Method and apparatus for synchronizing applications for data recovery using storage based journaling
a data recovery and application technology, applied in the field of computer storage, can solve the problems of inability to conveniently, if at all, service any kind of request, and no way to recover data at any point in time, and achieve the effect of facilitating the recovery of the desired data sta
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
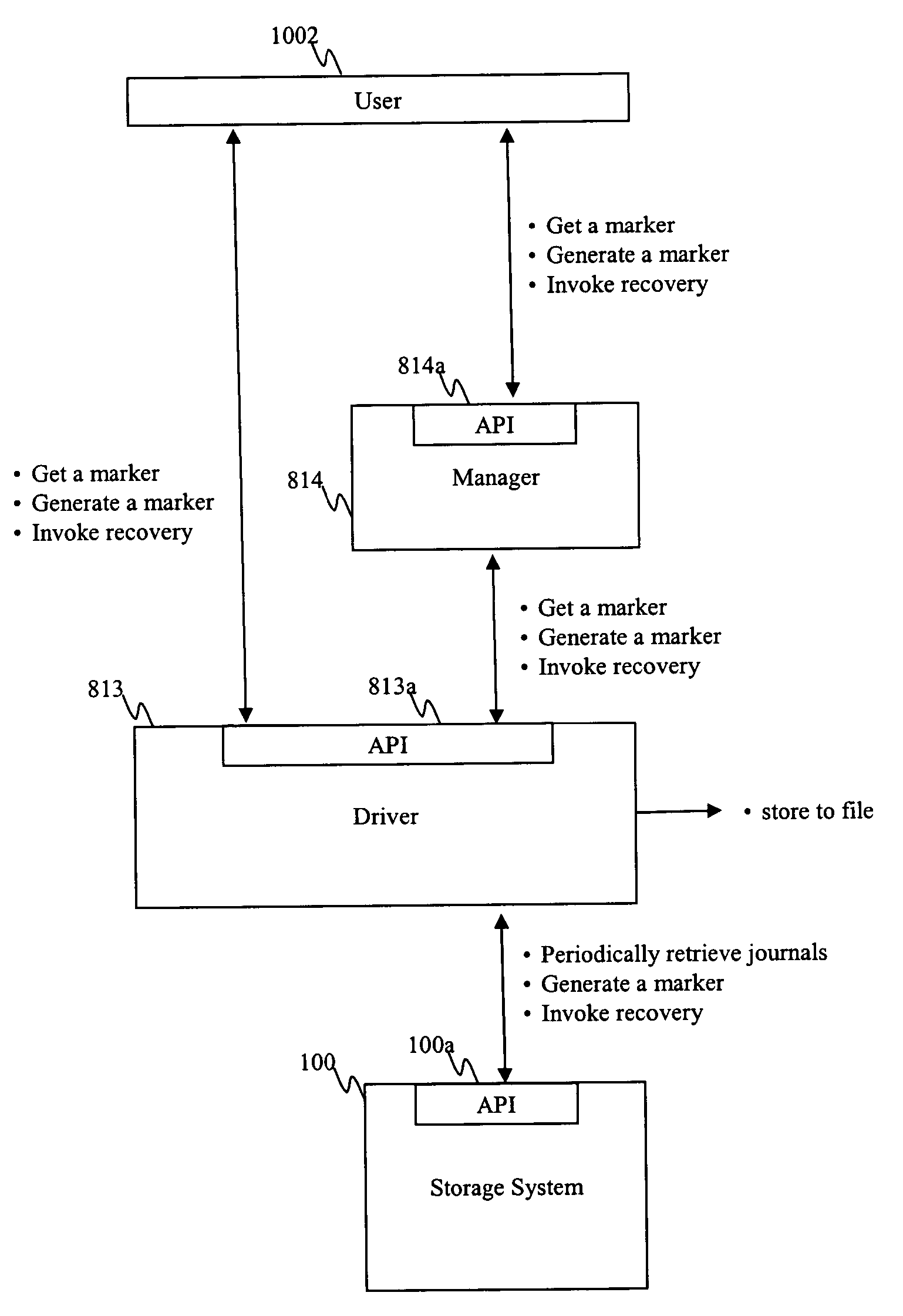
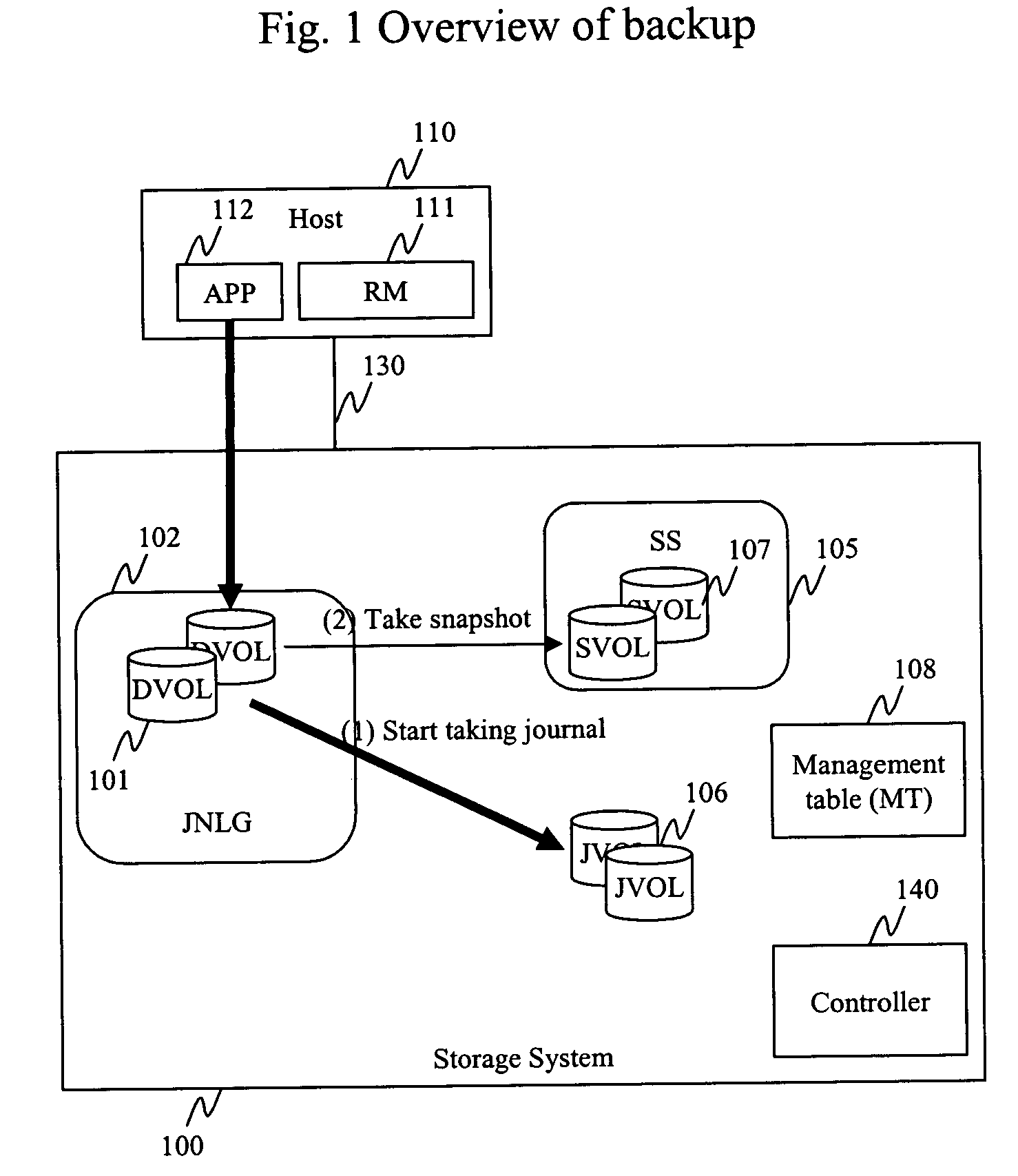
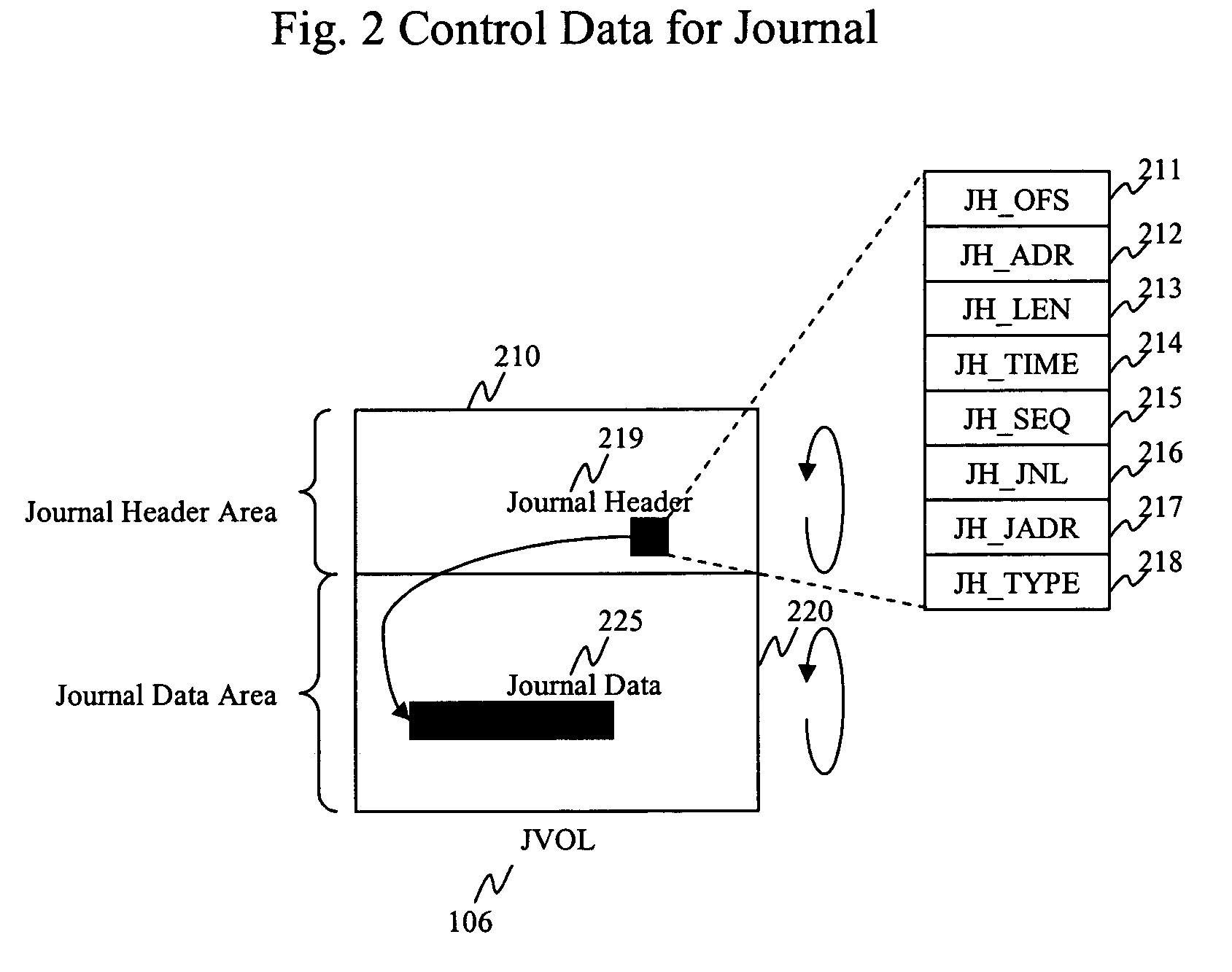
FIG. 1 is a high level generalized block diagram of an illustrative embodiment of a backup and recovery system according to the present invention. When the system is activated, a snapshot is taken for production data volumes (DVOL) 101. The term “snapshot” in this context conventionally refers to a data image of at the data volume at a given point in time. Depending on system requirements, implementation, and so on, the snapshot can be of the entire data volume, or some portion or portions of the data volume(s). During the normal course of operation of the system in accordance with the invention, a journal entry is made for every write operation issued from the host to the data volumes. As will be discussed below, by applying a series of journal entries to an appropriate snapshot, data can be recovered at any point in time.
The backup and recovery system shown in FIG. 1 includes at least one storage system 100. Though not shown, one of ordinary skill can appreciate that the storage ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com