Novel synthetic peptides with antimicrobial and endotoxin neutralizing properties for management of the sepsis syndrome
a technology of synthetic peptides and sepsis, which is applied in the direction of bactericidal/permeability-increasing proteins, peptide sources, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of sepsis, sepsis, sepsis, inadequate organ perfusion, etc., and achieve the effect of preventing septic shock and preventing septic shock
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
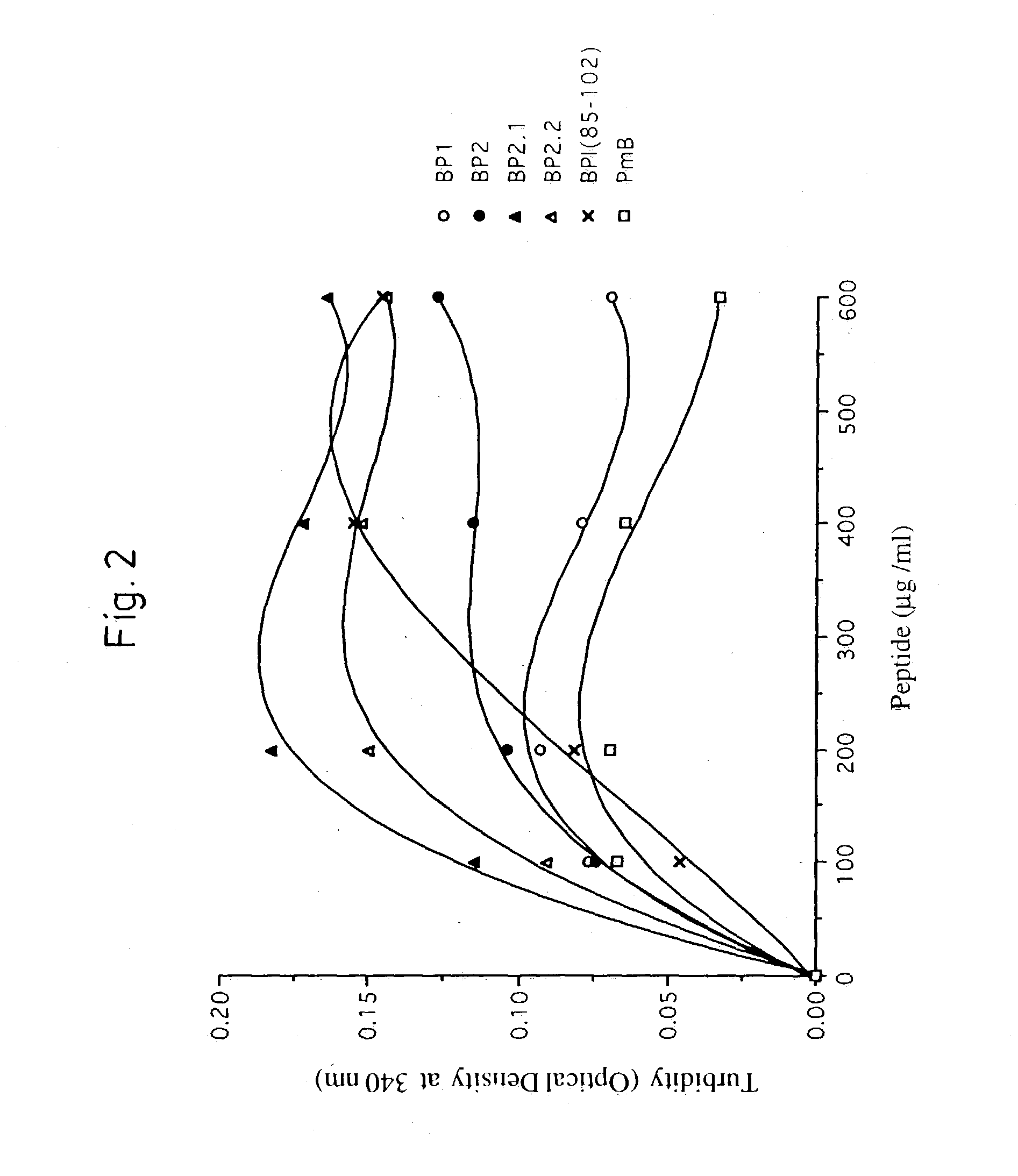
[0008] The applicants have derived a new generation of LPS-binding peptides termed bactericidal peptides (BP) by means of molecular modelling and rational design techniques. General properties included in the design of the peptides were restricted size, unique conformational and chemical characteristics, solubility and low cytoxicity. Specific characteristics included in the structure of the peptides were the presence of multiple sequence elements constituting potential LPS-binding domains presented in a specific conformation for optimal binding (high avidity) to the lipid A component of LPS. The peptides can be synthesized by solid-state chemistry with Fmoc (9-fluorenylmethoxy-carbonyl) amino acid derivatives, purified to homogeneity by reverse-phase high-pressure liquid chromatography and verified by analytical HPLC, amino acid analysis and mass-spectrometry in a manner known per se. Any known methodology of peptide synthesis can be applied and is readily available to a person ski...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentrations | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentrations | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentrations | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com