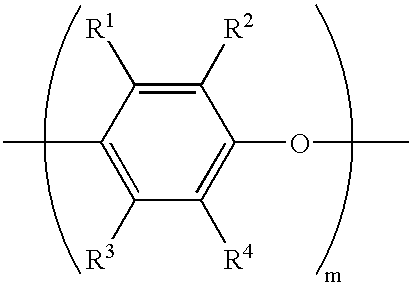
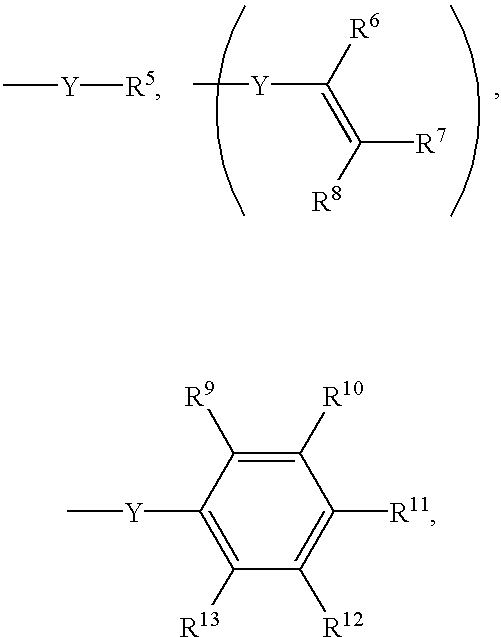
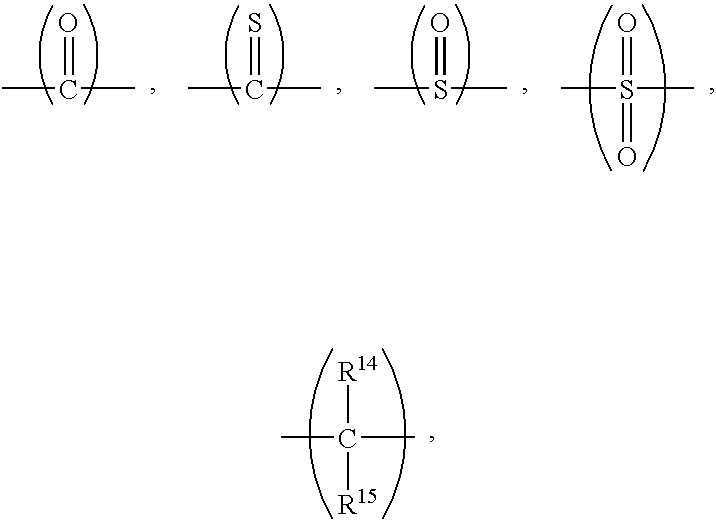Thermoset composition, method, and article
a technology of thermoset and composition, applied in the field of thermoset composition, method and article, can solve the problem that the low-profile additives known for polyester thermoset are ineffective in the poly(arylene ether)-containing composition, and achieve the effect of reducing its viscosity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples 25-30
[0150] Six samples were prepared varying in crosslinker amount, and polymeric additive and amount. The base resin for all samples was a 50 weight percent solution in styrene of a methacrylate-capped poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene ether) having an intrinsic viscosity of 0.12 dL / g.
[0151] The crosslinker was trimethylolpropane triacrylate (TMPTA) or trimethylolpropane trimethacrylate (TMPTMA). The initiator was t-butyl peroxy-2-ethylhexanoate, obtained as LUPEROX.RTM. 26 from Atofina Chemicals.
[0152] Three different polymeric additives were used. The additive designated "PEB Kraton L1203" in Table 3 was a monohydroxy-terminated poly(ethylene-butylene) having a hydroxyl equivalent molecular weight of 4,200 AMU, an approximate hydroxyl functionality of 0.9, and a specific gravity of 0.88 g / cc, obtained as KRATON.RTM. L1203 from Kraton Polymers. "PB Lithene N4-9000" was a liquid polybutadiene having a number average molecular weight of 9,000, 10-20% 1,2 vinyl microstructure, 50-60% trans...
example 37
, COMPARATFVE EXAMPLE 5
[0158] Two samples were prepared with and without 10 weight percent of a 50:50 weight / weight mixture of polybutadiene and poly(ethylene-butylene). Components were the same as those described above for Examples 38-43.
[0159] Molding was performed at 150.degree. C. and 1,200 psi. Shrinkage, orange peel, and waviness values represent averages for two samples.
[0160] Compositions and properties are presented in Table 5. The results show that the combination of polybutadiene and poly(ethylene-butylene) is particularly effective at reducing shrinkage (to the point of causing slight expansion in Ex. 44), orange peel, and waviness.
5 TABLE 5 C. Ex. 5 Ex. 37 50 / 50 0.12 IV PPO-MAA / styrene (pbw) 80 80 Trimethyloipropane trimethacrylate (pbw) 20 20 Polybutadiene (pbw) -- 5 Poly(ethylene-butylene) (pbw) -- 5 Shrinkage (%) 0.095 -0.016 Orange Peel 45 26 to 35 Waviness 1670 135 to 330
examples 38-55
[0161] Eighteen samples were prepared varying in the type and amount of crosslinker, the type and amount of polymeric additive, the type and amount of initiator, and the molding temperature.
[0162] The base resin for all examples was a methacrylate-capped poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene ether) having an intrinsic viscosity of 0.12 dL / g. It was used in the form of a 50 weight percent solution in styrene. The initiator t-butyl peroxy-2-ethylhexanoate was obtained as LUPEROX.RTM. 26 from Atofina Chemicals. The initiator t-butyl perbenzoate was obtained as LUPEROX.RTM. P from Atofina Chemicals. The crosslinker was either trimethylolpropane triacrylate (TMPTA) or trimethylolpropane trimethacrylate (TMPTMA).
[0163] Five different polymeric additives were employed. A dihydroxy-terminated poly(ethylene-butylene) having a weight average molecular weight of 1,700 AMU was obtained as KRATON.RTM. L2203 from Kraton Polymers. A monohydroxy-terminated poly(ethylene-butylene) having a weight average ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| weight percent | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| shrinkage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com