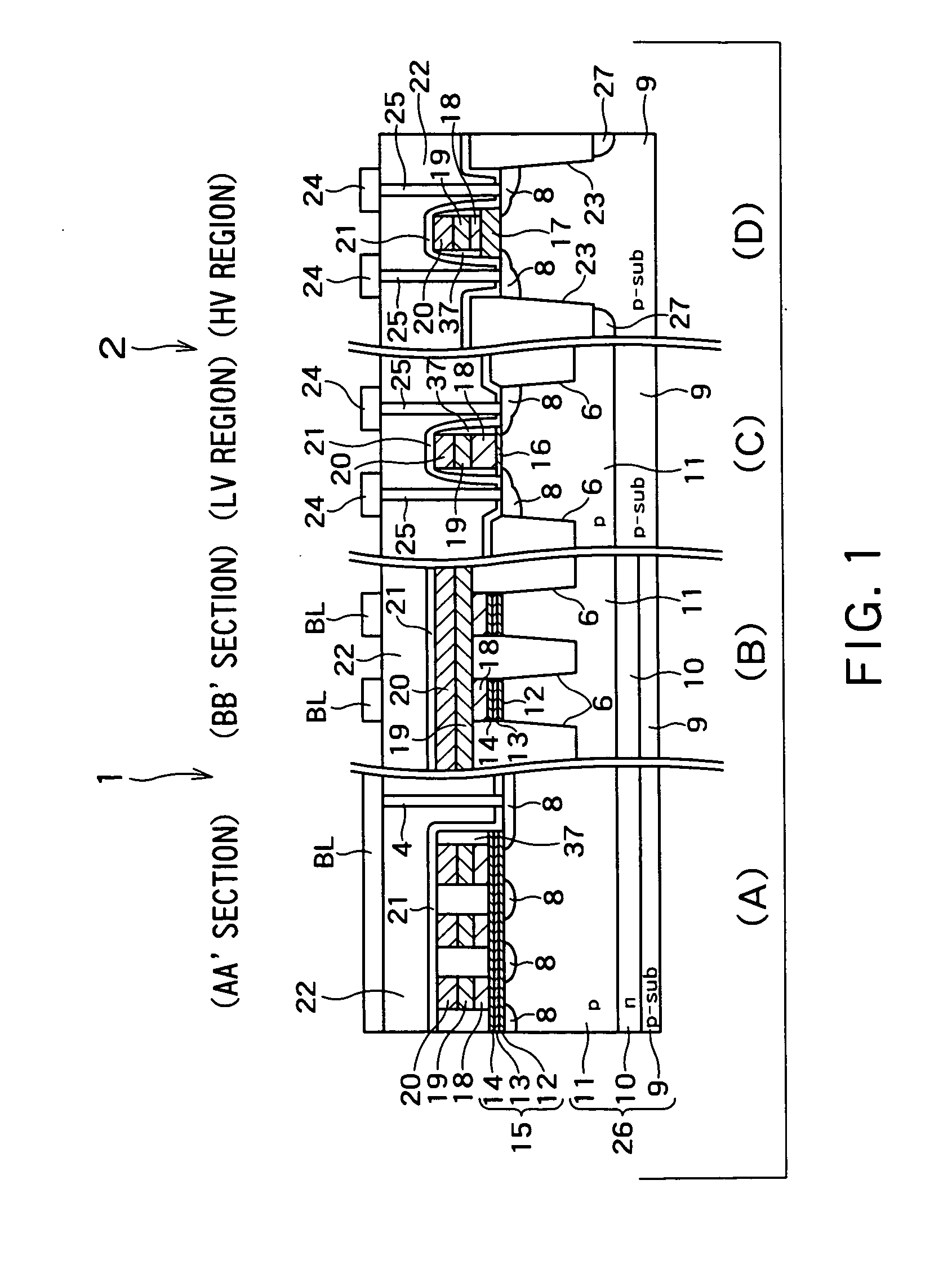
[0137]FIG. 1 shows sectional views of a semiconductor memory device according to a first embodiment of the present invention, in which (A) is a sectional view of a gate of a memory cell region (corresponding to the A-A′ section of FIG. 46), (B) is a sectional view of an element isolation region in the memory cell region (corresponding to the B-B′ section of FIG. 46), (C) is a sectional view of a low voltage transistor region (LV region) of a peripheral circuit portion, and (D) is a sectional view of a high voltage transistor region (HV region).
[0138]FIG. 1 differs from FIG. 47 in that the element isolation groove 23 in the high voltage transistor region of the peripheral circuit portion is deeper than the element isolation grooves 6 in the element isolation region in the memory cell region and the low voltage transistor region in the peripheral circuit portion, as shown in the sections (A), (B), and (C).
[0139] That is, as shown in the sections (B) and (C), in the...
second embodiment
(Second Embodiment)
[0203]FIG. 25 shows sectional views of a semiconductor memory device according to a second embodiment of the present invention, in which (A) shows the gate section in the memory cell region, (B) shows the element isolation section in the memory cell region, (C) shows the low voltage transistor region, and (D) shows the high voltage transistor region.
[0204] The difference between FIGS. 1 and 25 lies in that the gate section in the memory cell region shown in FIG. 25(A).
[0205] In the first embodiment, all of the transistors in the memory cells region, i.e., the transistors for storage, and the transistors for selecting and controlling other transistors, have the same MONOS structure. However, in the second embodiment, the transistors in the memory cell region are divided into two groups, i.e., those located in a storage region 41 for storing information, and those located in a control region 42 for selecting memory cells. The transistors located in the storage reg...
third embodiment
(Third Embodiment)
[0208]FIG. 26 shows sectional views of a semiconductor memory device of the third embodiment. The difference between FIGS. 1 and 26 lies in that the depth of the element isolation grooves 6 in the low voltage transistor region is deeper than the depth of the element isolation grooves 6 in the memory cell region, and substantially the same as the depth of the element isolation grooves 23 in the high voltage transistor region.
[0209] According to the semiconductor memory device of the third embodiment, the element isolation grooves 6 and 23, which should desirably be as deep as possible in order to maintain an element isolation withstand voltage, in the high and low voltage transistor regions are deeper than those in the memory cell region. That is, the semiconductor memory device of this embodiment has a structure suitable for improving withstand voltage.
[0210] In addition, according to the semiconductor memory device of the third embodiment, the element isolation ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com