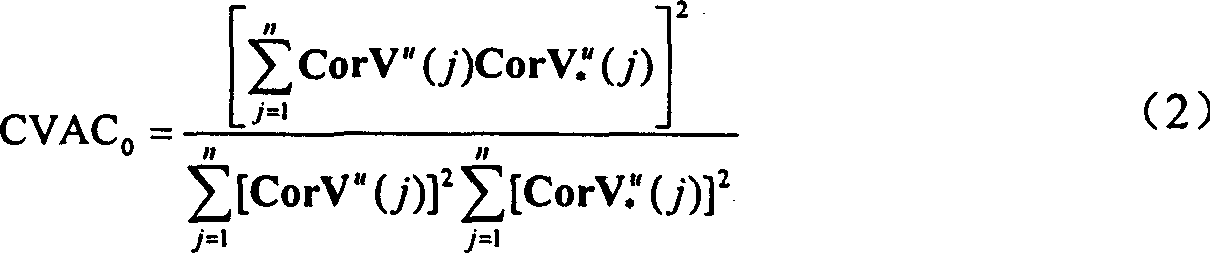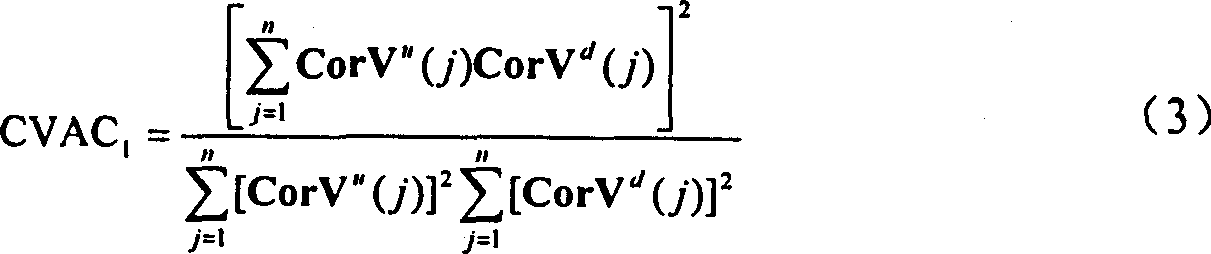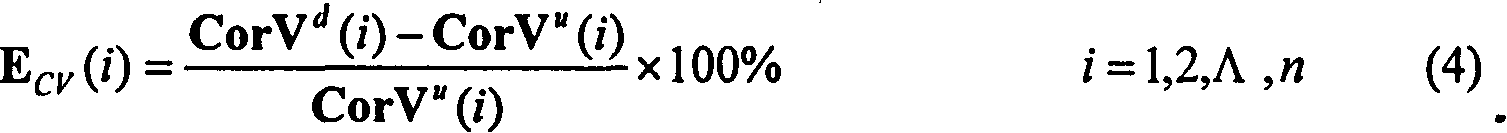Detection method for damage of random vibration structure based on correlation function amplitude vector
A cross-correlation function, random vibration technology, applied in electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, processing response signals of detection, etc., can solve problems such as damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Embodiment 1: Using the strain response to perform damage detection on a simply supported beam, the two ends of the beam are subjected to transverse random excitation.
[0030] a. Step 1: Establish and test the magnitude vector of the cross-correlation function of the intact beam
[0031] 8 measuring points are evenly arranged on the beam, each measuring point is equipped with a strain sensor, and these 8 strain sensors are numbered sequentially from one end of the beam: 1, 2, ..., 8. Denote the response signals of sensors 1 to 8 as X 1 (t), x 2 (t), Λ, x 8 (t). The signal of sensor 5 is stronger and the signal-to-noise ratio is higher, so point 5 is selected as the reference point. Calculate x separately 5 (t) and x 1 (t), x 2 (t), Λ, x 8 (t) cross-correlation function, and respectively recorded as: R 51 (τ), R 52 (τ), Λ, R 58 (τ), and their values at the point of maximum absolute value are r 51 , r 52 , Λ, r 58 , compose it into a vector, recorded as C...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Embodiment 2: Using the acceleration response to perform damage detection on a simply supported beam, the two ends of the beam are randomly excited in the transverse direction.
[0052] a. Step 1: Establish and test the magnitude vector of the cross-correlation function of the intact beam
[0053] 8 measuring points are evenly arranged on the beam, and an acceleration sensor is installed on each measuring point. The 8 acceleration sensors are numbered sequentially from one end of the beam: 1, 2, ..., 8. Denote the response signals of sensors 1 to 8 as x 1 (t), x 2 (t), Λ, x 8 (t). The signal acquisition time is 6 seconds. The signal of sensor 5 is stronger and the signal-to-noise ratio is higher, so point 5 is selected as the reference point. Calculate x separately 5 (t) and x 1 (t), x 2 (t), Λ, x 8 (t) cross-correlation function, and denoted as R 51 (τ), R 52 (τ), Λ, R 58 (τ), and their values at the point of maximum absolute value are r 51 , r 52 , Λ, ...
Embodiment 3
[0076] Embodiment 3: Damage detection is performed on a four-story building, and the top of the building is randomly excited in the horizontal direction.
[0077] a. The first step: establish and test the magnitude vector of the cross-correlation function of the intact building
[0078] An acceleration sensor is installed on the top of each floor of the building, and the four acceleration sensors are numbered sequentially from the first floor: 1, 2, 3, 4. Denote the response signals of sensors 1 to 4 as x 1 (t), x 2 (t), x 3 (t), x 4 (t). Choose 3 points as reference points and calculate x respectively 3 (t) and x 1 (t), x 2 (t), x 3 (t), x 4 (t) cross-correlation function, denoted as R31 (τ), R 32 (τ), R 33 (τ), R 34 (τ), and their values at the point of maximum absolute value are r 31 , r 32 , r 33 , r 34 , compose it into a vector, recorded as CorV={r 31 r 32 r 33 r 34}. The CorV is tested twice, the signal acquisition time is 15 seconds, and the t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com