Radio frequency-based repeater in a waveguide system
a frequency-based repeater and waveguide technology, applied in the field of electromagnetic communication, can solve the problems of increasing the number of system components, increasing failure probabilities, and the inability of troubleshooting systems to identify the contributing faulty components reliably
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0026]A detailed description of one or more embodiments of the disclosed apparatus and method are presented herein by way of exemplification and not limitation with reference to the Figures.
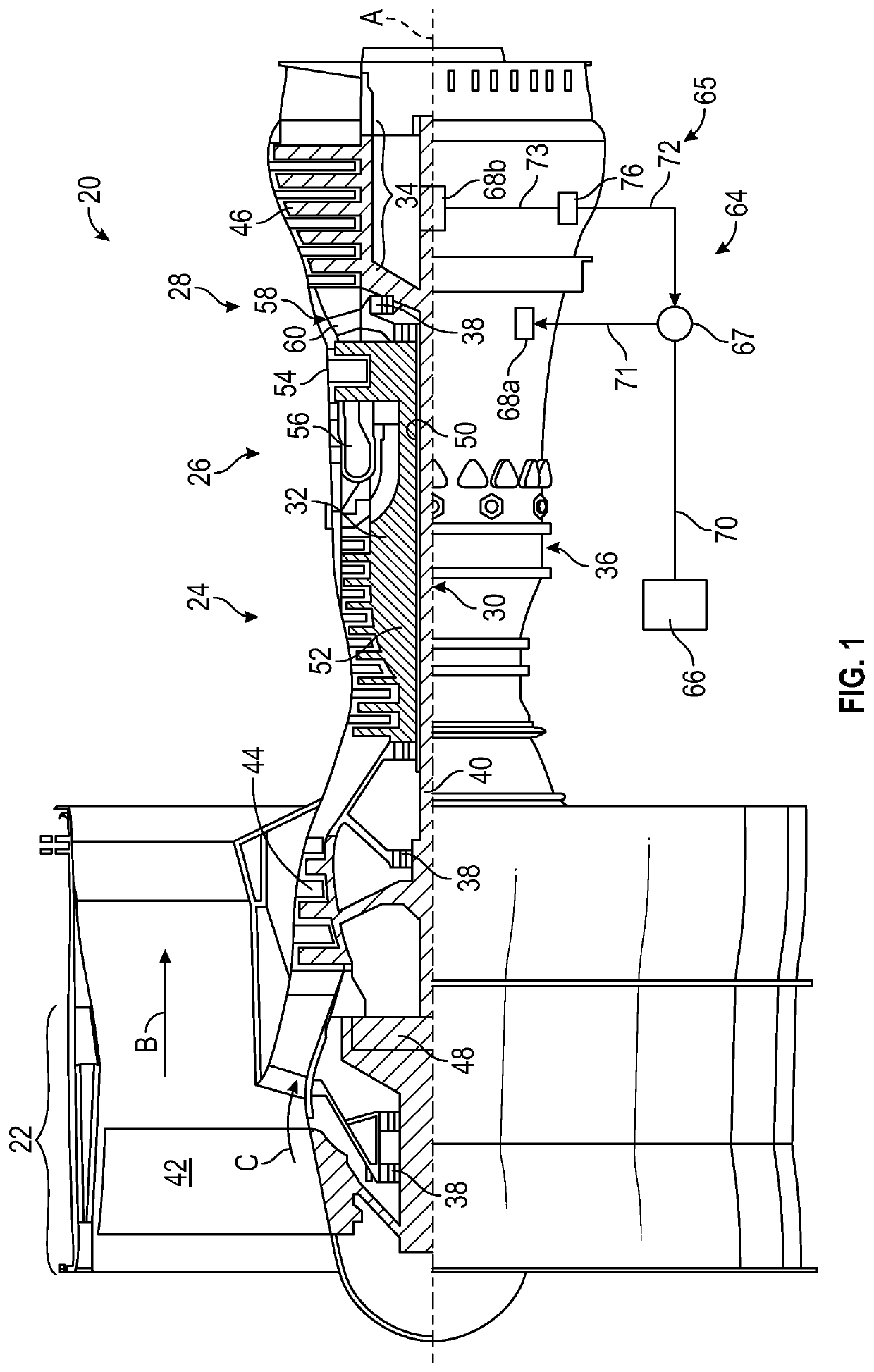
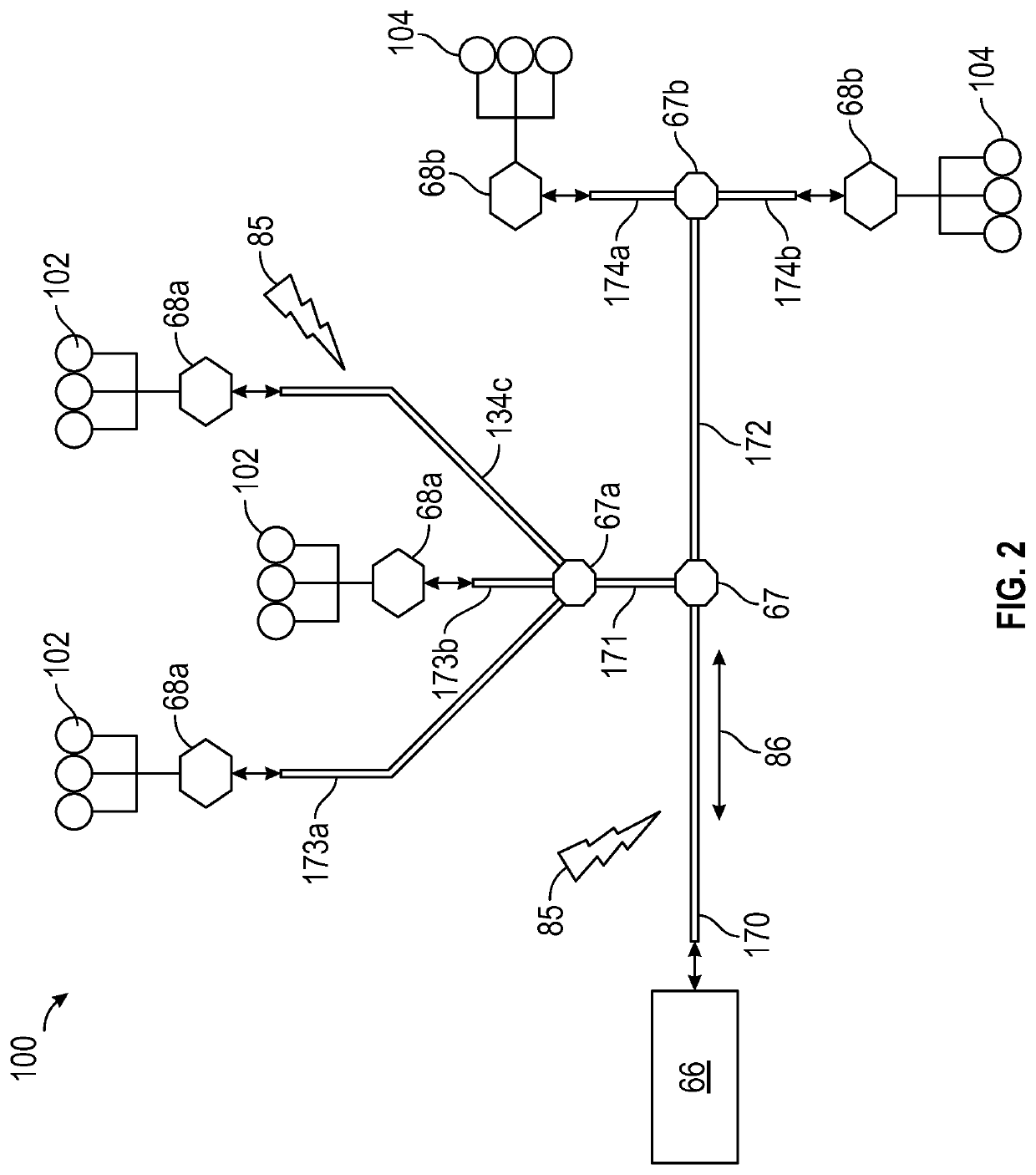
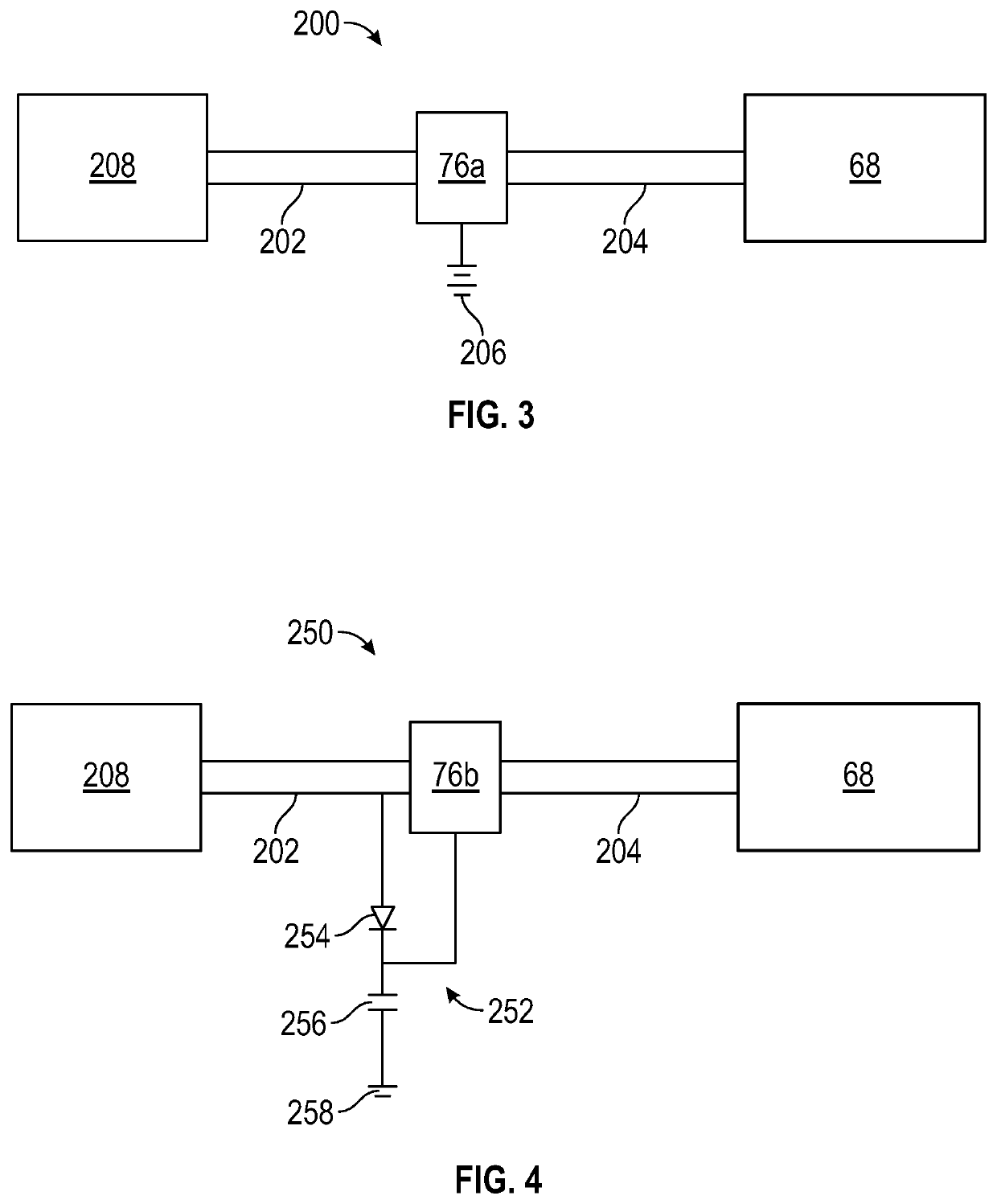
[0027]Various embodiments of the present disclosure are related to electromagnetic communication through and to components of a machine. FIG. 1 schematically illustrates a gas turbine engine 20 as one example of a machine as further described herein. The gas turbine engine 20 is depicted as a two-spool turbofan that generally incorporates a fan section 22, a compressor section 24, a combustor section 26 and a turbine section 28. Alternative engines may include an augmentor section (not shown) among other systems or features. The fan section 22 drives air along a bypass flow path B in a bypass duct to provide a majority of the thrust, while the compressor section 24 drives air along a core flow path C for compression and communication into the combustor section 26 then expansion through the turbin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com