Method of processing an input image by means of multi-resolution
A technology for inputting images and images, which is applied in the field of multi-resolution decomposition and gradient adaptive filtering, and can solve problems such as large amount of computation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
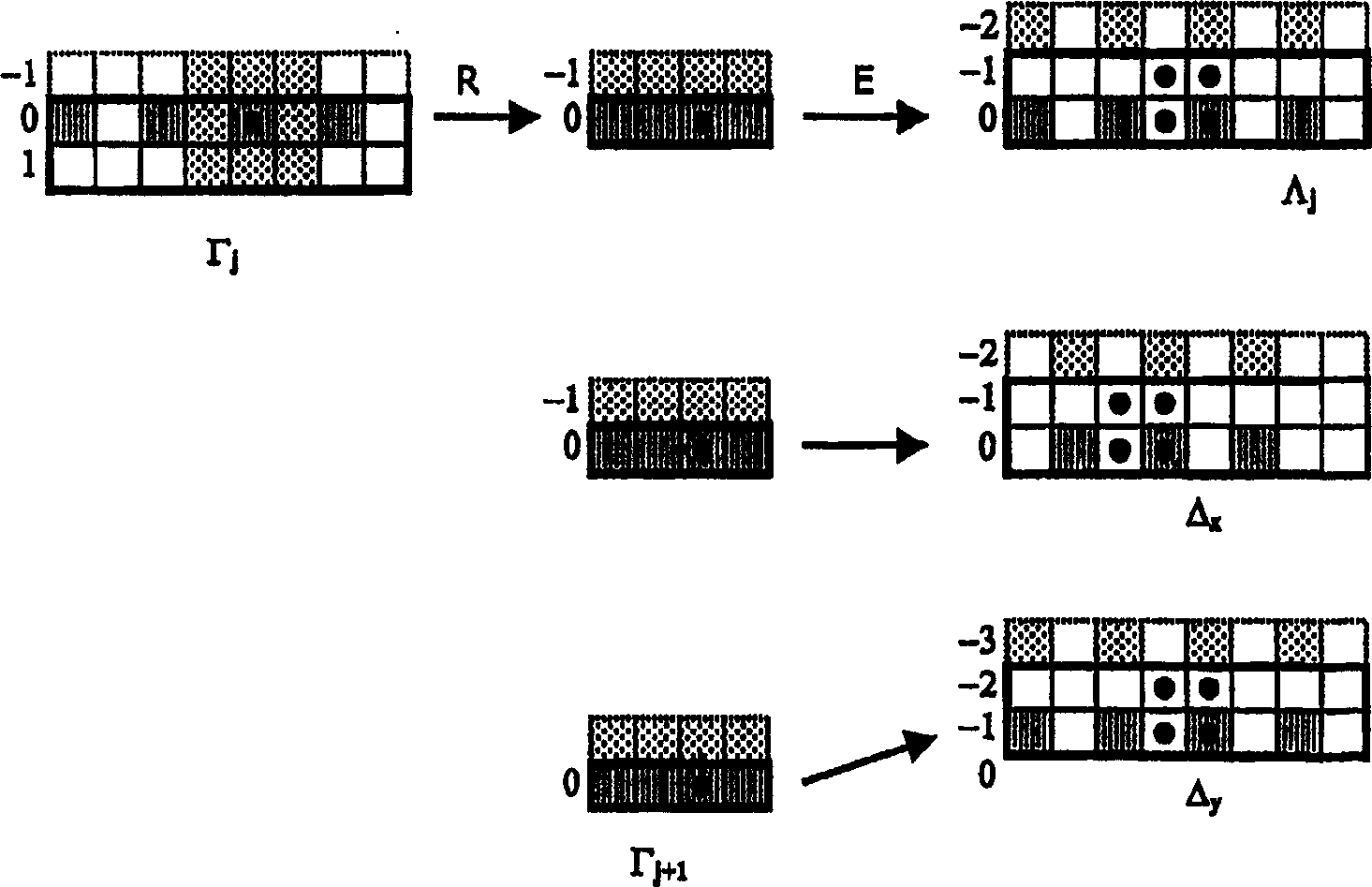
[0046] described in detail in EP 996090A2 and WO 98 / 55916A1 figure 1 The MRGAF algorithm schematically given in , so the following will only be introduced in an overview way. The goal of the MRGAF algorithm is to significantly reduce the noise in the input image I while maintaining image detail and image sharpness. The basic idea of the algorithm lies in multiresolution decomposition and anisotropic low-pass filtering of the resulting detail image as a function of local image gradients.
[0047] exist figure 1 In the example shown, the decomposition of the input image I (comprising 512×512 image points (pixels)) occurs in the form of K=4 decomposition levels. In each term called the Laplacian pyramid expression Λ j On the decomposition level j=0, 1, 2, 3, the Gaussian pyramid expression Γ is generated j as a detail image. In all cases, the level input expression is the Gaussian pyramid expression Г of the previous level (j-1) j-1 Or the original input expression I. Ga...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com