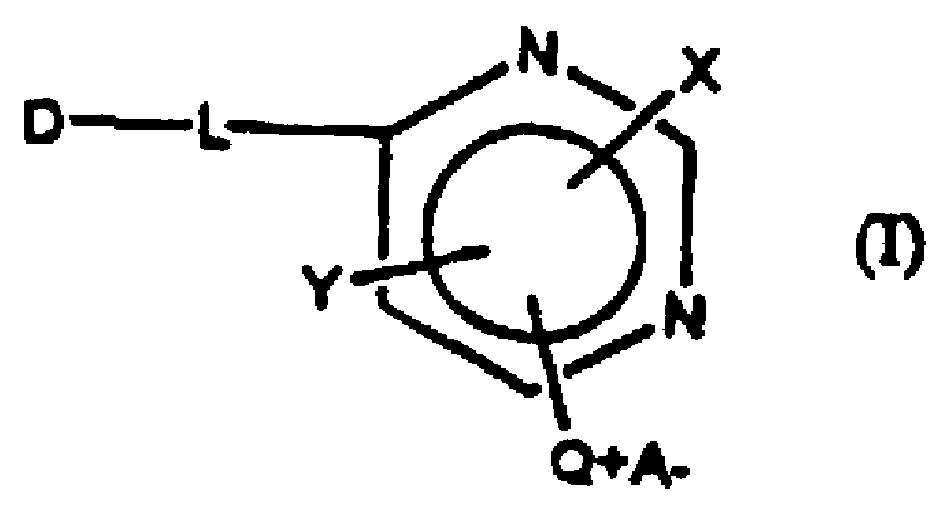
Reactive dye compounds
A technology of reactive dyes and dye compositions, which is applied in the field of reactive dye compounds, can solve the problems of dye retention, etc., and achieve the effects of improving exhaustion rate, increasing affinity, and strong dyeing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0060] 5-Chloro-4-nicotinyl-2-fluoropyrimidine dye was prepared using the synthetic route described in Scheme 1.
[0061] Reaction scheme 1
[0062] In this scheme, D is a chromophore and varies depending on the starting dye used. In this example, Drimarene Brill Red4-KBL was used as a starting material. However any suitable pyrimidine-containing dye can be used as a starting material, including any Drimalan F dye, any Drimarene R dye and any Drimarene K dye commercially available from Clariant.
[0063] Synthesis of 5-chloro-4-nicotinyl-2-fluoropyrimidine dye
[0064] 0.1 mol of pure Drimarene Brill Red K-4BL dye and 150 ml of distilled water were added to the flask. Then, 0.1 mol of nicotinic acid was added dropwise from the dropping funnel to the reaction mixture under stirring. The total addition time is 1-1.5 hours. During the addition of nicotinic acid, the pH value of the reaction system was kept at 5-5.5, and the temperature was kept at 40-45°C.
[0065] The re...
Embodiment 2
[0068] All of the dye compounds prepared in Example 1 above can be used to dye cotton using the dyeing method described below. Following the cotton dyeing process, the soaping process can also be performed on the cotton fibers.
[0069] cotton dyeing method
[0070] An aqueous dye solution containing the dye compound of Example 1 was prepared. Described dye solution contains the dyestuff of 1.2% by fiber quality, the Na of 80g / L 2 SO 4 and 5% sodium acetate by mass of fiber. The cotton fabric was immersed in water, and then the cotton fabric was dyed in the above dyeing bath at pH 7 and 25° C. for 30 minutes. Then at pH11.5 by adding 30g / L sodium formate and 5g / L Na 2 CO 3 The dyed cotton fabric was fixed in a dye bath and dyed for 30 minutes at 25°C. Dyed fabrics are rinsed with water.
[0071] In the above dyeing process, the dyebath of each dye compound was almost completely exhausted, indicating that the compounds prepared in Example 1 each had a high exhaustion va...
Embodiment 3
[0079] All of the dye compounds prepared in Example 1 can be used to dye nylon or wool using the dyeing method described below. After the nylon / wool dyeing method, a wash fastness test can be performed on the dyed fabric to test the wash fastness of the dye compound.
[0080] Wool / Nylon Dyeing Method
[0081] The wool / nylon fabric was soaked in a 2% solution of Alcopol-O (40% w / w sodium d-isooctyl sulfate succinate from Allied Colloids). The fabric was then dyed for 1 hour at 100° C. and pH 3.5 in a dyebath containing the following composition: 1.2% by mass of fiber of the dye prepared in Example 1, 14% by mass of fiber of sodium acetate and 1% of Albegal B (commercially available from Ciba Geigy). Rinse dyed wool / nylon fabrics with water.
[0082] Each of the compounds prepared in Example 1 provided strong staining in the above method.
[0083] Test method for Co2 (ISO) wash fastness of wool / nylon fabrics
[0084] Dyed wool / nylon fabrics were washed at 50°C for 45 minute...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com