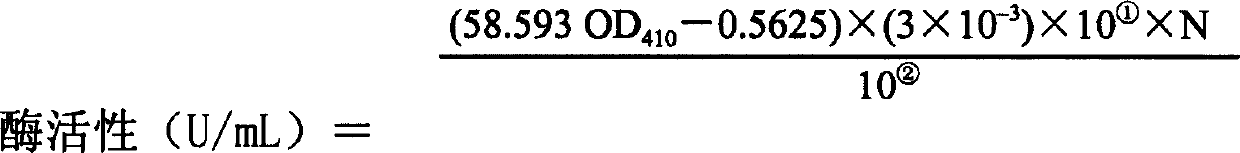Organophosphorus degradating enzyme and coding gene
A technology for organophosphorus pesticides and enzyme degradation, applied in the fields of enzymes, biochemical equipment and methods, bacteria, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] This embodiment illustrates the screening process of screening natural bacterial strain C2-1 capable of degrading various organophosphorus pesticides. The main steps are as follows:
[0037] 1. Take 0.5 g of soil sample and put it in 100 mL of Burk inorganic salt liquid medium, and culture it with shaking at 32°C overnight.
[0038] 2. Dilute the bacterial solution with sterile water, the dilution ratio is 10, 10 2 , 10 3 , 10 4 , 10 5 , 10 6 , respectively coated on the Burk inorganic salt solid medium plate with 0.2mg / mL dichlorvos (pure product) and 0.2mg / mL methyl parathion (pure product), placed in a 32°C incubator, and picked A single colony was taken and purified by plate streaking.
[0039] 3. The isolated single colony strains were inoculated with organophosphorus pesticides methyl parathion (0.05%), parathion (0.05%), methamidophos (0.05%) and omethoate (0.05%) respectively. , phoxim (0.05%) (both v / v) (the above pesticides were purchased from China Nation...
Embodiment 2
[0042] This experiment illustrates the purification process of organophosphorus pesticide degrading enzyme OPHC2. The main steps are as follows:
[0043] 1. Extraction of crude pesticide-degrading enzyme (OPHC2) enzyme solution: culture C2-1 bacterial cells with 1000 mL of LB complete medium, shake culture at 32 °C overnight, centrifuge at 5000 rpm for 10 minutes, discard the supernatant, and resuspend the bacteria in In 100 mL of 50 mmol / L Tris-Cl (pH 8.0) buffer containing 0.1 mmol / L protease inhibitor PMSF, the cells were disrupted with an ultrasonic disrupter (Branson, USA), centrifuged at 12,000 rpm for 20 minutes, and the supernatant was collected and saturated with Ammonium sulfate at 20%-90% precipitates proteins. The precipitate was resuspended in 20 mL of 50 mmol / L, pH8.0 Tris-HCl buffer, and dialyzed to desalt and concentrated to obtain OPHC2 crude enzyme solution.
[0044] 2. Separation and purification of OPHC2: by polyacrylamide (PAGE) non-denaturing gel electro...
Embodiment 3
[0046] This example illustrates the research on the enzymatic properties of the pesticide-degrading enzyme OPHC2, and the main steps are as follows:
[0047] 1. Determination of the enzymatic activity of organophosphorus degrading enzymes
[0048] Organophosphorus degrading enzymes can decompose methyl parathion into diethyl phosphorothioate and yellow p-nitrophenol in an equimolar amount, and the activity of the enzyme can be determined by measuring the amount of the product p-nitrophenol.
[0049] The determination of the content of p-nitrophenol and the preparation of the standard curve are as follows: weigh 0.08346g of p-nitrophenol, dissolve it with a small amount of 95% ethanol, and then dilute to 100 mL with water, and the concentration is 6 mmol / L. Add different amounts of p-nitrophenol solution and 50mmol / L Tris-Cl (pH8.0) buffer solution according to the following table, the total volume is 1mL, then add 1mL 10% trichloroacetic acid to each tube, and then add 1mL 10%...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com