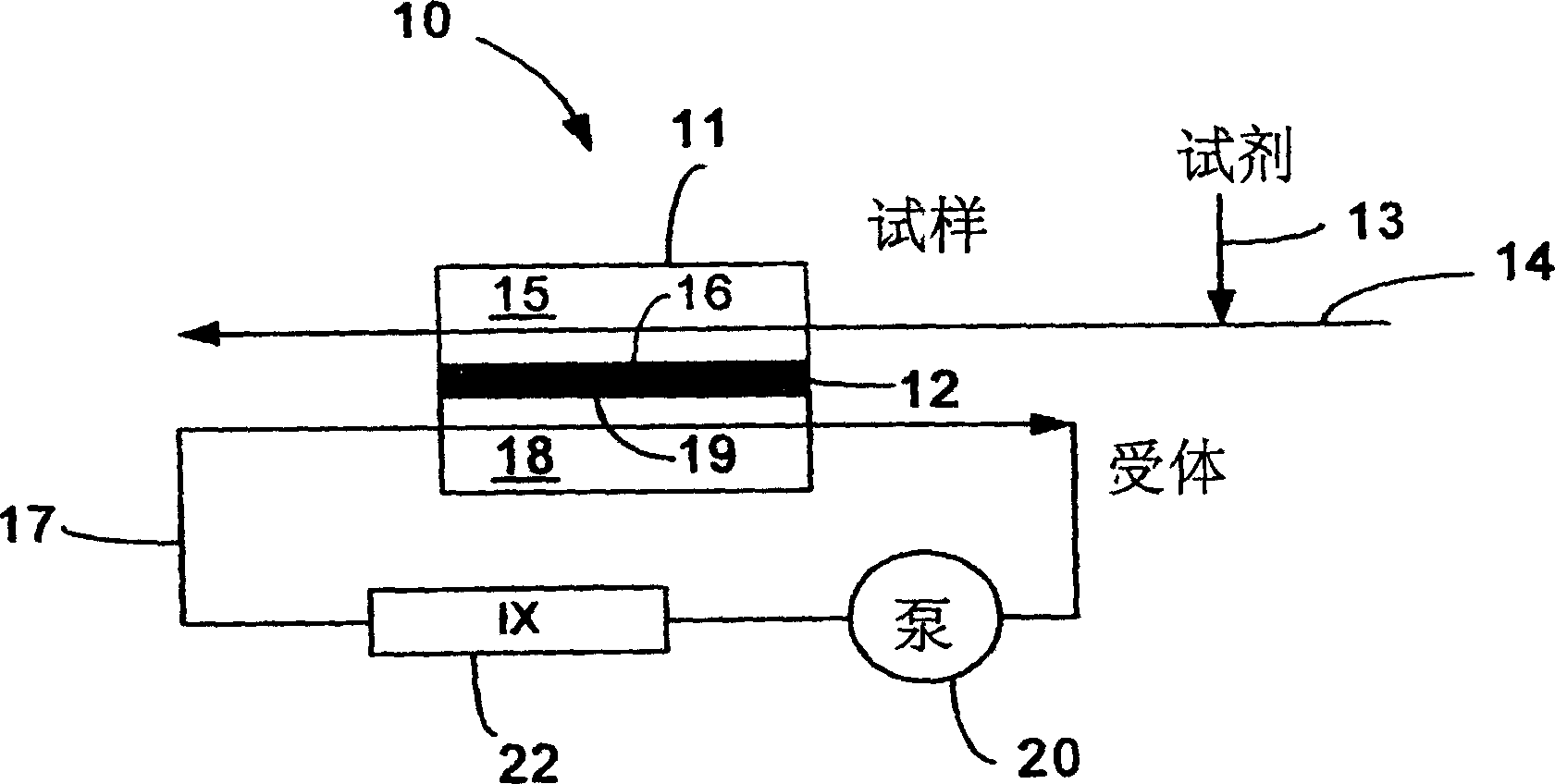
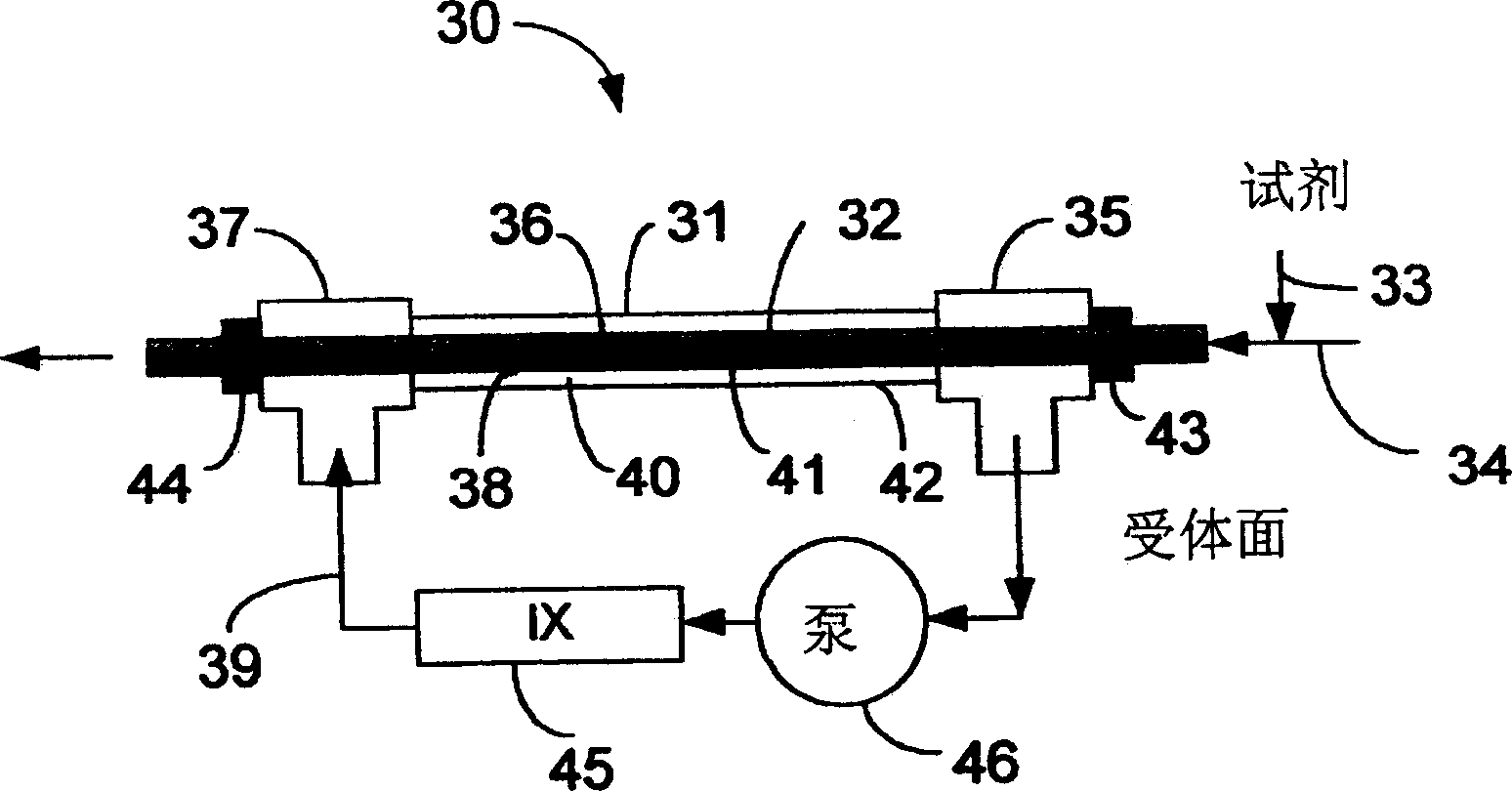
Inorganic carbon removal
A technology of inorganic carbon and total organic carbon, which can be used in organic anion exchangers, preparation of samples for testing, testing of organic pollutants in water, etc., which can solve the problems of complicated devices, wetting and expensive
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0068] The following experiments were performed to demonstrate the practice and effectiveness of the present invention in removing volatile electrolytes (such as carbon dioxide) from aqueous samples at various temperatures.
[0069] This example uses something like figure 2 The tubular design of the gas transfer assembly. Carbon dioxide at a concentration of 28 ppm C in water passes through the inside of the tubular Teflon AF membrane. The acceptor stream in the form of deionized water was heated to change the temperature.
[0070] The results are presented in Figure 4, which shows the IC removal efficiency as a function of the residence time of the sample in the IC transfer unit at three temperatures of 30°C, 50°C and 70°C. Figure 4 shows that at each temperature, nearly 100% removal of IC from the sample stream was achieved within three minutes (less than 180 seconds).
Embodiment 2
[0072] Use something like figure 1 Another set of experiments was performed for the IC transfer assembly of flat or planar PFA membranes of the membrane configuration shown. For this set of experiments, the residence time of the sample in the IC transfer assembly was varied by varying the sample flow rate. The results are presented in Figure 5, which shows the IC removal efficiency as a function of the residence time of the sample in the IC transfer unit for three concentrations of C and IC in the sample: 5 ppm C, 25 ppm C, and 50 ppm C . Figure 5 shows that for any given residence time, the removal efficiency does not vary appreciably with IC concentration over a large range.
Embodiment 3
[0074] Generally, solutions containing volatile organic compounds will lose very small amounts of such organic compounds as they flow through the IC assembly of the present invention. However, the amount thus lost can be minimized by the choice of membrane material and by minimizing the sample residence time.
[0075] In this example, two different films were tested for IC removal according to the invention. Concentrations of various volatile organic compounds in the aqueous sample stream were measured before and after passage of the sample through two IC transfer units (one with a Teflon AF membrane and the other with a Gortex membrane) according to the invention. In addition, the IC (CO 2 form) concentration. A relatively short dwell time in the IC transfer member of 15 seconds was used for these tests.
[0076]The results of this example are shown in FIG. 6 . Figure 6 shows that the Gortex membrane achieves approximately 62% IC removal, while the Teflon AF achieves appr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com