Method for determining hemodynamic state
A technology of hemodynamics and status, applied in vascular assessment, blood flow measurement, blood pressure measurement devices, etc., can solve problems such as insufficient perfusion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
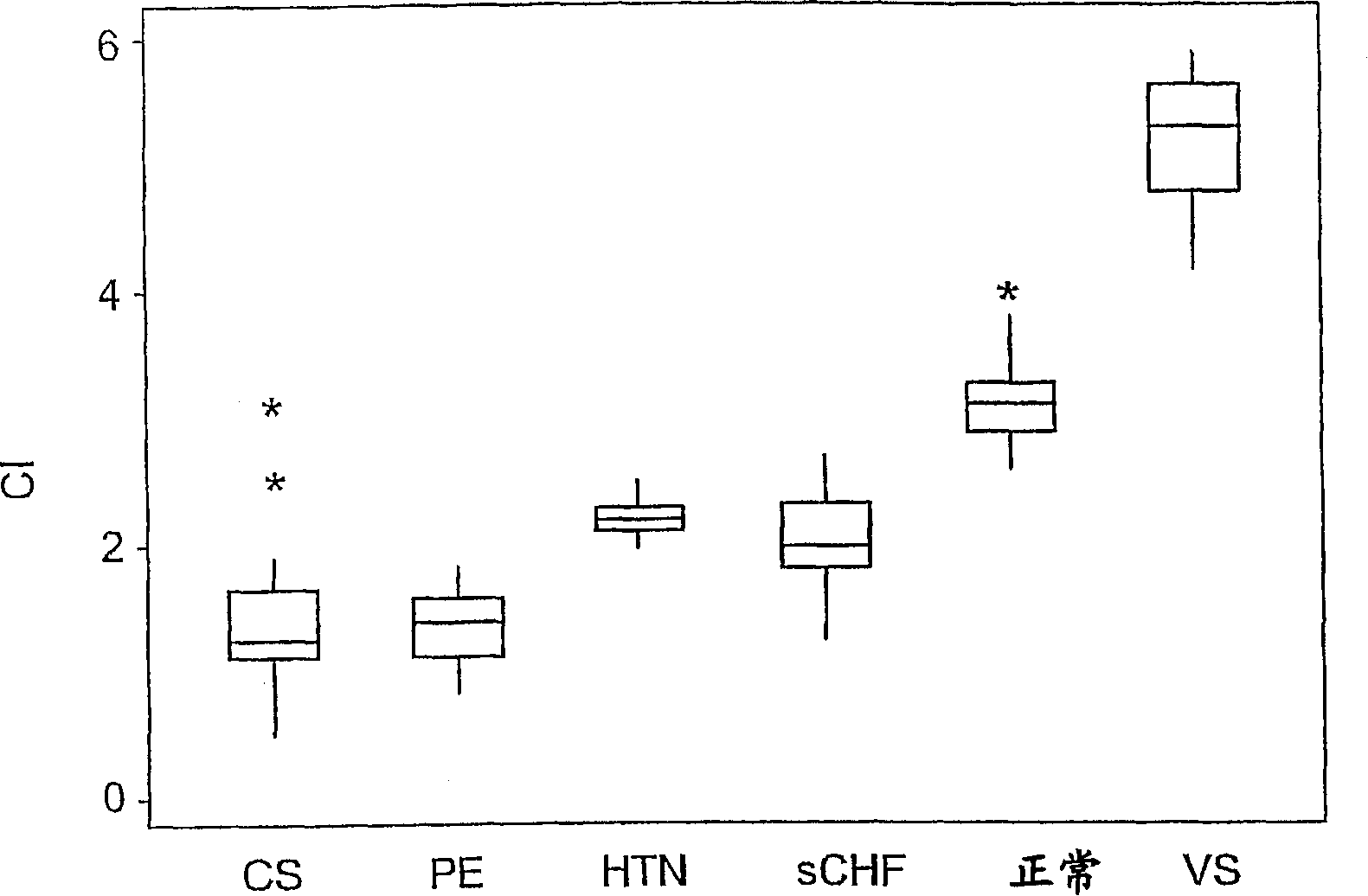
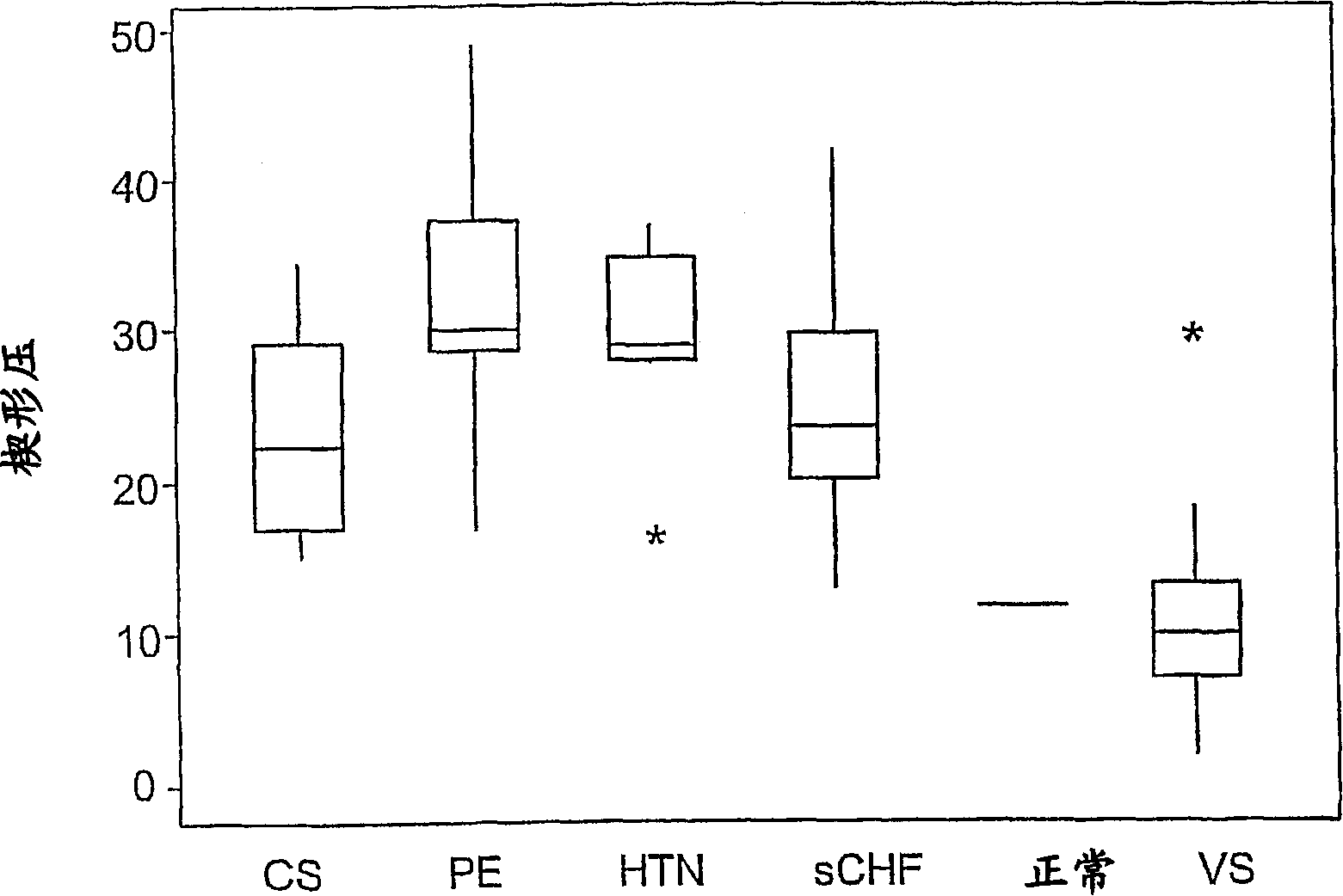
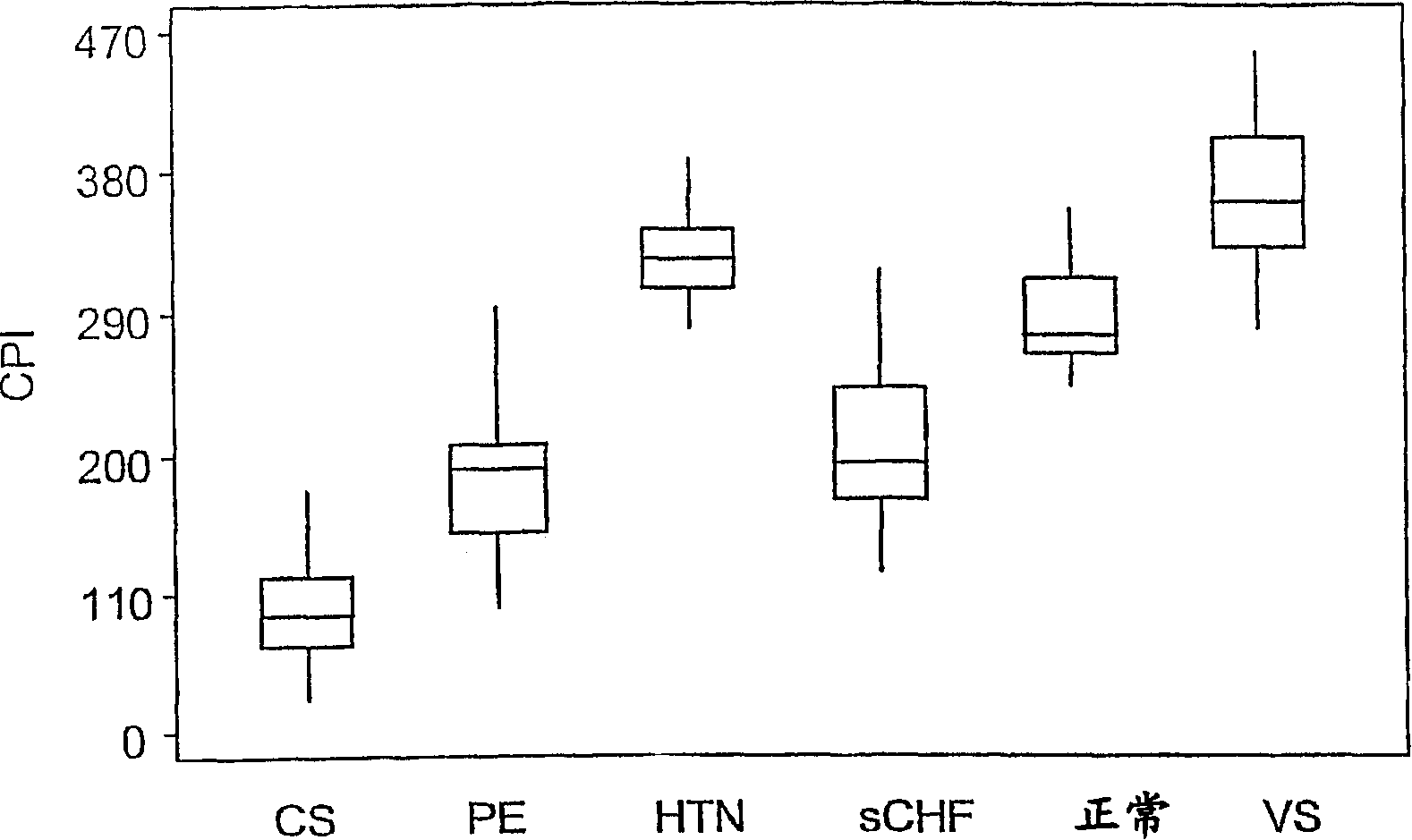
[0042] DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT Example 1: Determination of Hemodynamic Status by Graphical Method patients and methods
[0043] Hemodynamic data were obtained in patients undergoing right heart catheterization. Inclusion Standard:
[0044] All patients diagnosed with systolic CHF (sCHF), hypertensive crisis, acute pulmonary edema (PE), vasodilatory shock or cardiogenic shock by conventional clinical criteria (see below) were included. Exclusion criteria:
[0045] Significant valvular heart disease, significant bradycardia or tachycardia, or renal failure (creatinine > 2.5 mg / dl). Clinical diagnostic criteria:
[0046] 1) Systolic CHF: Patients consented to invasive hemodynamic evaluation due to exacerbation of CHF, defined as clinical symptoms and signs of CHF, NYHA class III-IV, accompanied by EF <35% on echocardiography And did not use any oral drug treatment for 6 hours or no intravenous drug treatment for the last 2 hours; did not meet the cr...
Embodiment II
[0069] Another embodiment of the process of the invention will now be described by the examples given below. However, it will be clear to those skilled in the art that other embodiments using other statistical analysis methods are also possible. 1. Data statistical methods:
[0070] All parameters of the 5 clinical groups were compared using one-way analysis of variance. The Ryan-Einot-Gabriel-Welsch Multiple Range Test was used for pairwise comparisons between these groups, while Dunnett's T test was used to compare all groups with healthy controls.
[0071] A 1-sample t-test was performed to compare the average wedge pressure of each group with that of normal subjects (less than 12 mmHg).
[0072] To determine the usefulness of hemodynamic parameters to differentiate between clinical syndromes, ROC curves from logistic regression models were applied to the data to determine the best cut-off points for the different parameters, according to highest sensitivity and specifi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com