Method for preparing tea pigment
A technology of tea pigments and tea polyphenols, which is applied in the field of oxidizing tea polyphenols to produce tea pigments, can solve the problems of low yield of theaflavins and cumbersome process, and achieve improved yield and purity, mild reaction, easy control, and good dissolution sexual effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
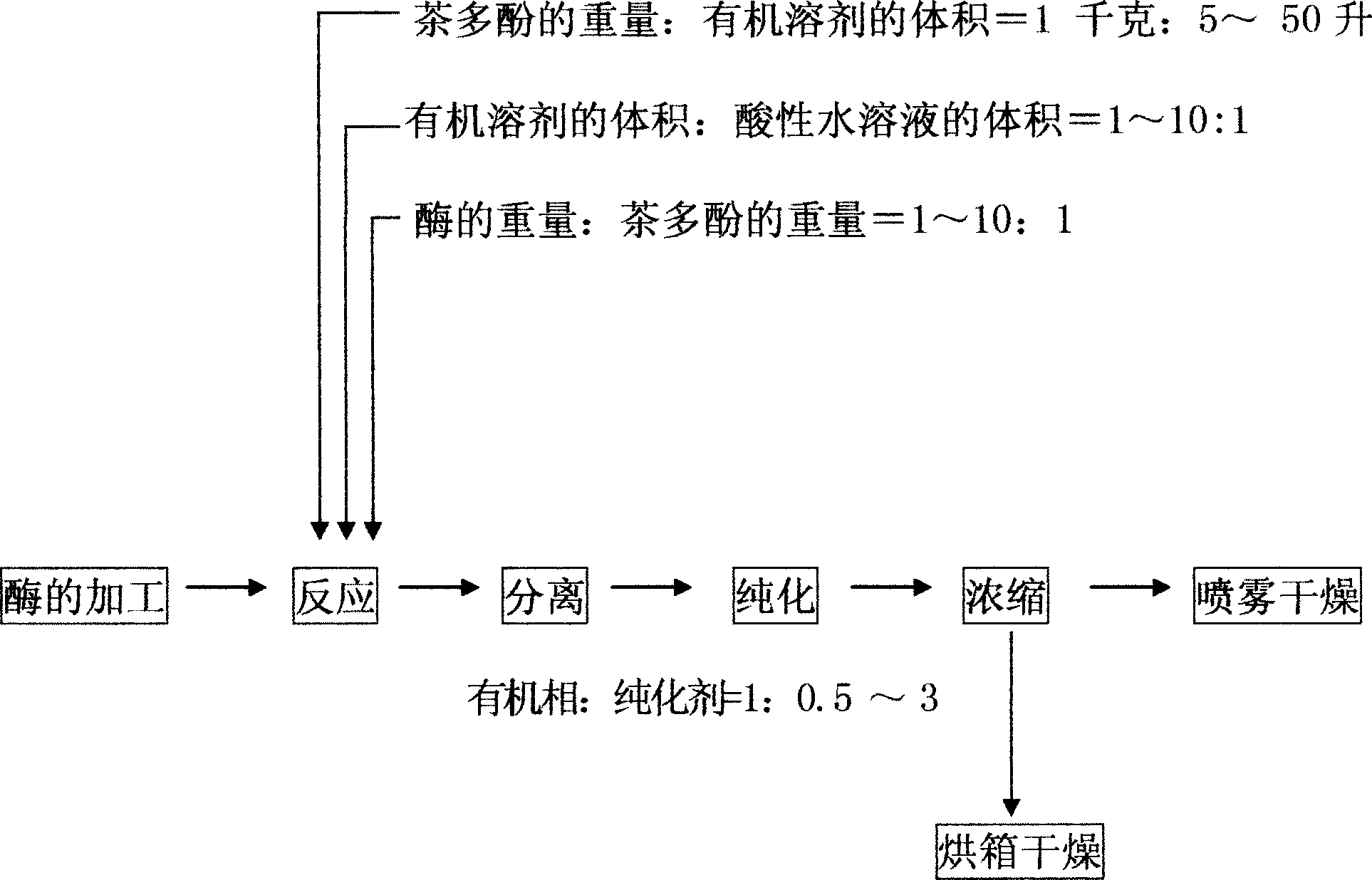
[0016] Example 1: Put 100Kg of pre-cooled fresh tea leaves freshly picked into a reaction kettle after crushing them with a masher, add 100Kg of tea polyphenols, then add 500L of ethyl acetate solution, and then add acetic acid with pH=6.5 500L aqueous solution, ventilated and stirred for 300 minutes at 65°C, cooled to 15°C, kept warm for 1 hour, separated the organic phase, added water with a ratio of 1:0.5, stirred thoroughly for 20 minutes, and then centrifuged to obtain the organic phase. Send it to a scraper concentrator with a temperature of 60°C and a vacuum of 0.06Mpa to concentrate to a paste, and then send it to a vacuum oven with a temperature of 45°C and a vacuum of 0.06Mpa to dry to powder. The yield of thea pigment is 70%. According to the Roberts method detection: theaflavin is 45%, thearubigin is 4.5%, and theabrownin is 3.3%.
Embodiment 2
[0017] Example 2: Put 100Kg of pre-cooled fresh tea leaves freshly picked into the reaction kettle after crushing them with a masher, add 10Kg of tea polyphenols, then add them to 500L of ethanol solution, and then add pH=5 citric acid aqueous solution 50L, ventilate and stir at 40°C for 240 minutes, cool down to 15°C, keep warm for 1 hour, separate the organic phase, add water at a ratio of 1:1, stir thoroughly for 20 minutes, then centrifuge to obtain the organic phase, send Concentrate to a paste in a scraper concentrator with a temperature of 62°C and a vacuum of 0.07pa, and then send it to a vacuum oven with a temperature of 50°C and a vacuum of 0.07Mpa to dry to powder. The yield of tea pigment is 70%, and according to Roberts method detection: theaflavin is 60%, thearubigin is 4.5%, theabrown is 2.8%.
Embodiment 3
[0018] Embodiment 3: 100Kg of pre-cooled fresh tea leaves freshly picked are crushed with a masher and then put into the reactor, add tea polyphenols 33Kg, polysaccharide hydrolase 500g, then add in 660L of isopropanol solution, and then add 220L of citric acid aqueous solution with pH=6, ventilated and stirred at 30°C for 180 minutes, cooled to 15°C, kept warm for 1 hour, separated the organic phase, added water in a ratio of 1:2, stirred thoroughly for 20 minutes, and cooled to 15°C ℃, keep warm for 1 hour, and then centrifuge to obtain the organic phase, send it to a scraper concentrator with a temperature of 63°C and a vacuum of 0.08Mpa to concentrate to a paste, and then send it to a temperature of 55°C and a vacuum of 0.08Mpa Dry to powder in a vacuum oven. The yield of thea pigment was 78%. According to the Roberts method detection: theaflavin was 35%, thearubigin was 5.1%, and theabrownin was 3.1%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com