Treatment of male sexual dysfunction
A technology for erectile dysfunction and men, which is specifically applied in the fields of MED, prevention and/or treatment of MSD, compound assays, and male erectile dysfunction. It can solve problems such as priapism, injection therapy is not as convenient as oral therapy, and achieves Effects of increasing penile blood flow and enhancing normal libido arousal response
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
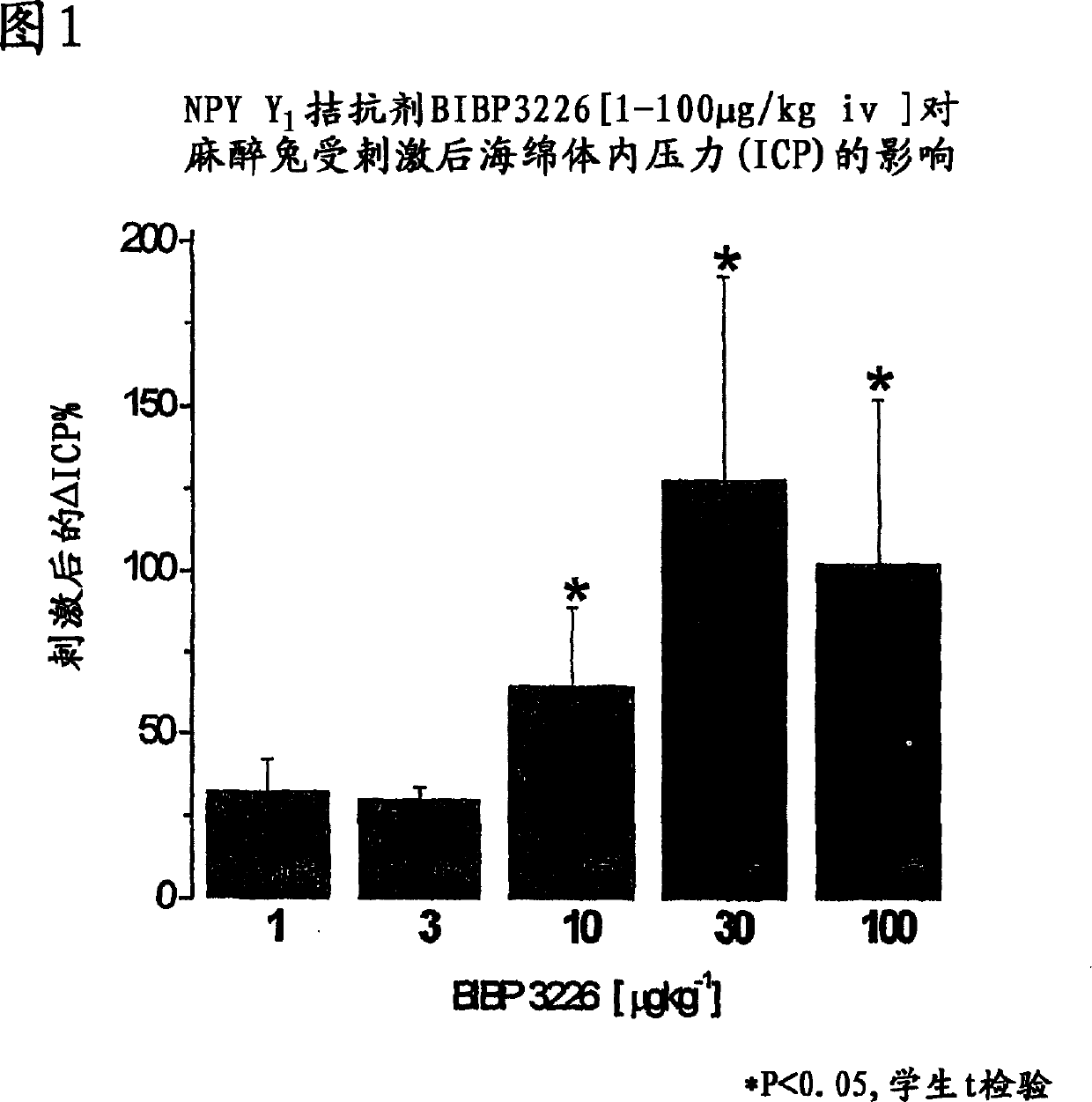
[0814] Inhibition of the NPY Y1 receptor dose-dependently potentiates nerve-stimulated intracavernous pressure increases in an anesthetized rabbit model of erection
[0815] Submaximal increases in intracavernous pressure (ICP) induced by nerve stimulation were significantly increased (iv bolus) in the presence of increasing doses of a selective NPY Y1 receptor antagonist (BIBP3226). This increase became more pronounced at doses of 30 μg / kg and above. The greatest potentiation (approximately 127%) was observed at 30 [mu]g / kg. Data are expressed as percent increase (%), compared to the increase in control stimulation. Values are expressed as mean ± s.e. mean. Unpaired comparison with control increase, *P<0.05, Student's t-test (see Figure 1).
[0816] NPY Y1 receptor antagonism had no apparent effect on basal / unstimulated intracavernous pressure.
Embodiment 2
[0818] PDE5 inhibition significantly increases the efficacy of PDE5 inhibitors to enhance penile erection in an anesthetized rabbit model
[0819] Intravenous administration (1 mg / kg) of a selective PDE5 inhibitor significantly enhanced the increase in ICP of nerve stimulation by 133±22% compared to the control increase. Data are presented as percent increase in ICP over control increase. Values are expressed as mean ± s.e. mean. Unpaired comparison with control increase, *P<0.01, Student's t-test (see Figure 2).
[0820] PDE5 inhibition had no effect on basal / unstimulated intracavernous pressure.
Embodiment 3
[0822] Effects of drugs that increase intracavernous pressure on mean arterial blood pressure in anesthetized rabbits
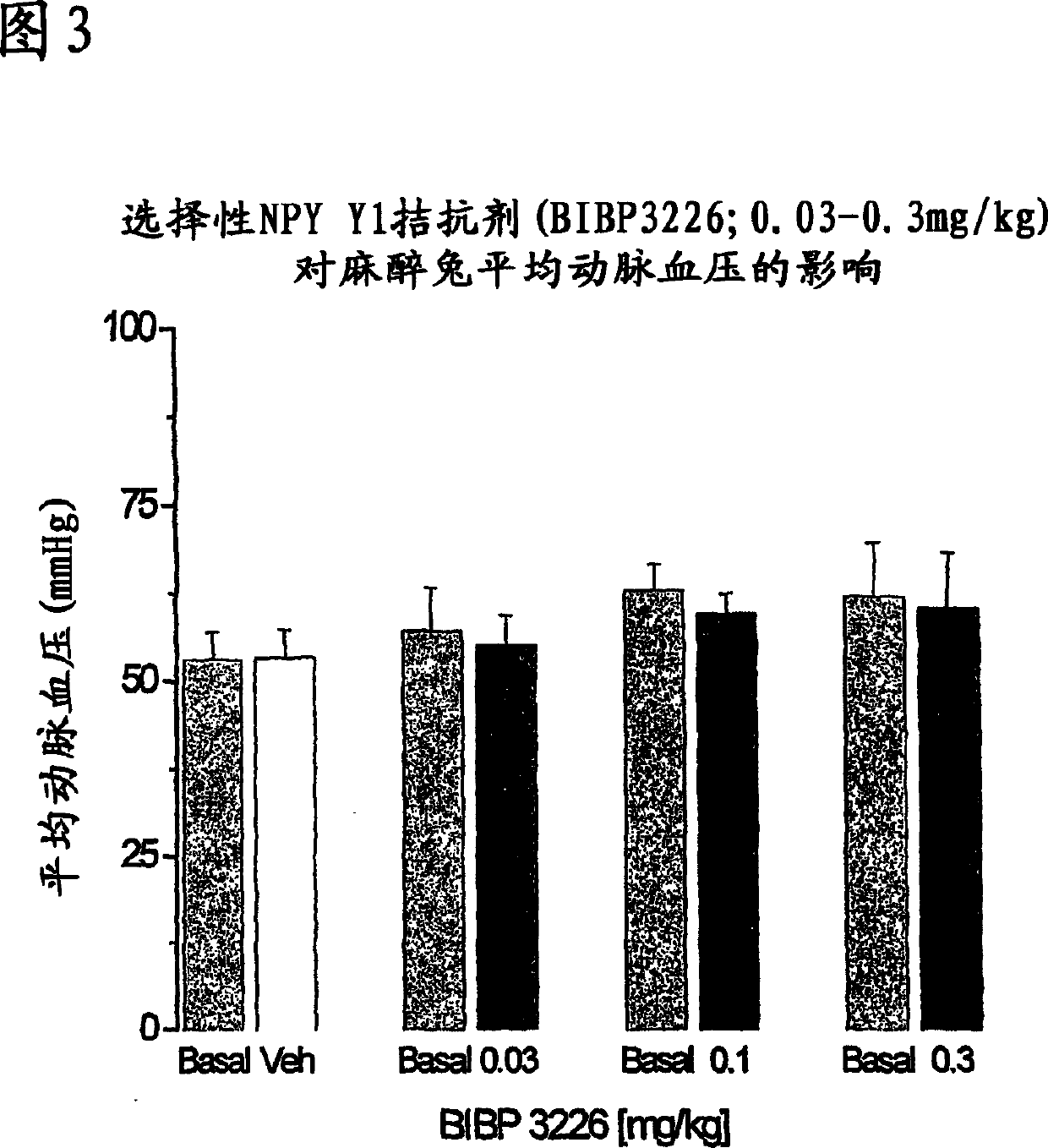
[0823] In finding new treatments for male sexual dysfunction, such as MED, it is desirable that there be no associated cardiovascular side effects, such as effects on blood pressure or heart rate. In our study, we have found that the NPY Y1 receptor antagonist BIBP3226 (0.03-0.3mg / kg) has no substantial effect on blood pressure or heart rate, and this dose is similar to the increase in intracavernosus pressure induced by enhanced pelvic nerve stimulation.
[0824] Intravenous administration of BIBP3226 (a selective NPY Y1 antagonist) had no substantial effect on mean arterial blood pressure in an anesthetized rabbit model of penile erection. Figure 3 demonstrates that BIBP3226 has no significant effect on mean arterial pressure in anesthetized rabbits, and its dose-enhanced pelvic nerve stimulation increases cavernosal pressure. Mean arterial pressure (MAP) ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com