Metod and installation for the treatment of a radioactive wastes
A radioactive waste, reactive technology, used in radioactive purification, nuclear engineering, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
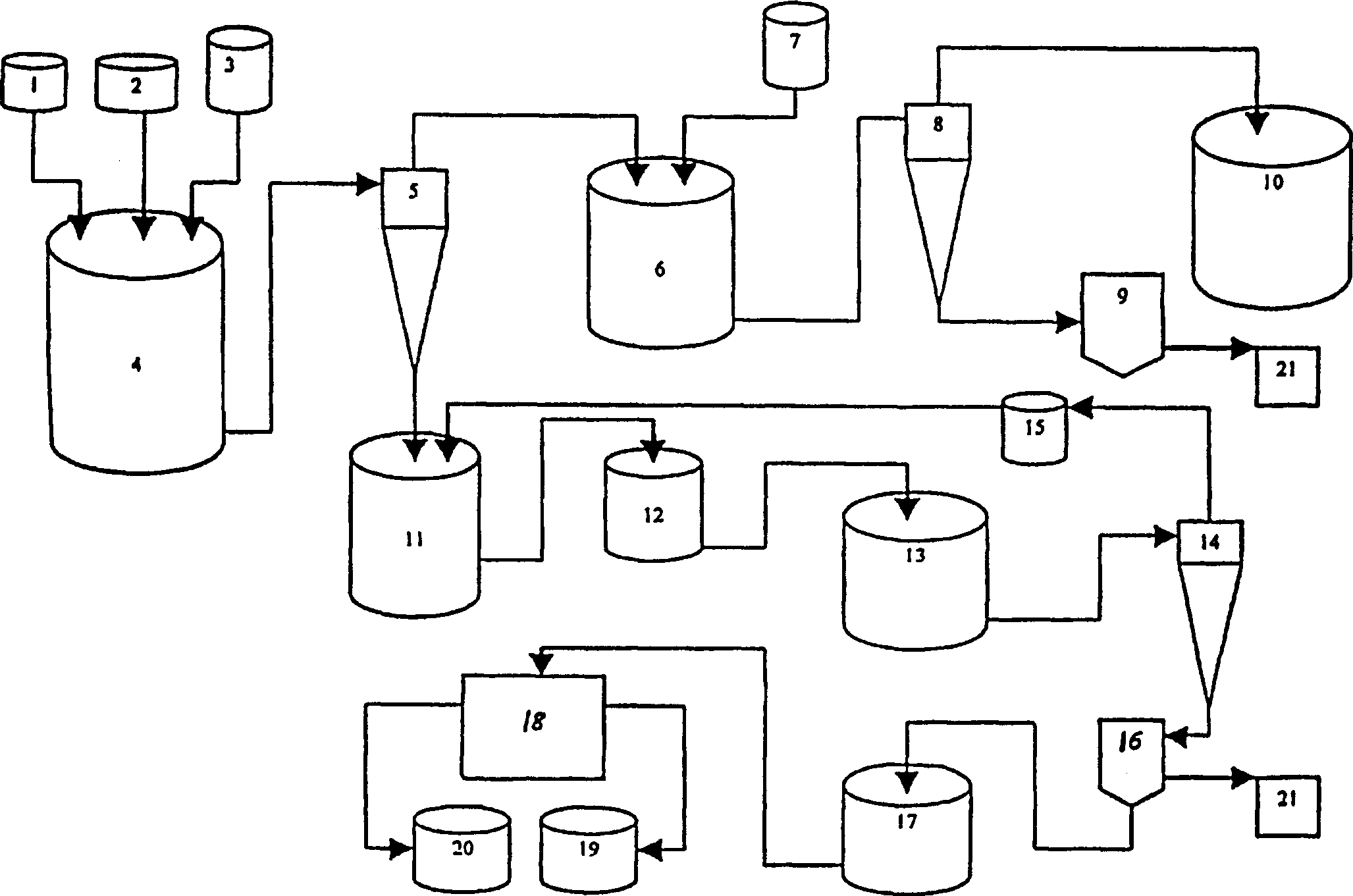
[0057]1 liter of radioactive waste having a pH of 8.0 and containing 35 g / l of boric acid (boron-containing salts) was mixed with radioactive waste having a pH of 10.1 until the pH of the mixture was 9.1. The hard crystalline phase of borax was then separated off, and 9.0 ml of a calcium borate solution having a concentration of 900 g / l was added to the remaining portion of the liquid radioactive waste. The thus obtained insoluble calcium borate was separated from the mixture and the liquid radioactive waste was concentrated until the concentration of boric acid in the waste was 2.2 g / l. The separated calcium borate was washed several times with water and isolated as a radioactive product. A solution with a concentration of 20 g / l was prepared from the isolated and recrystallized borax and subjected to electrodialysis. A heat resistant membrane and a current of 0.35 amps and a voltage of 5.2 volts were used in the electrodialysis unit. The products obtained were: boric acid ...
Embodiment 2
[0059] 1 liter of radioactive waste having a pH of 10.0 and containing 200 g / l of boric acid (boron-containing salts) was mixed with radioactive waste having a pH of 4.0 until the pH of the mixture was 8.2. After the borax had separated as a hard crystalline phase, 9.4 ml of a 500 g / l magnesium chloride solution was added to the residual liquid radioactive waste. The resulting dissolved magnesium borate was then separated from the mixture and the liquid radioactive waste was concentrated to 3.4 g / l of boric acid.
[0060] The isolated borax was recrystallized and a solution of 25 g / l concentration was prepared from the refined borax and treated with an electrodialysis unit using a heat-resistant membrane and a current of 45 amperes and a voltage of 55 volts. The products obtained were: a boric acid solution with a concentration of 59 g / l and a sodium hydroxide solution with a concentration of 150 g / l.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com