Frequency domain equalization in communications systems with scrambling
A technology of frequency domain equalization and equalization, applied in multi-frequency code system, transmission control/equalization, secure communication, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
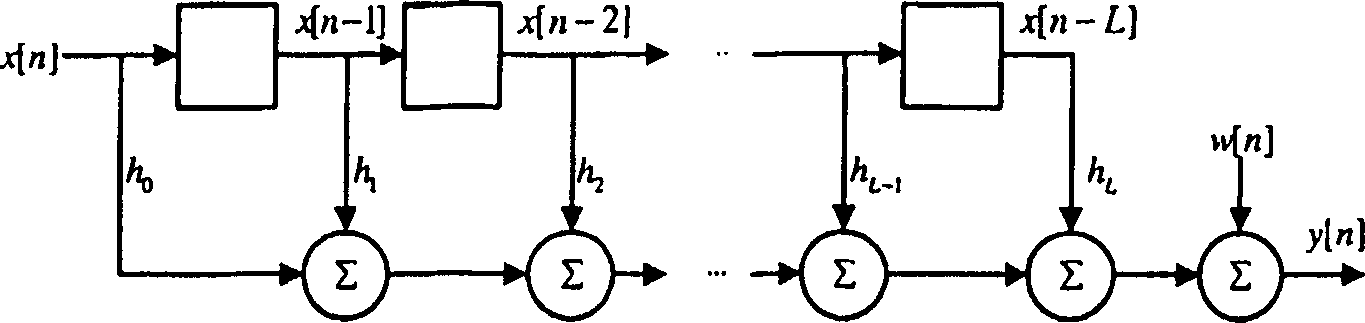
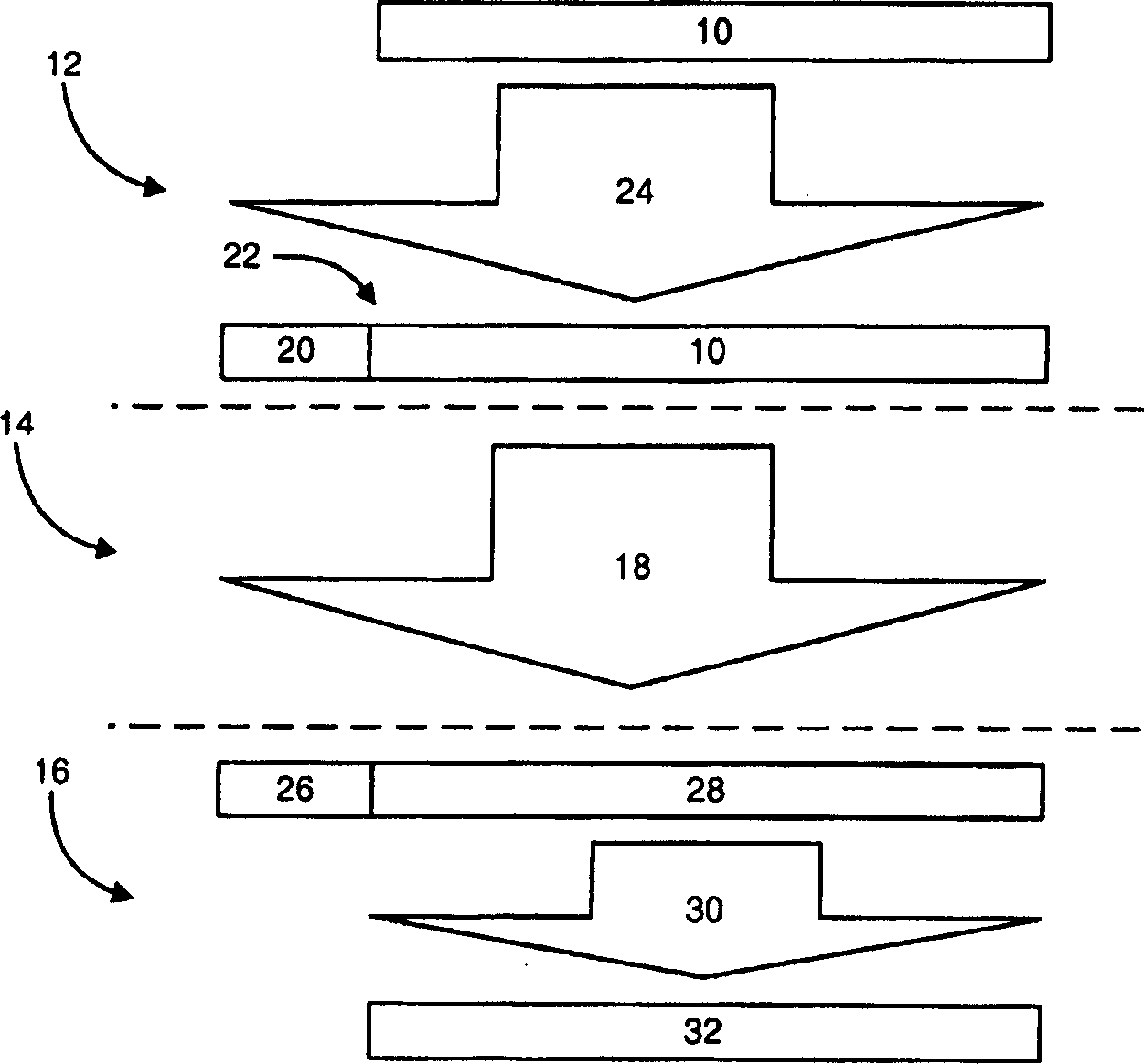
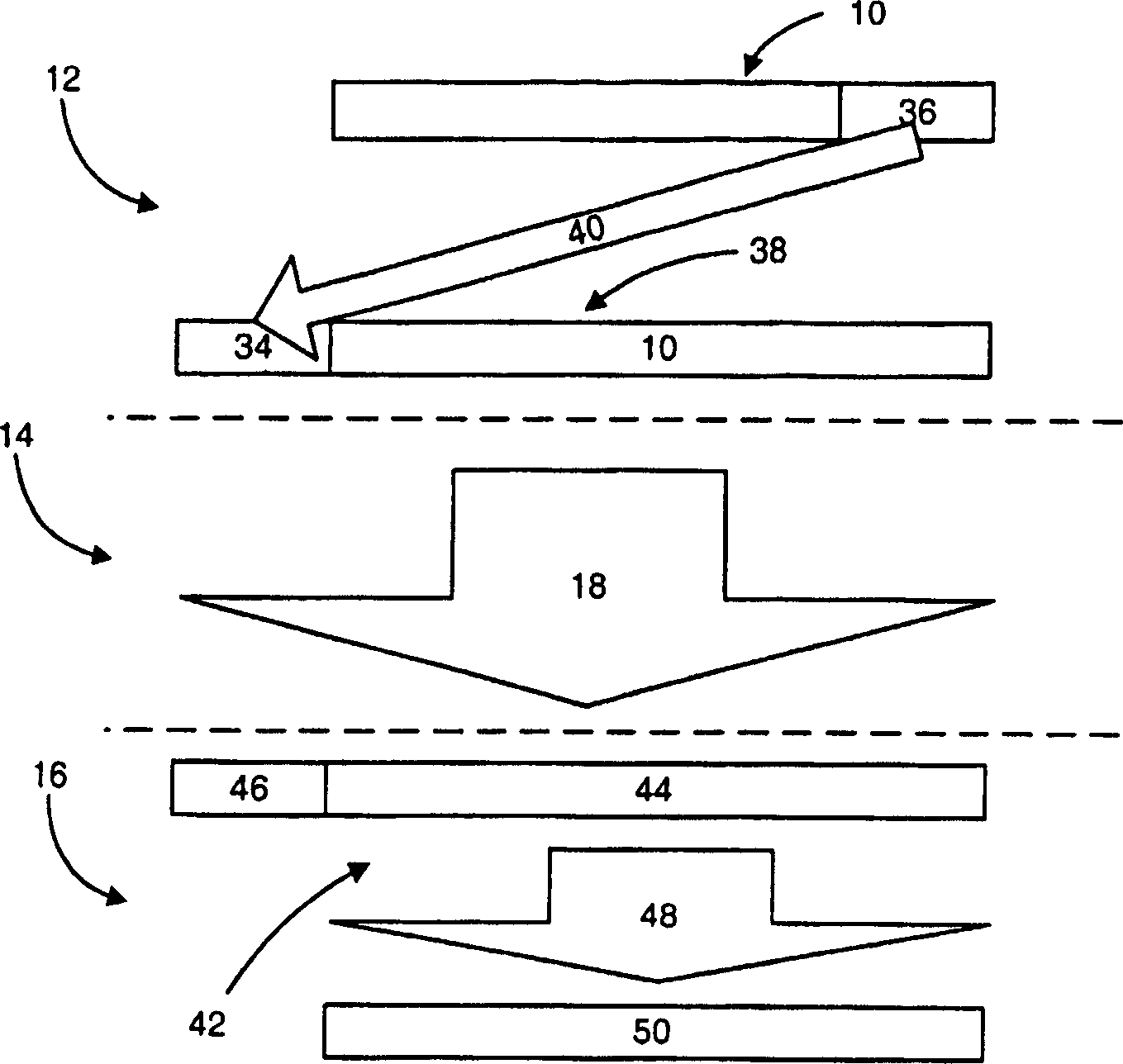
[0056] As mentioned above, so far, frequency domain equalization in DS-CDMA system is still not feasible. According to an embodiment of the present invention, in order to apply frequency domain equalization to the DS-CDMA system, the transmitted data block is spread by adding a prefix and suffix known to the receiver before being scrambled, or the transmitted data block is Spreading is done after scrambling but before transmission so it has a scrambled cyclic prefix. In the former case, the receiver synthesizes the prefixes, data blocks or suffixes that would have been received if the scrambled spread transmitted data blocks had a cyclic prefix. In each variant embodiment of the invention, the above-described diagonalization process is performed on the receiving block or the compositing block. To simplify the discussion below, it is assumed that the receiver "knows" (has previously determined) the channel response.
[0057] In the discussion below and the attached Figure 4 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com