Transgenic insect
An insect and gene technology, applied in the field of genetic manipulation of insects, can solve problems such as difficulty in injecting DNA
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
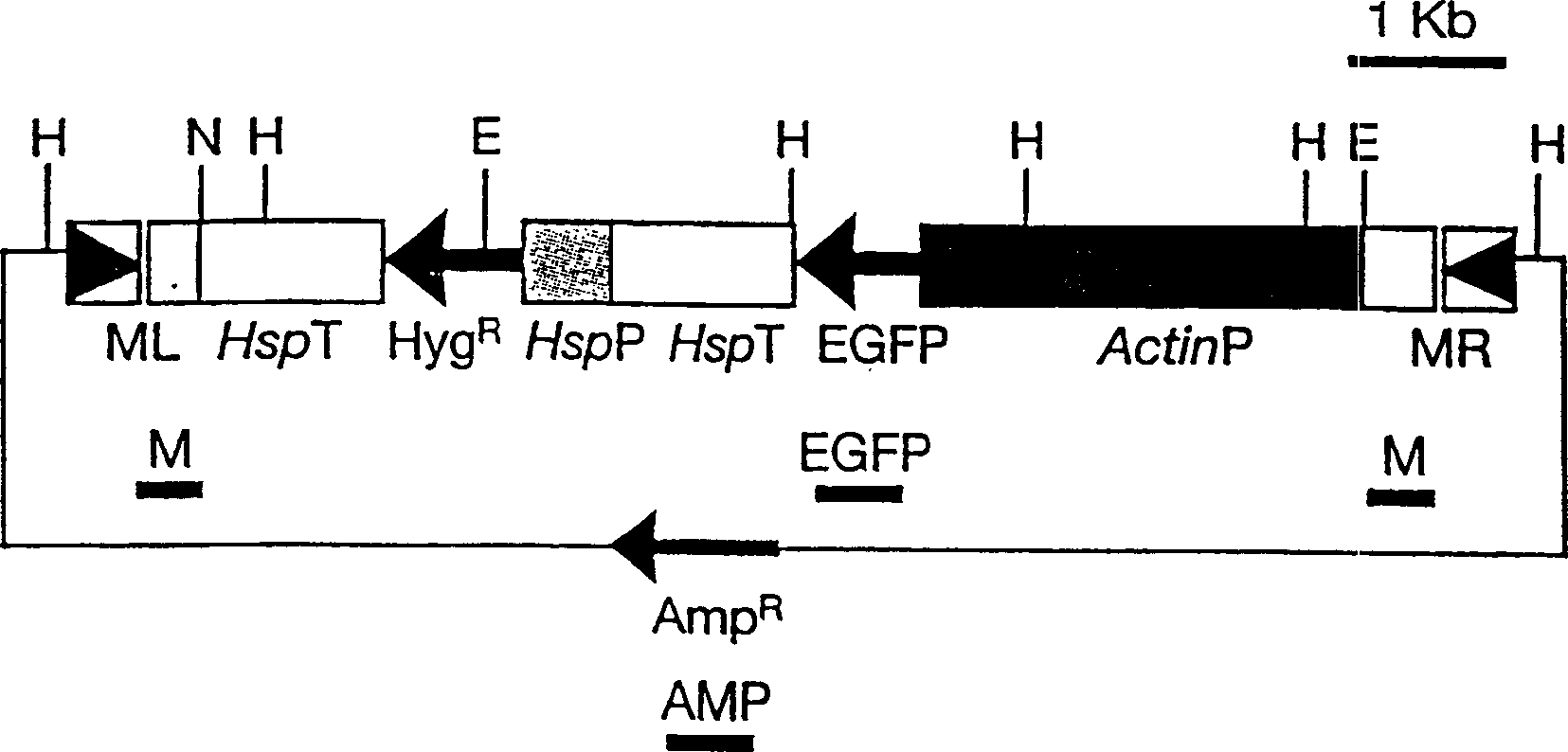
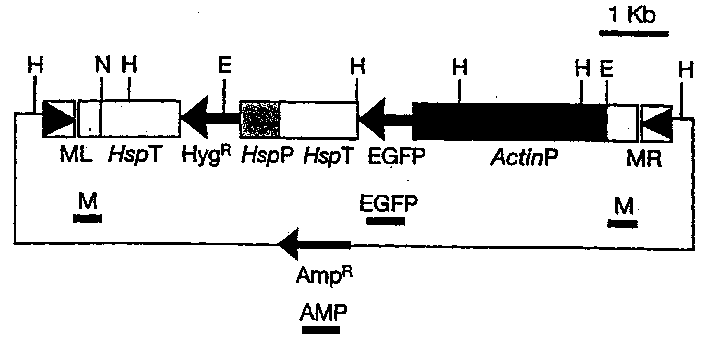
[0047] In the following experiments, a plasmid vector called MinHyg (shown in figure 1 ) to complete the integration of the heterologous gene into the Anopheles genome. Such as figure 1 As indicated, the green fluorescent protein gene GFPS65T (GFP) (Heim et al., Nature, 1995; 373: 663-664) was chosen as a reporter gene to show the successful integration of the completed DNA.
[0048] The actin promoter from the D. melanogaster actin5C gene was selected to drive expression of the GFPS65T marker (Fyrberg et al., Cell, 1983; 33:115-123).
[0049] A hygromycin gene under the control of the inducible heat shock protein 70 (hsp70) promoter was also incorporated into the vector as a selectable marker in events where GFP selection was not possible.
[0050] The experiment was performed as follows. The blood-sucking Anopheles stepheni mosquito lays eggs 48-72 hours after sucking blood. Eggs were placed in Petri dishes containing a solution in isotonic buffer (150 mM NaCl, 5 mM KCl,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com