Diffuser for terrestrial or aviation gas turbine
a technology for diffusers and gas turbine engines, applied in the direction of gas turbine plants, hot gas positive displacement engine plants, machines/engines, etc., can solve the problems of affecting the efficiency of the diffuser, the risk of boundary layer thickening, and the loss of pressure in the exhaust casing, so as to reduce the drawbacks of pressure loss and mitigate the effect of such drawbacks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
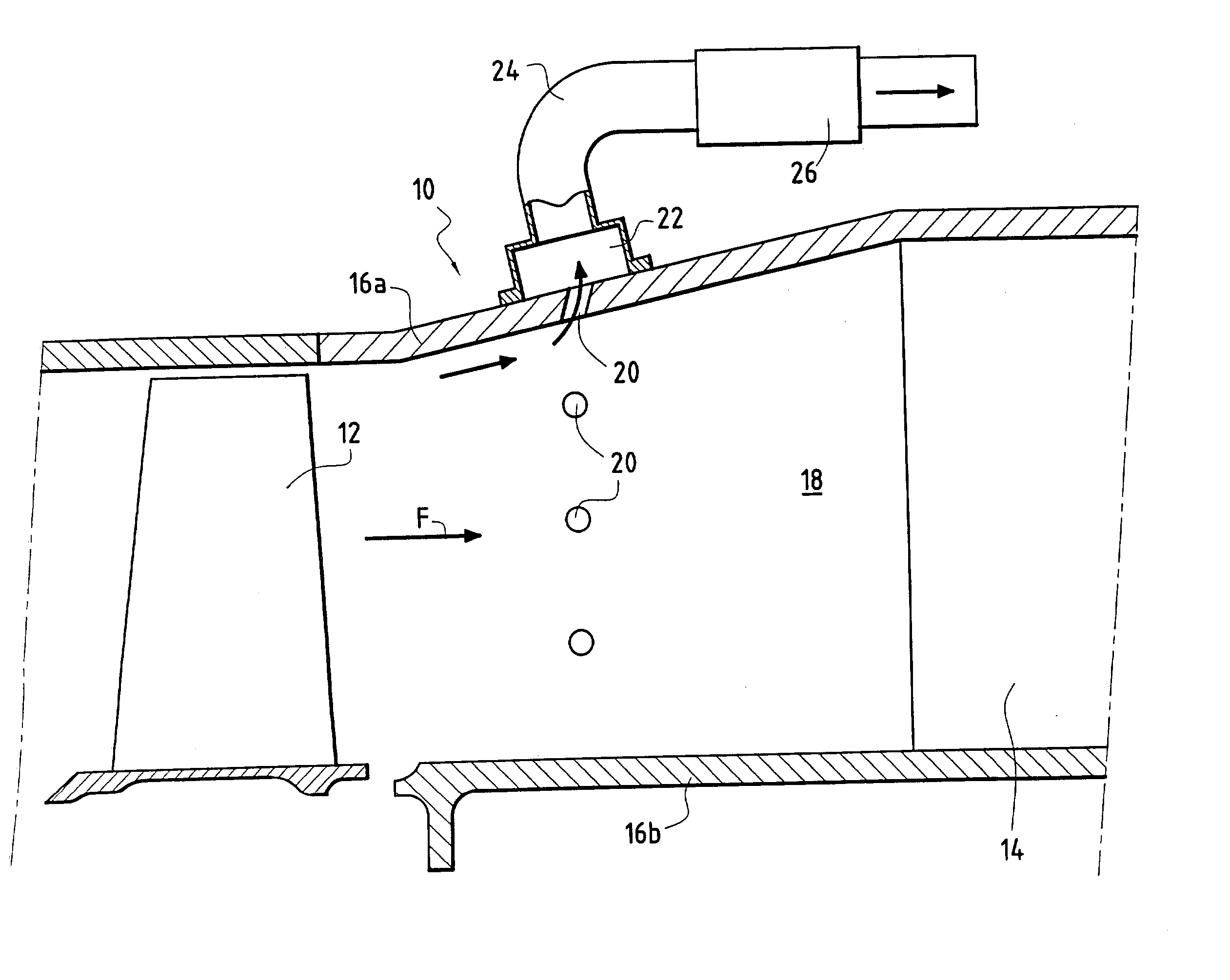
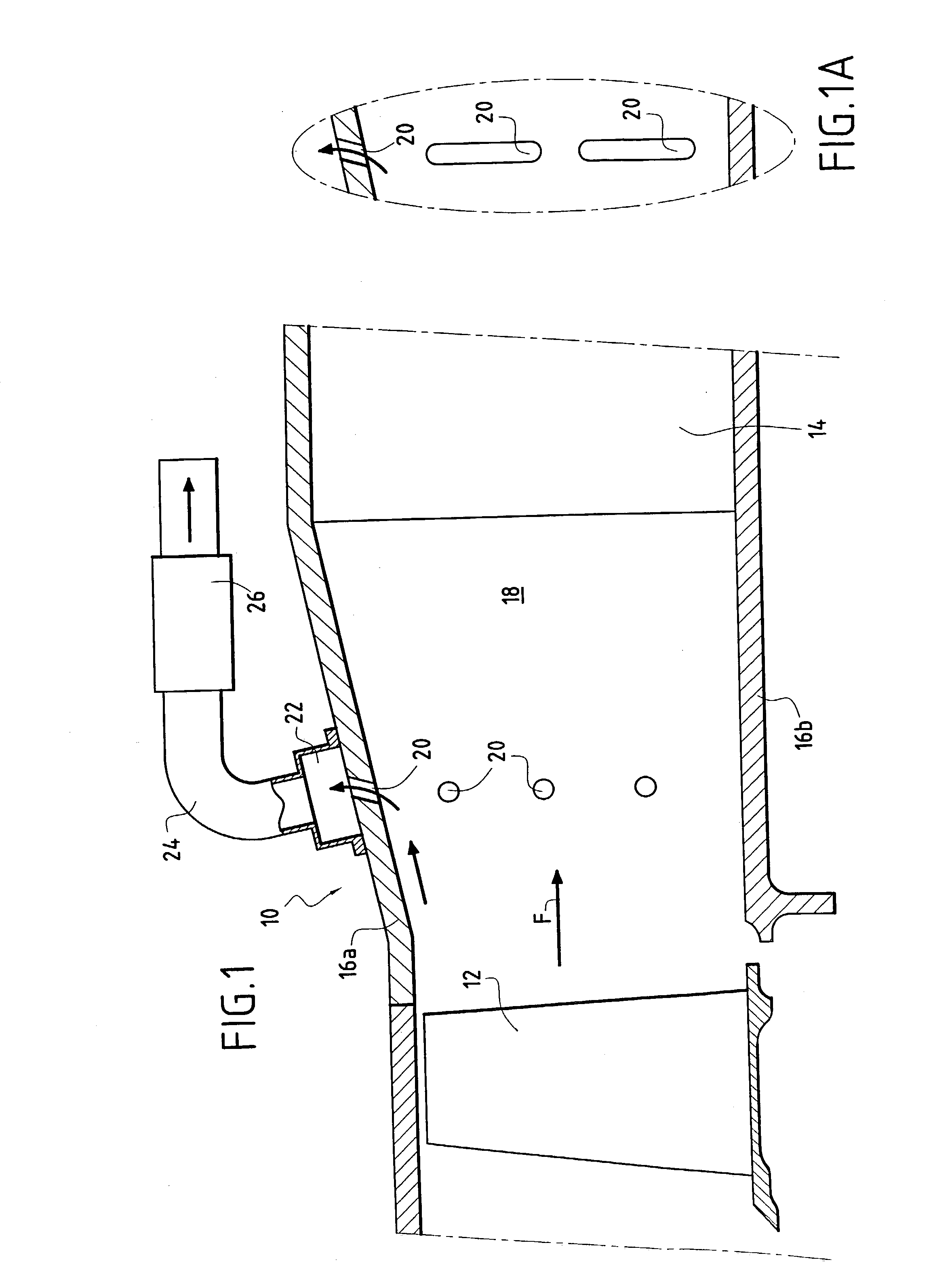
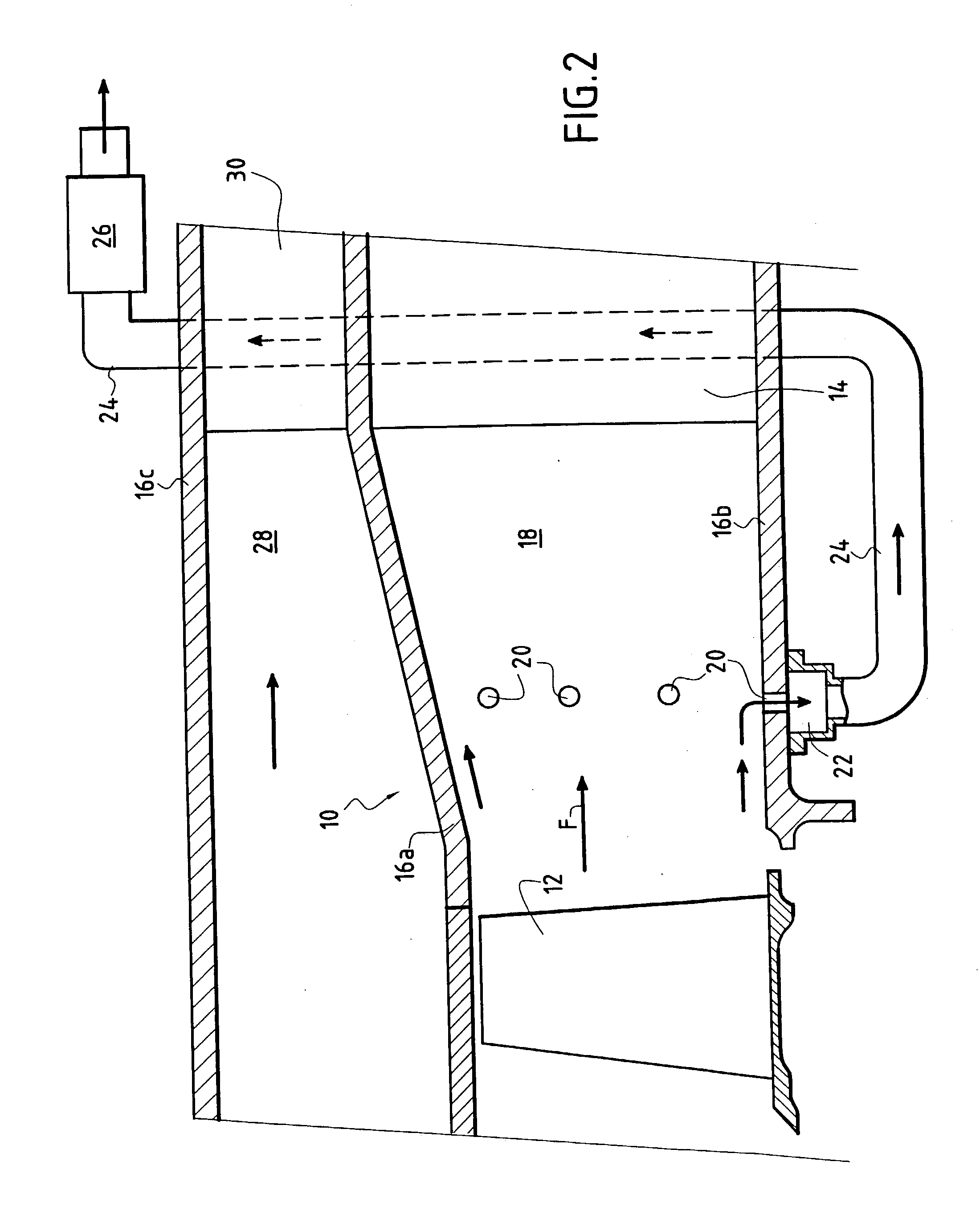
[0013] In FIG. 1, there can be seen a diffuser 10 disposed immediately downstream from a moving wheel 12 of a last stage of a gas turbine, where "downstream" is in the flow direction of a gaseous fluid coming from said turbine and marked by arrow F. A casing arm 14 serving in particular to straighten the gas flow is mounted downstream from the diffuser 10.
[0014] The diffuser 10 has an outer annular wall 16a and an inner annular wall 16b so as to form an annular passage 18 for the gas from the turbine. The walls 16a and 16b are arranged in such a manner that the annular passage 18 diverges in the gas flow direction F so as to reduce the flow speed and increase the pressure of the gas passing therethrough. The outer wall 16a diverges while the inner wall 16b is substantially parallel to the axis (not shown) of the engine fitted with this diffuser. It is also possible to devise a diffuser in which the inner wall 16b diverges (relative to the fluid) while the outer wall 16a is parallel ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com