Semiconductor manufacturing apparatus and chemical exchanging method
A technology for chemical reagents and manufacturing devices, applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, chemical instruments and methods, cleaning methods using liquids, etc., can solve problems such as mixing new chemical reagents and waste chemical reagents
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
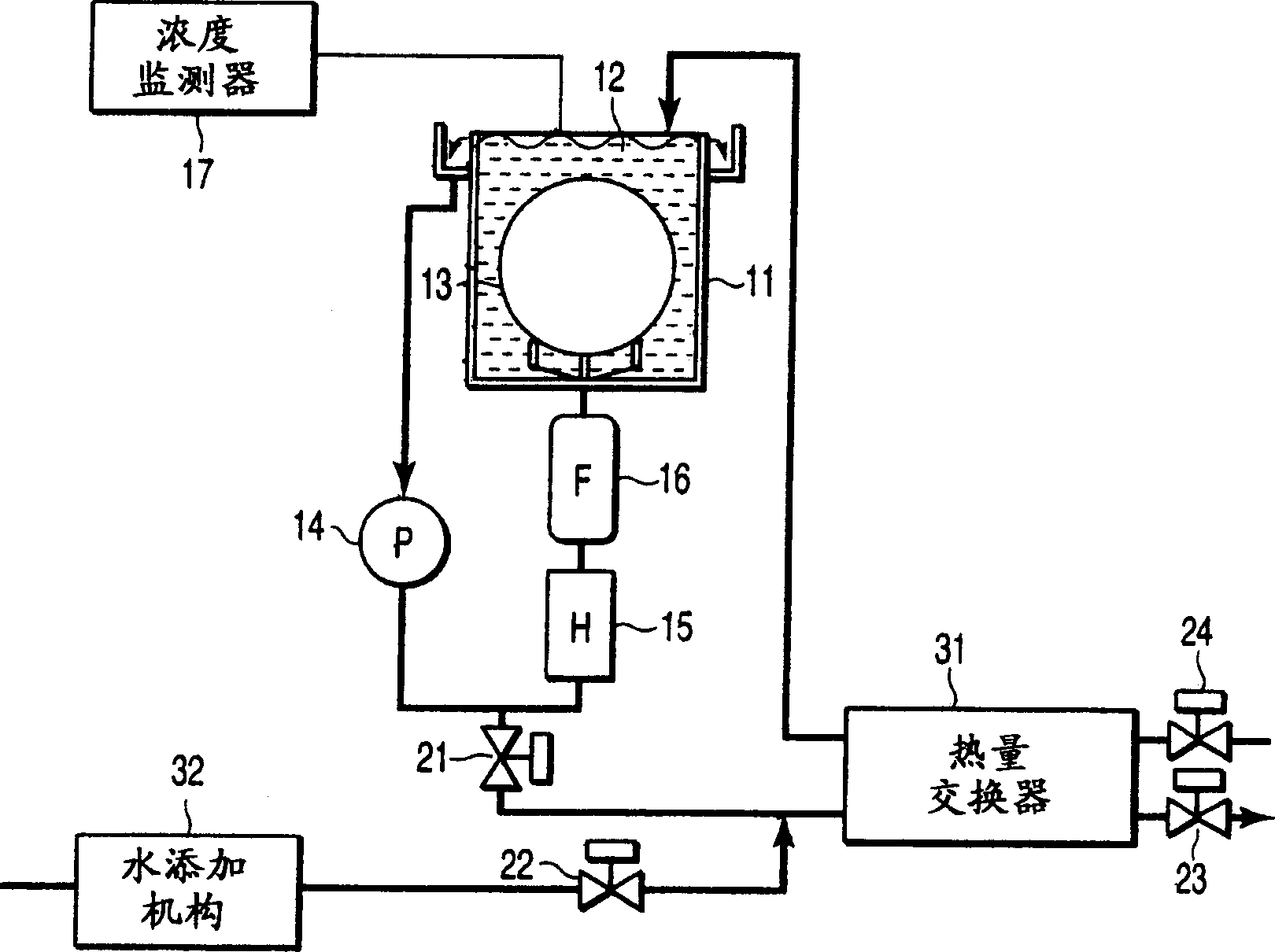
[0019] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram showing a semiconductor manufacturing apparatus according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
[0020] Reference numeral 11 denotes a processing tank (a high-temperature circulation type chemical reagent tank) for cleaning semiconductor substrates such as Si wafers. The treatment tank 11 is filled with, for example, a high-temperature chemical reagent 12 based on sulfuric acid. The semiconductor substrate 13 is immersed in the chemical reagent 12 in the processing tank 11 and then cleaned.
[0021] The chemical reagent 12 in the treatment tank 11 is circulated by the pump (P) 14. That is, the chemical reagent is supplied from the bottom of the processing tank 11 by the pump 14, and the chemical reagent overflowing from the top of the processing tank 11 is supplied again from the bottom of the processing tank 11 through the chemical reagent circuit. A heater (H) 15 that controls the temperature of the chemical reagent and a ...
no. 2 example
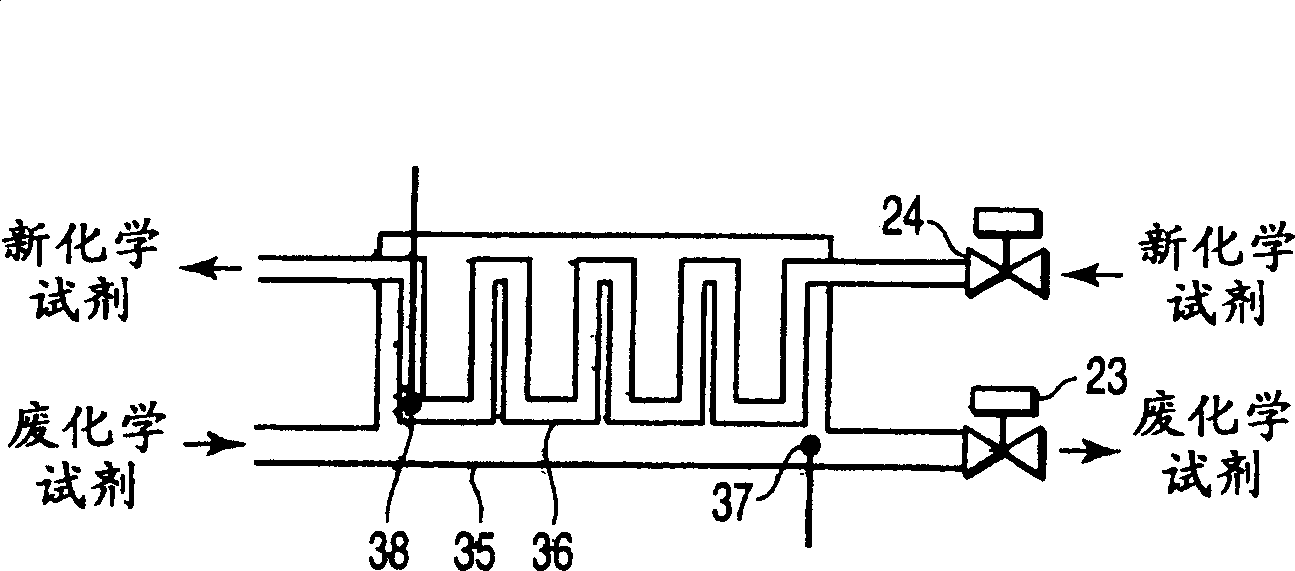
[0043] Figure 4 It is a schematic diagram showing a semiconductor manufacturing apparatus according to a second embodiment of the present invention. The same or similar components as those disclosed in the first embodiment are denoted by similar reference numerals and will not be described in detail here.
[0044] The difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment is that the water addition mechanism 32 sets the water addition amount according to the measurement result of the concentration monitor 17. In addition, a valve 25 is provided between the waste chemical reagent valve 21 and the heat exchanger 31. The valve 25 does not allow the waste chemical reagent part to pass through the heat exchanger 31, but allows the waste chemical reagent to be directly discharged. A valve 26 is provided at the new chemical reagent side conduit of the heat exchanger 31, and the valve 26 does not allow the new chemical reagent part to pass through the heat exchanger 31, but allows ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com