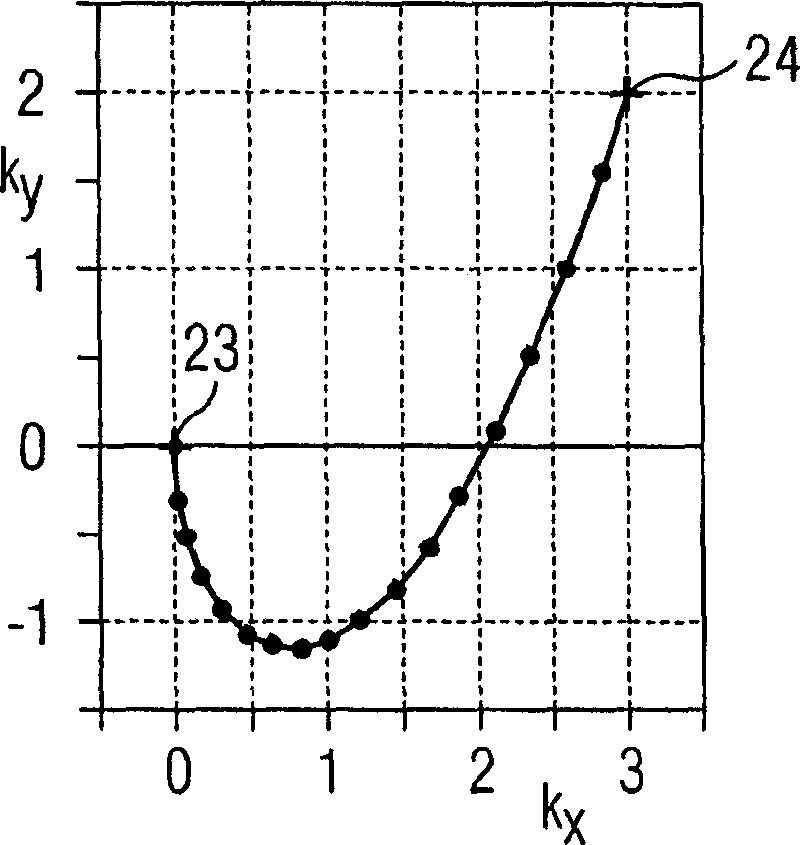
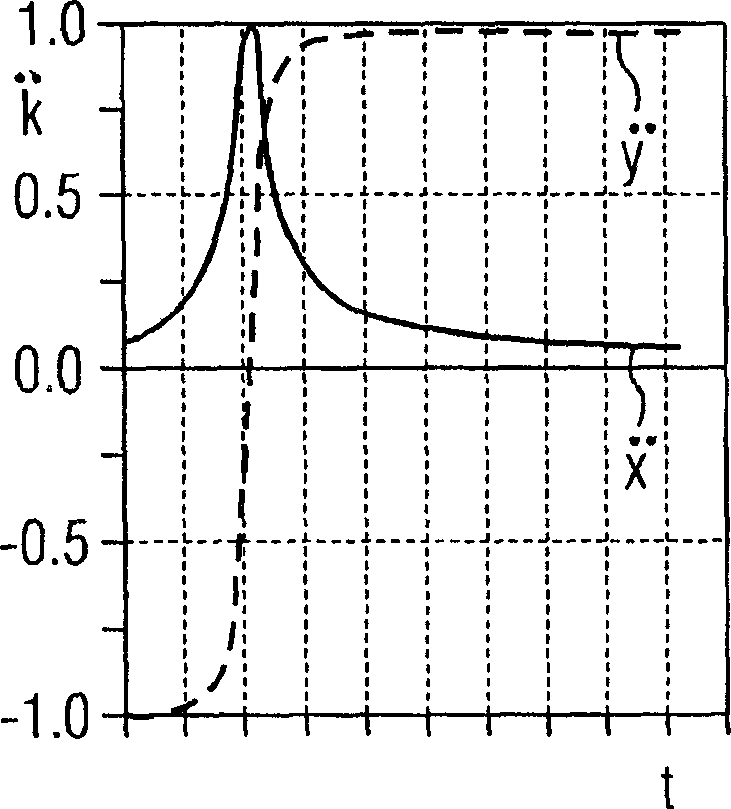
Method for optimizing the K-space trajectories in the location encoding of a magnetic resonance tomography apparatus
A technology of magnetic resonance tomography and equipment, applied in magnetic resonance measurement, measurement using nuclear magnetic resonance image system, material analysis through resonance, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0047] FIG. 1 shows a schematic diagram of a nuclear spin tomography apparatus for generating gradient pulses according to the invention. In this case, the structure of the nuclear spin tomography system corresponds to that of a conventional tomography system. The basic field magnet 1 generates a temporally stable strong magnetic field in order to polarize or orient the nuclear spins in the examination region of an object, for example a part of the human body to be examined. The highly uniform basic magnetic field required for nuclear spin resonance measurement is defined in the spherical measurement space M placed in the part of the human body to be examined. In order to support this homogeneity requirement, in particular to eliminate time-invariant influences, so-called shims made of ferromagnetic material are provided at suitable locations. Time-varying influences are eliminated by the shim coil 2 controlled by the shim power supply 15 .
[0048] In the basic field magnet...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com