Assembled ceramic electric thermo-couple
An assembled, thermocouple technology, used in measuring devices, measuring heat, thermometers with electrical/magnetic components directly sensitive to heat, etc., can solve the problem that ceramic thermocouples cannot work in high temperature environments for a long time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
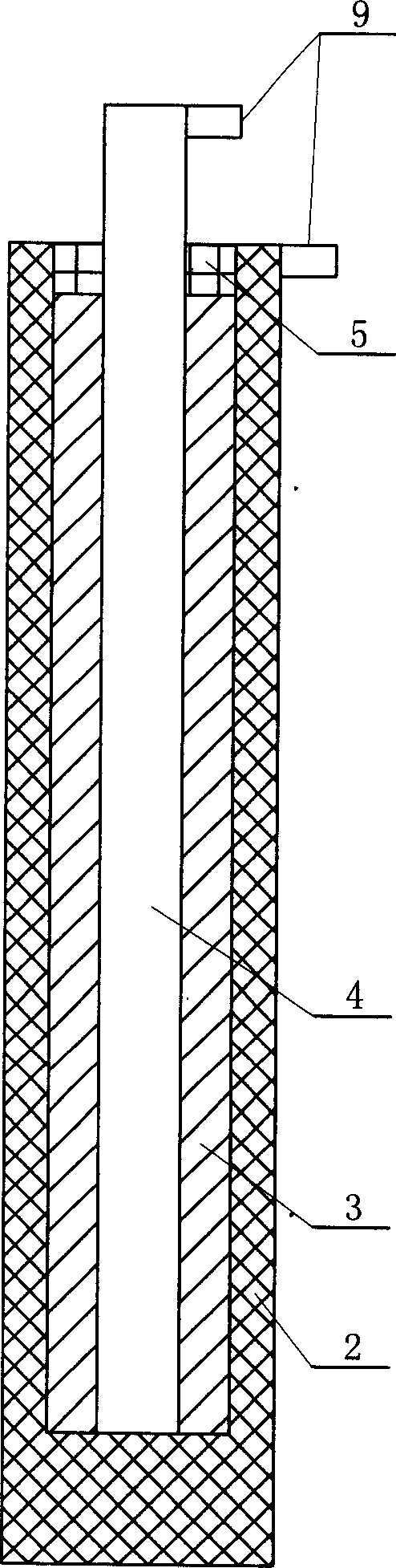
[0006] Specific implementation mode one: the following combination figure 1 To illustrate in detail, this embodiment includes a tubular electrode 2, a high-temperature insulating layer 3 and a rod-shaped electrode 4, wherein the rod-shaped electrode 4 is made of MoSi 2 The tubular electrode 2 is made of SiC, the lower end of the tubular electrode 2 is closed, the lower end of the rod electrode 4 is inserted into the interior of the tubular electrode 2, and the lower end surface of the rod electrode 4 is connected to the inner bottom surface of the tubular electrode 2, A high-temperature insulating layer 3 is provided between the side of the rod-shaped electrode 4 and the inner wall of the tubular electrode 2, and a high-temperature elastic silicon sealant 5 is poured into the sealing part of the upper end of the tubular electrode 2. The upper end of the tubular electrode 2 and the top of the rod-shaped electrode 4 are respectively provided There are signal output terminals 9, ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
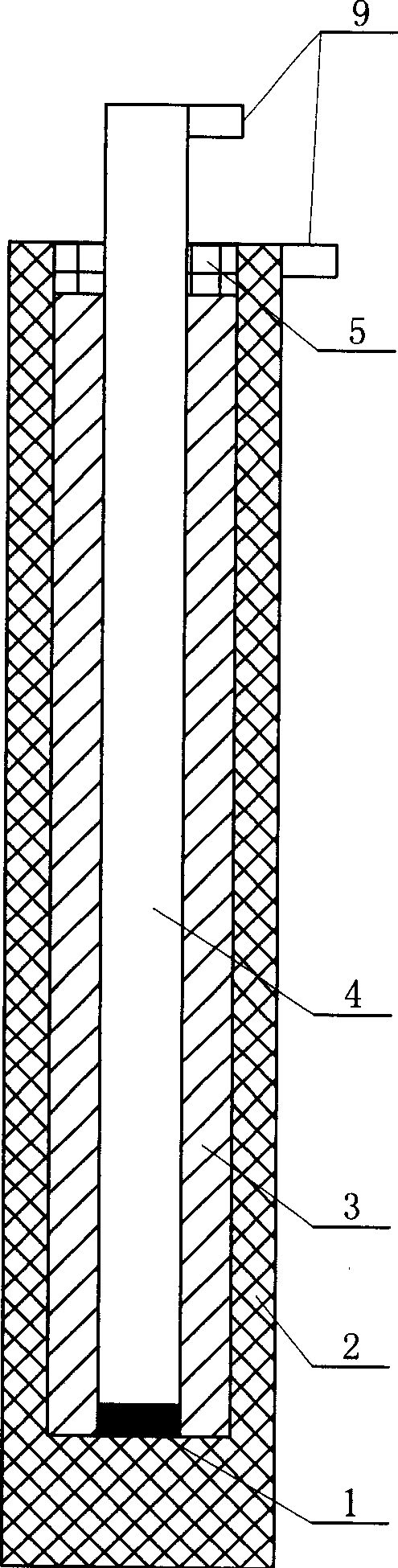
[0007] Specific implementation mode two: the following combination figure 2 To be specific. The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that a conductive connection layer 1 is added between the lower end surface of the rod-shaped electrode 4 and the inner bottom surface of the tubular electrode 2, and the conductive connection layer 1 is formed on the lower end surface of the rod-shaped electrode 4. and the inner bottom surface of the tubular electrode 2 using Ti 3 SiC 2 Welded. In this embodiment, due to the use of Ti between the two electrodes 3 SiC 2 Welding can ensure that the two electrodes in the present invention are measured in a high-temperature environment below 1600° C. and keep the two electrodes in good contact.
specific Embodiment approach 3
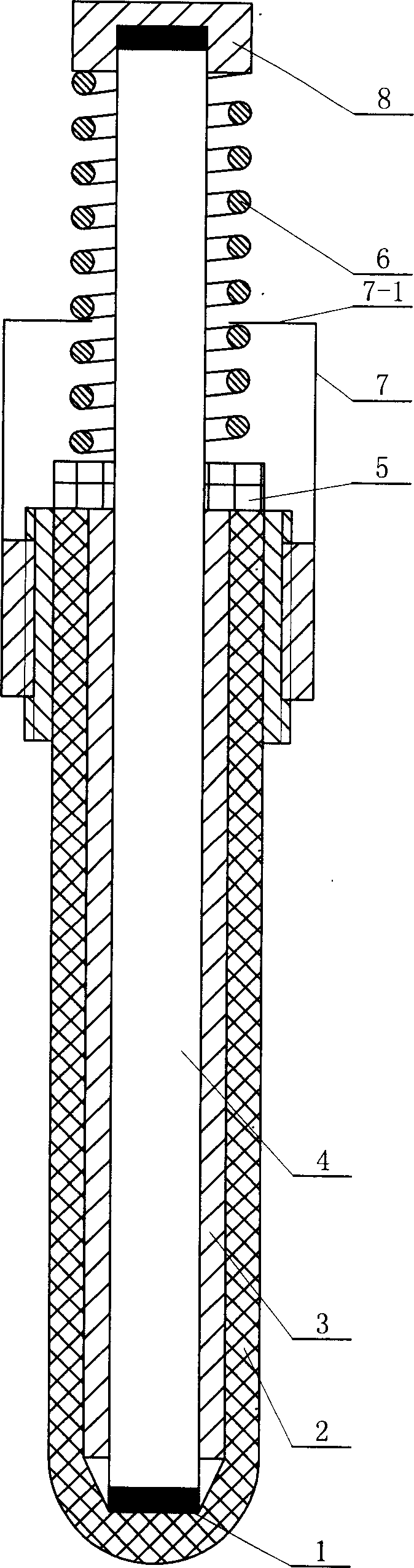
[0008] Specific embodiment three: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is that the conductive connection layer 1 added is coated with conductive platinum on the lower end surface of the rod-shaped electrode 4 and the inner bottom surface of the tubular electrode 2 after diamond grinding. Platinum metal cladding formed after the slurry was sintered at 900°C for 1 hour. This embodiment enables the present invention to perform measurements at a high temperature of 1800°C.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com