NOGO receptor-mediated blockade of axonal growth
A technology of receptors and receptor proteins, applied in the field of NOGO receptor-mediated blocking of axon growth, can solve the problem that the mechanism of Nogo's inhibition of axon growth has not yet been elucidated
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Embodiment 1
[0178] EXAMPLES Example 1 - Identification of Nogo as a member of the Reticulon protein family
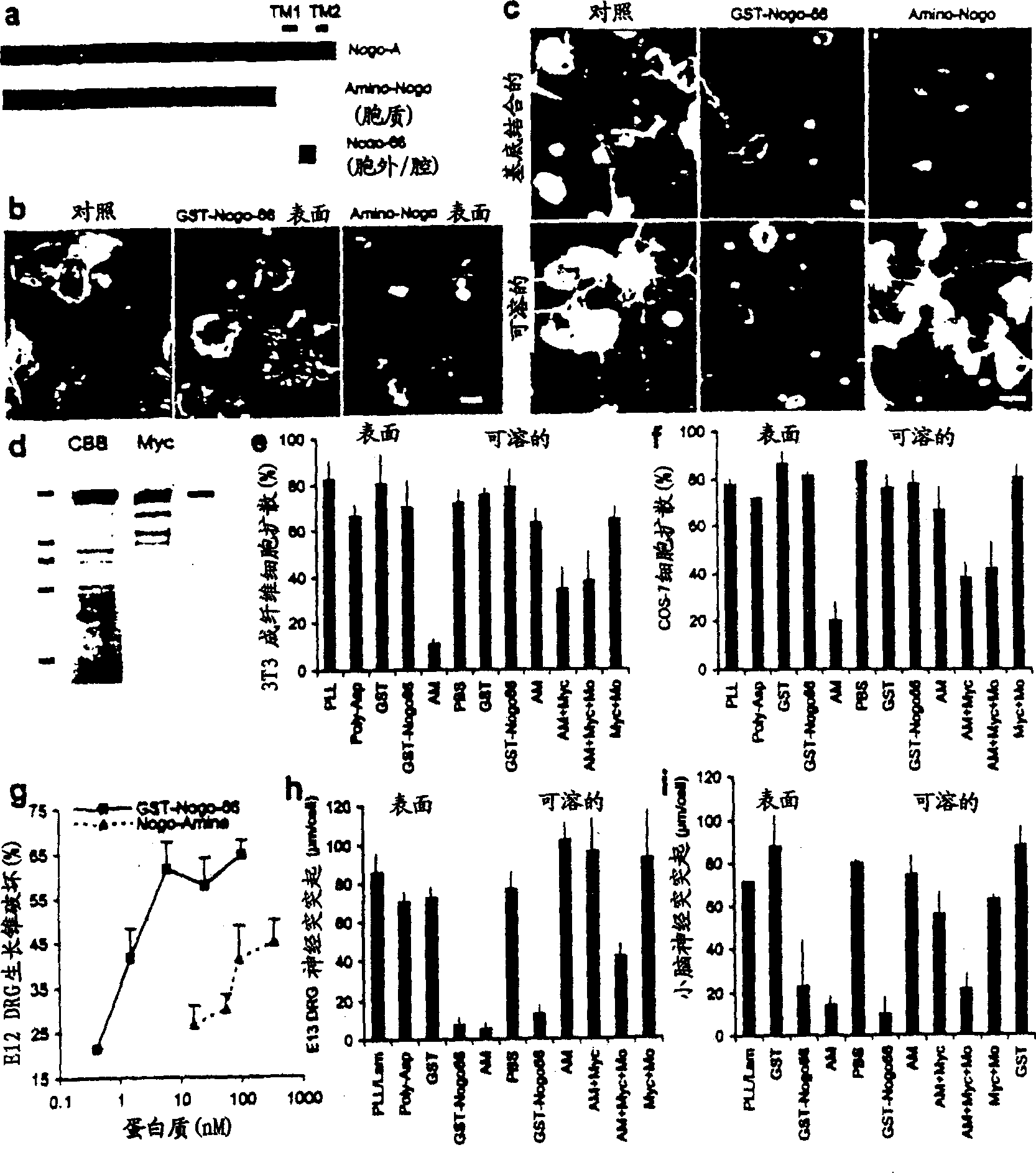
[0179] Axon regeneration in adult mammals is generally successful in the peripheral nervous system, but less so in the CNS. However, many classes of CNS axons extend longer distances in peripheral nerve grafts (Benfy and Aguayo (1982) Nature 296, 150-152). A comparison of CNS and peripheral nervous system (PNS) myelin revealed that CNS white matter selectively inhibits axonal outgrowth (Schwab and Thoenen (1985) J. Neurosci. 5, 2415-2423). Several components of CNS white matter - NI35, NI250 (Nogo) and MAG have been described to have inhibitory activity on axonal growth (Wang et al., (1999) Transduction of inhibitory signals by axonal growth cones. Neurobiology of Spinal Cord Injury Science", Kalb and Strittmatter (editors), Humanan Press; Caroni and Schwab, (1988) J. Cell Biol.106, 1281-1288; Spillmann et al., (1988) J. Biol. Chem.73, 19283-19293; McKerracher et al., (1994) Neur...
Embodiment 2
[0185] When overexpressed in kidney cells, the Rtn1 protein is located mainly in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) as fine particles, hence the name Reticulon (Van de Velde et al., (1994) J. Cell. Sci. 107, 2403-2416 ). There is a double lysine ER retention motif at the carboxyl terminus of Nogo and most Rtn proteins (Van de Velde et al., (1994) J. Cell. Sci. 107, 2403-2416; Jackson et al., (1991) EMBO J.9, 3153-3162). In neurons, Rtnl is expressed throughout neurites and is concentrated in growth cones (Senden et al. (1996) Eur. J. Cell. Biol. 69, 197-213). Its localization in transfected kidney cells has led to the proposal that Rtnl may regulate protein sorting or other aspects of ER function (Van de Velde et al. (1994) J. Cell. Sci. 107, 2403-2416). The A and C splice forms of Nogo when expressed in COS-7 cells showed a reticular distribution, similar to Rtn1-C. Example 2 - Anti-Nogo polyclonal antibody
[0186] The predicted intramembrane topology of the two hydrophobic ...
Embodiment 5
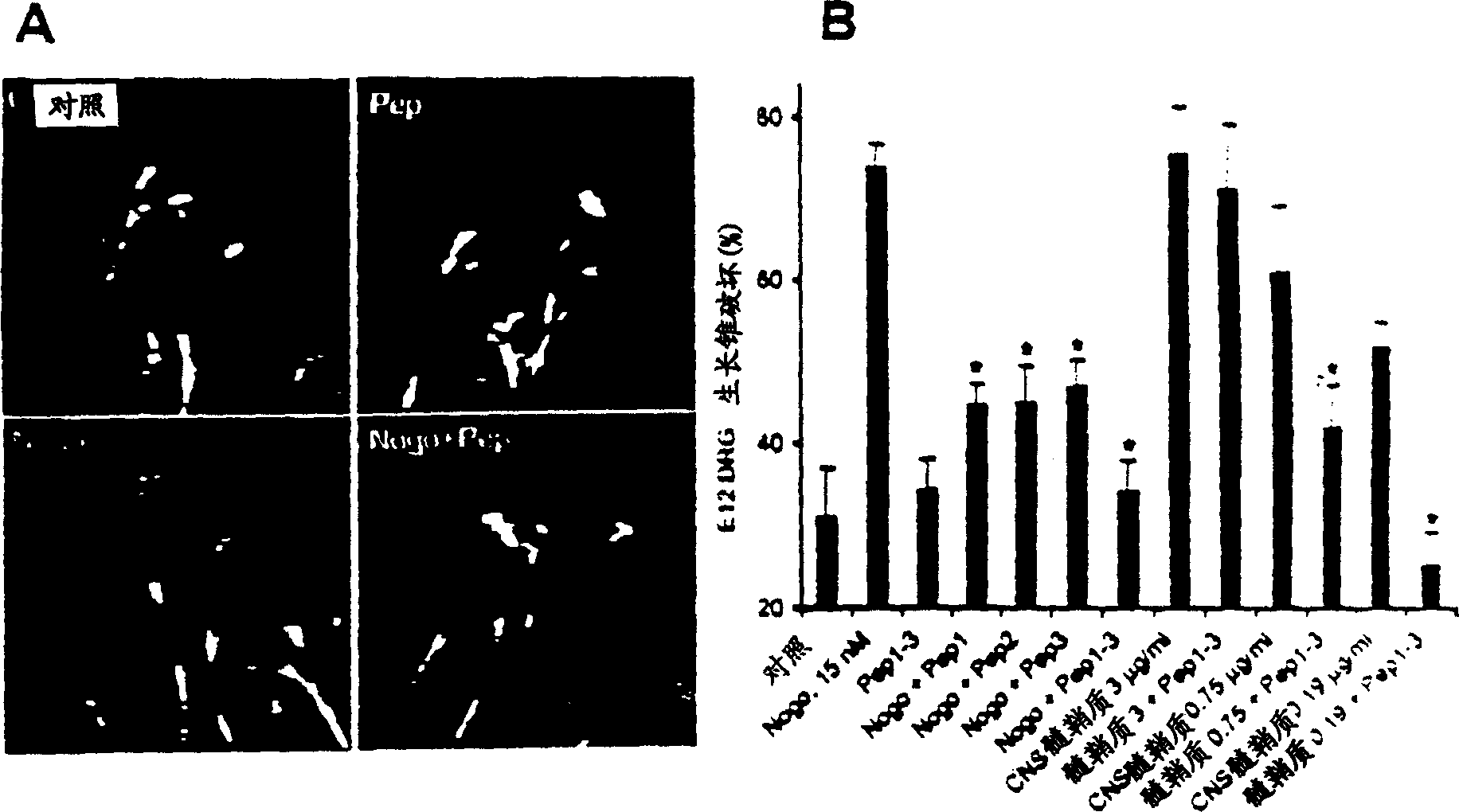
[0196]Oligodendrocytes appear to selectively express Nogo among Rtn proteins. To investigate the selectivity of Nogo's role in inhibiting axon regeneration, the axon outgrowth inhibitory activity of other Rtn proteins was considered. The predicted luminal-extracellular 66 amino acid fragments of Rtn1, Rtn2 and Rtn3 were expressed as GST fusion proteins and purified in native form. At concentrations where the Nogo fragment disrupted most E12 dorsal root ganglion growth cones, other Rtn proteins did not alter growth cone morphology (data not shown). Thus, the inhibitory activity of axon regeneration is specific for Nogo in the Rtn family. Embodiment 5-Nogo acceptor peptide reagent
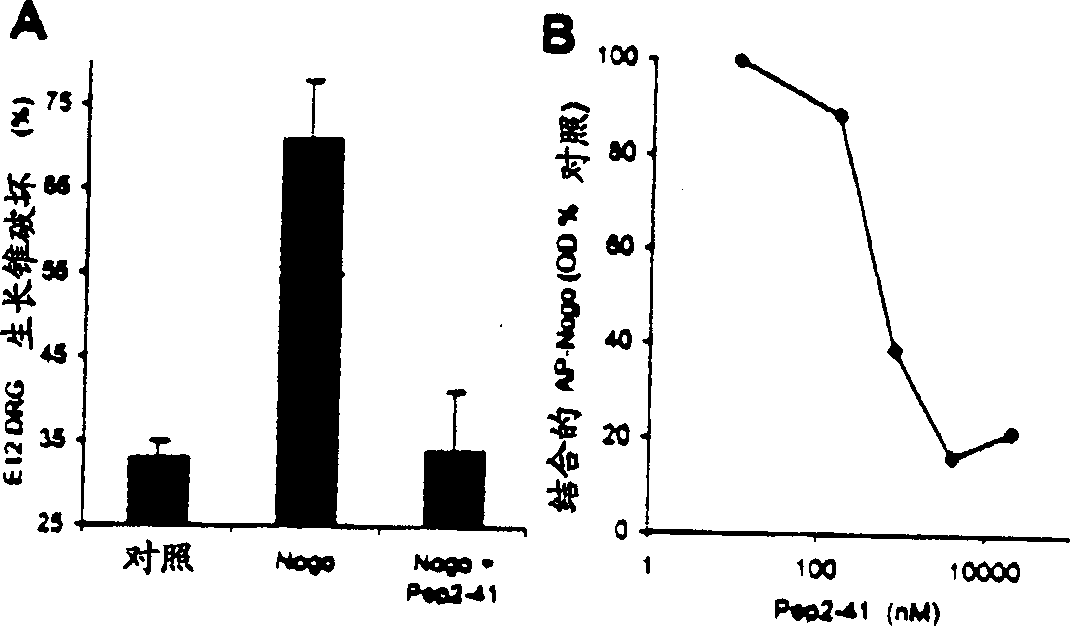
[0197] To further define the active domain of Nogo, a 25 amino acid residue peptide corresponding to a fragment of the 66 amino acid sequence was synthesized. This peptide corresponds to residues 31-55 of the extracellular fragment of Nogo and shows growth cone disruption at a concentration of 4 μ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com