Optical sensor
A technology of light sensor and photoelectric device, applied in the field of light sensor
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
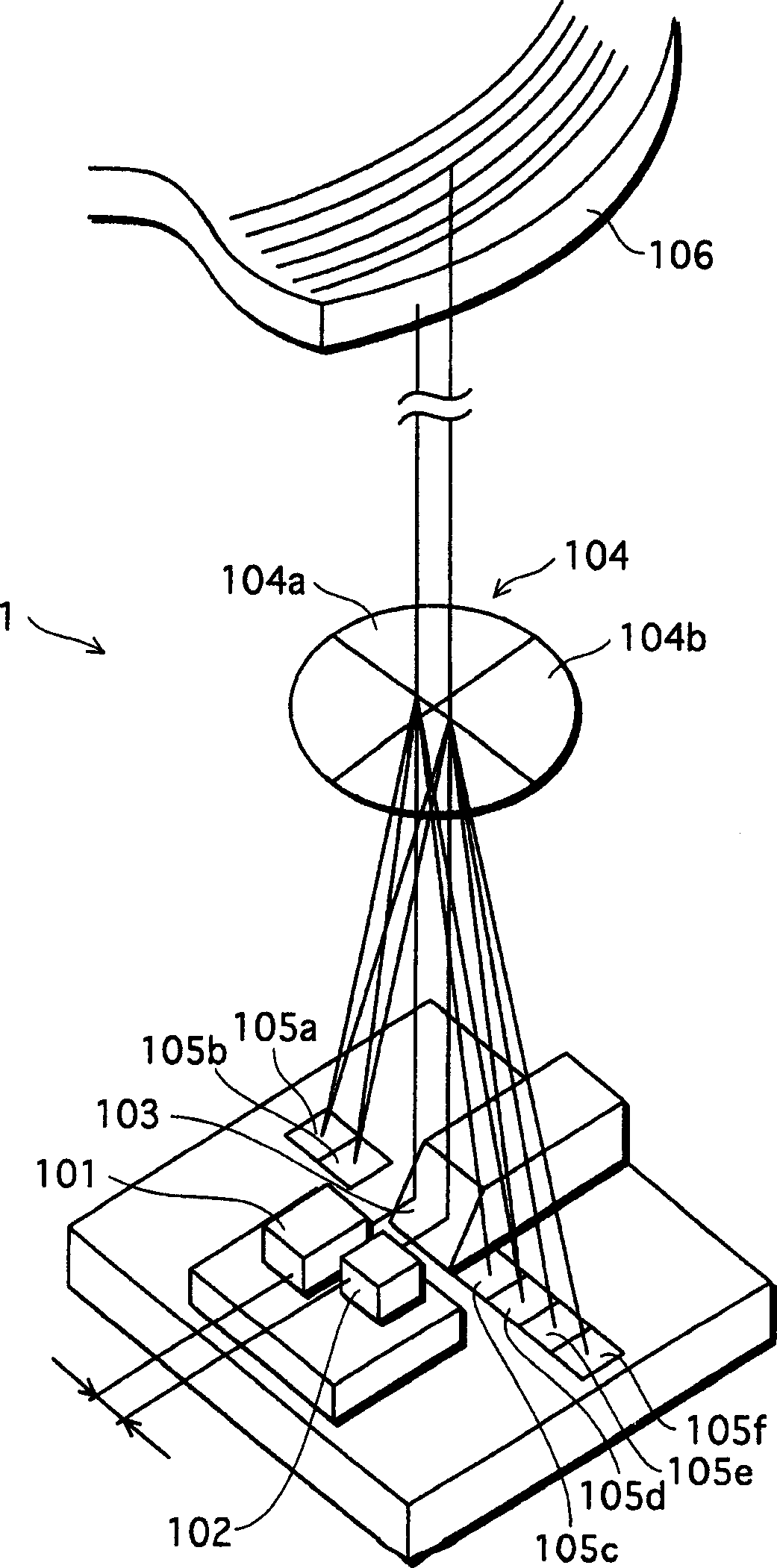
[0047] The photosensor according to the first embodiment has two light-emitting elements, and can obtain a focus error signal and a tracking error signal with high stability by using a holographic optical element having four regions whose characteristics are different from each other.
[0048] (1) The structure of the light sensor
[0049] First, the structure of the photosensor according to the first embodiment will be described.
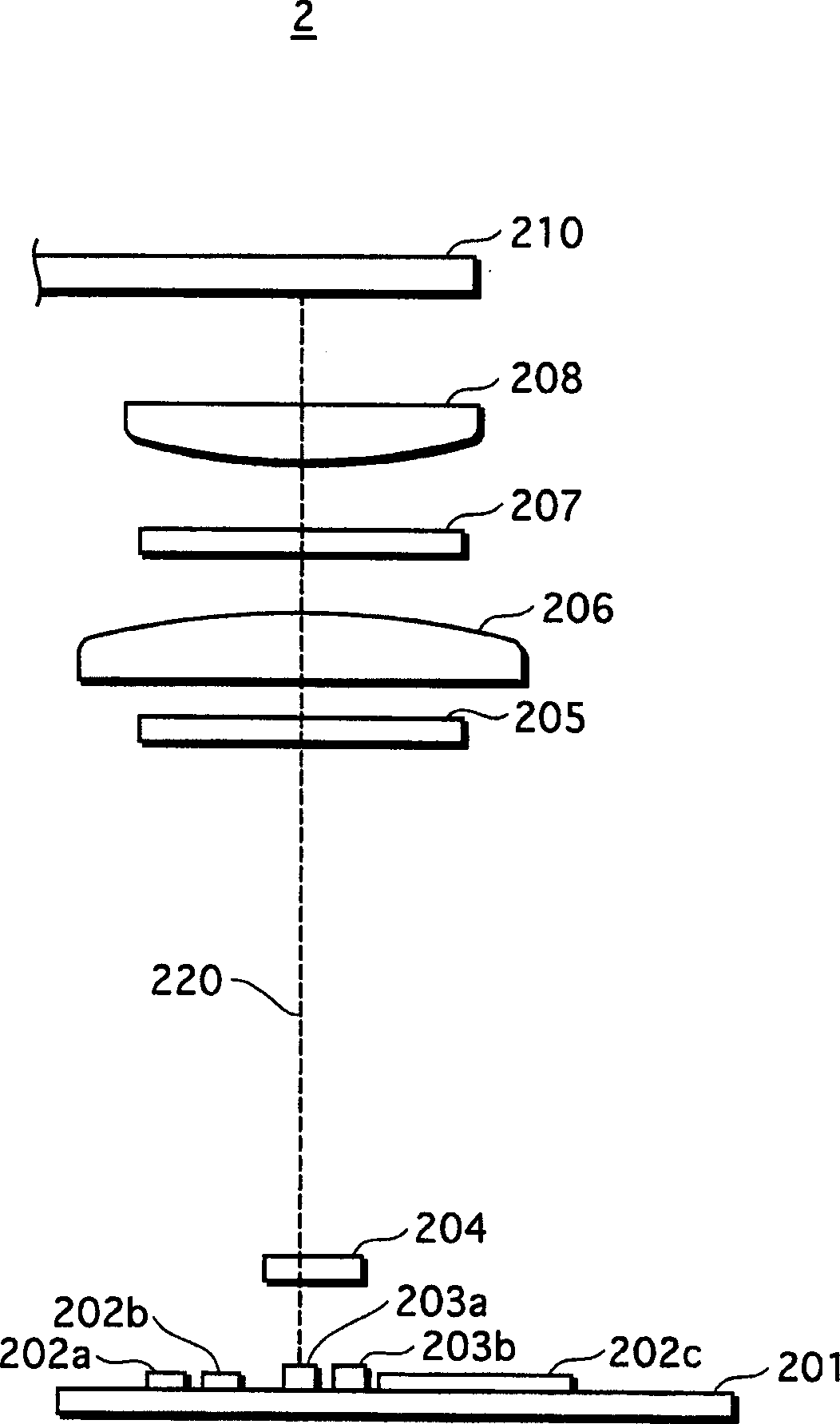
[0050] figure 2 is a sectional view schematically showing the structure of the photosensor according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
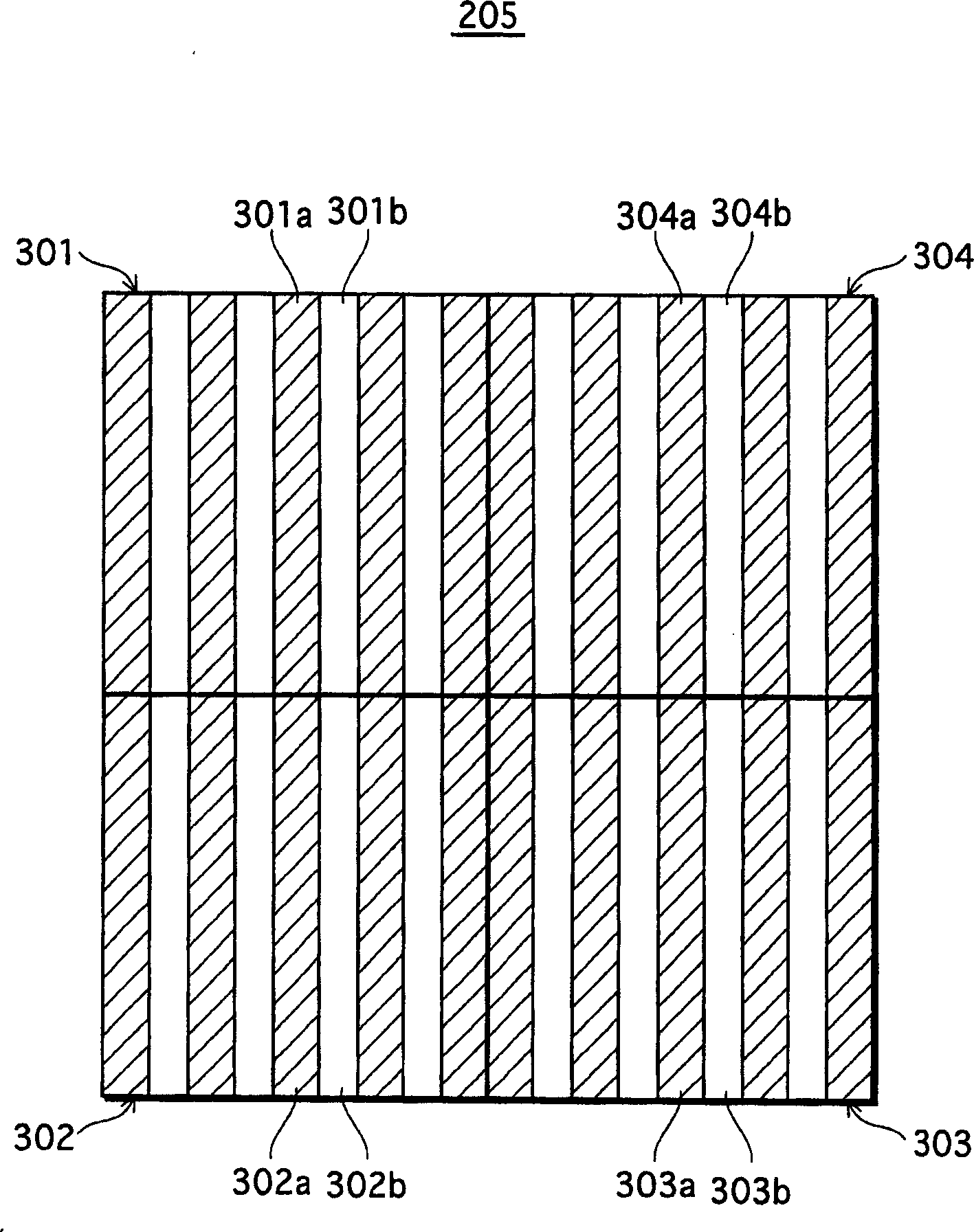
[0051] Such as figure 2 As shown, the optical sensor 2 includes an IC substrate 201, photoelectric device groups 202a to 202c, laser diodes 203a and 203b, a diffraction grating 204, a holographic optical element 205, a collimating lens 206, a quarter retardation plate 207 and an objective lens 208. The optical sensor records information on the optical recording medium 210 or reproduces informa...
no. 3 example
[0123] Next, a third embodiment of the present invention will be described. The photosensor according to the third embodiment has almost the same structure as that of the photosensor according to the first embodiment, but the structure of the diffraction grating is different. The main differences are described below.
[0124] First, the structure of the photosensor is described. Figure 9 is a sectional view schematically showing the structure of an optical sensor according to a third embodiment of the present invention. Such as Figure 9 As shown, just like the above-mentioned photosensor 2 according to the first embodiment, the photosensor 9 includes an IC substrate 901, photoelectric device groups 902a to 902c, laser diodes 903a and 903b, a holographic optical element 905, a collimator lens 906, 1 / 4 retardation plate 907 and objective lens 908, and additionally includes a diffraction grating plate 904 and a package 909.
[0125] The package 909 has a cylindrical shape ...
no. 4 example
[0131] Next, a fourth embodiment of the present invention will be described. The photosensor according to the fourth embodiment has almost the same structure as that of the photosensor according to the first embodiment, but the structure of the light-emitting element is different. The main differences are described below.
[0132] Figure 10 is a sectional view schematically showing the structure of a photosensor according to a fourth embodiment of the present invention. Such as Figure 10 As shown, the optical sensor 10 includes an IC substrate 1001, photoelectric device groups 1002a to 1002c, a laser diode 1003, a diffraction grating 1004, a holographic optical element 1005, a collimating lens 1006, a quarter retardation plate 1007 and an objective lens 1008.
[0133] The laser diode 1003 according to the fourth embodiment of the present invention is a monolithic dual-wavelength laser diode in which two laser diodes are integrated.
[0134] The positional relationship be...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com