Friction reducing bandage
a bandage and friction technology, applied in the field of friction reducing bandage, can solve the problems of scheinberg's devices, which are not particularly well adapted for mass production, erythema (red spots), blisters and pressure ulcers, etc., and achieve the effect of enhancing moisture and vapor transfer and adding flexibility to the skin contact layer
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
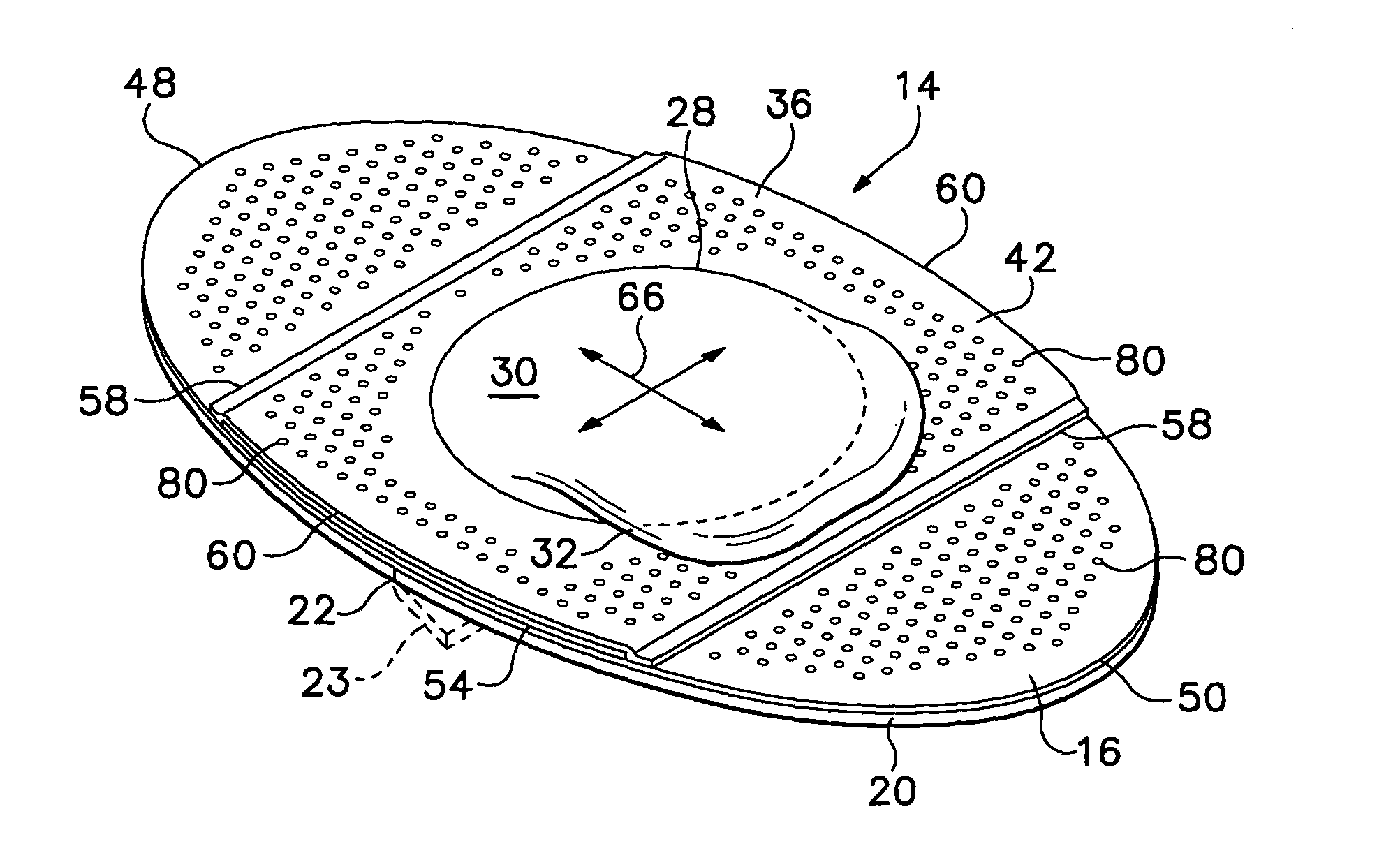
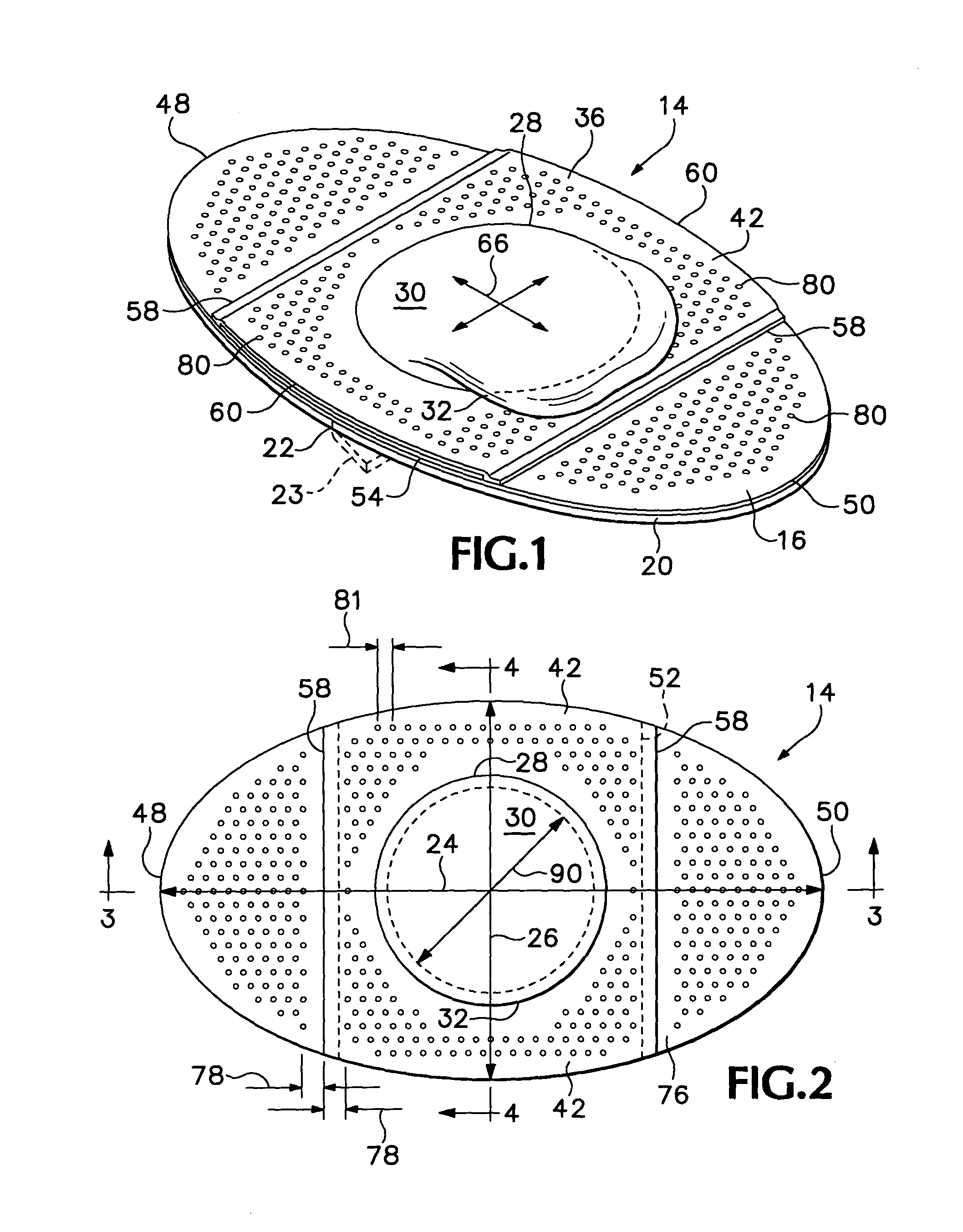
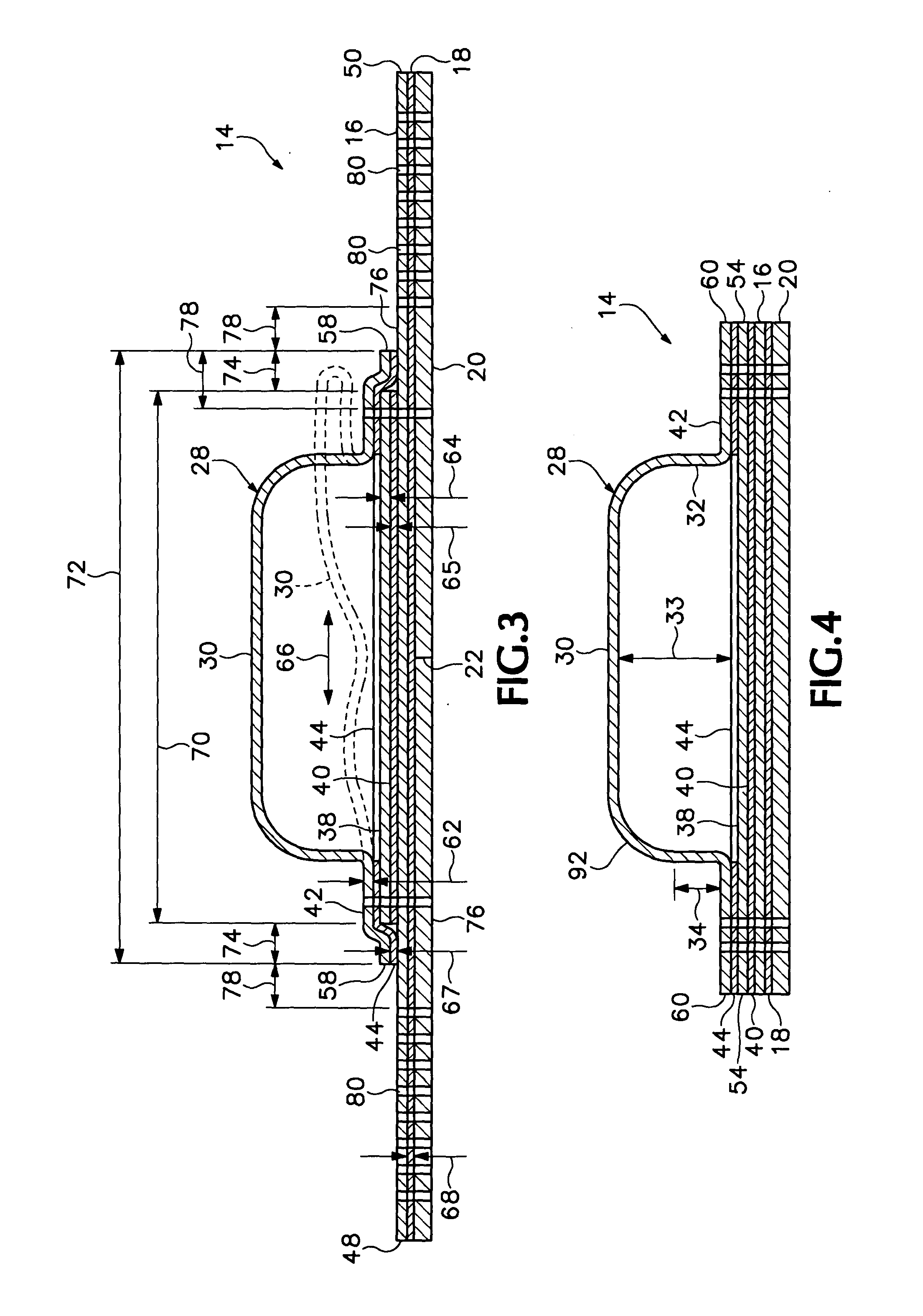
[0026] Referring to FIGS. 1-4 of the drawings which form a part of the disclosure herein, an elliptical bandage 14 which is one preferred embodiment of the present invention includes a skin contact layer 16 of flexible film material to which a layer 18 of an adhesive material is adhered. The layer 18 of adhesive material is protected by an easily removable liner 20 divided into two separate halves by a cut 22 extending across the liner 20 to allow the halves of the liner 20 to be removed separately during application of the bandage 14 to a person's skin. Alternatively, one part of the liner 20 can overlap the other along the location of the cut 22, with the overlying portion including a folded-back margin flap 23 shown in broken line, to facilitate removal of the liner 20 from the skin contact layer 20 to apply the bandage. As one preferred size, the bandage 14 may have a length 24 of 66.67 mm (2.625 in.) and a width 26 of 38.1 mm (1.5 in.).
[0027] A dome 28 is centrally located on ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com